Abstract
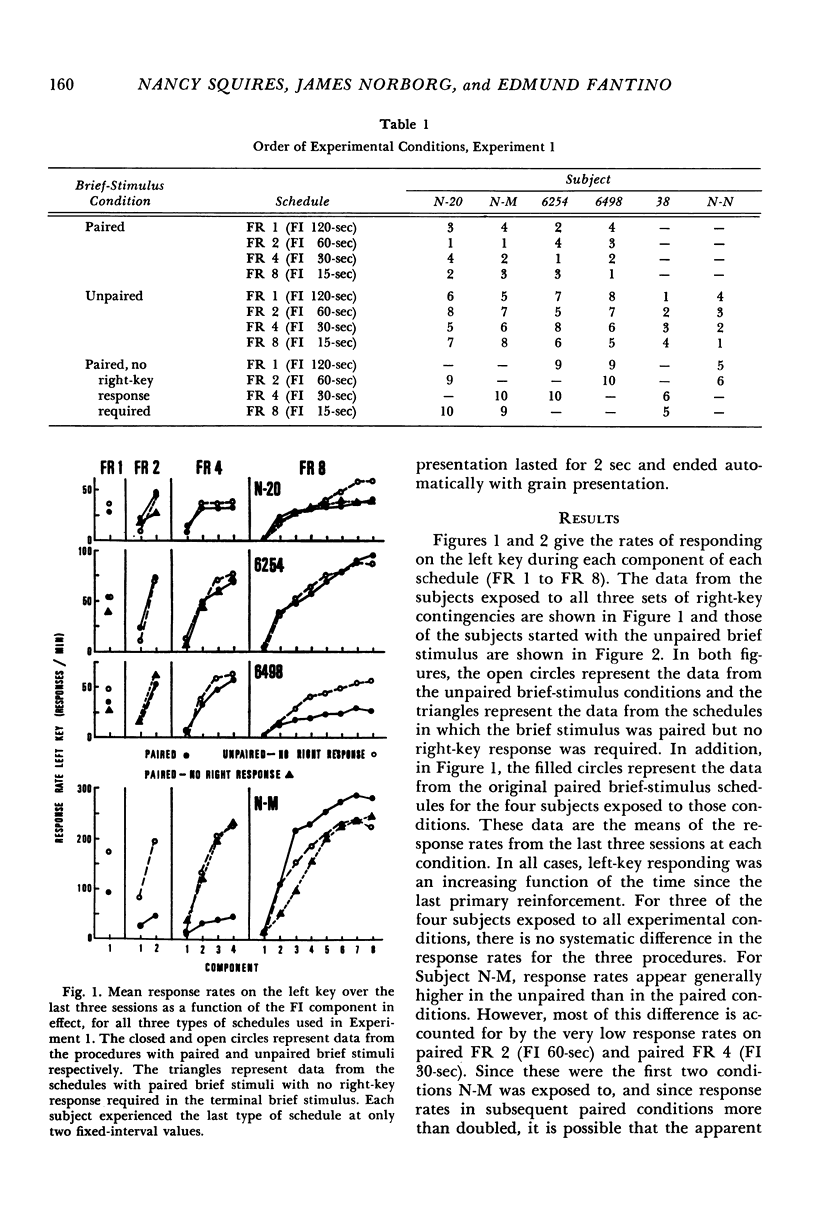
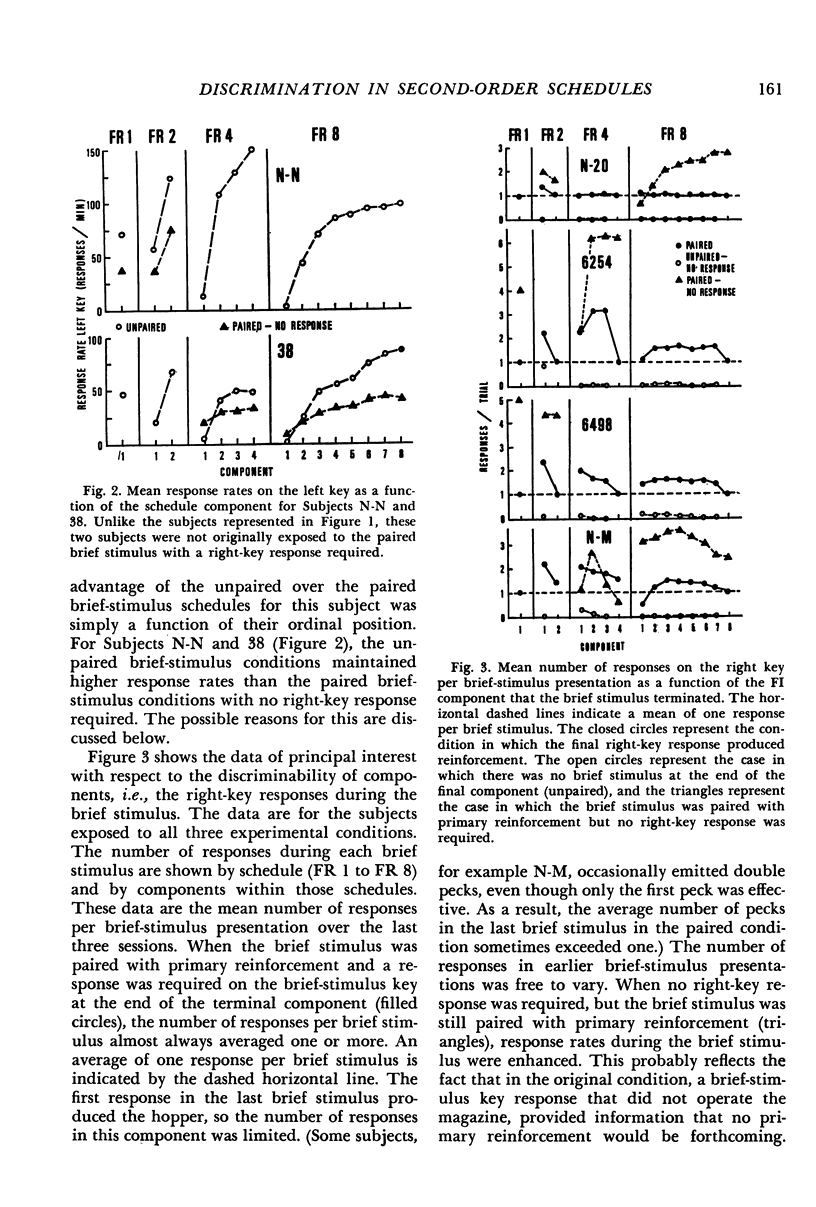
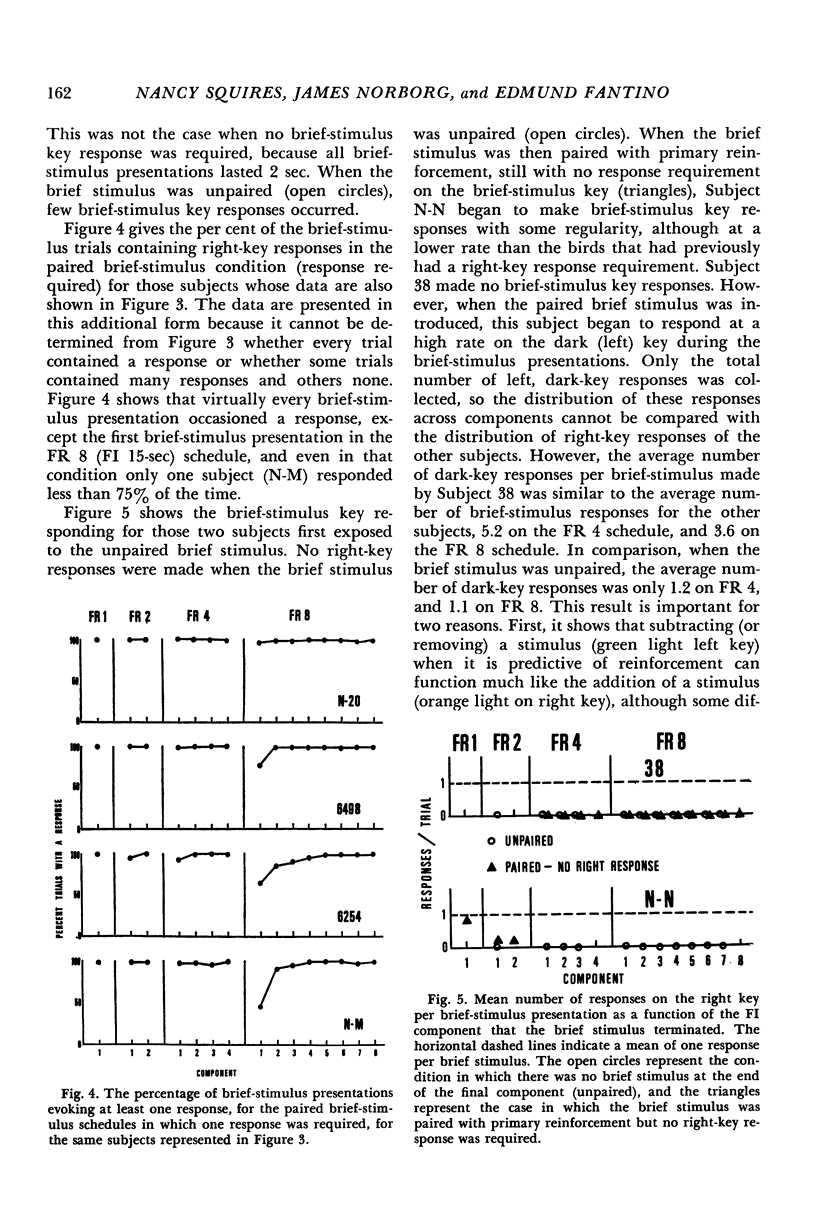
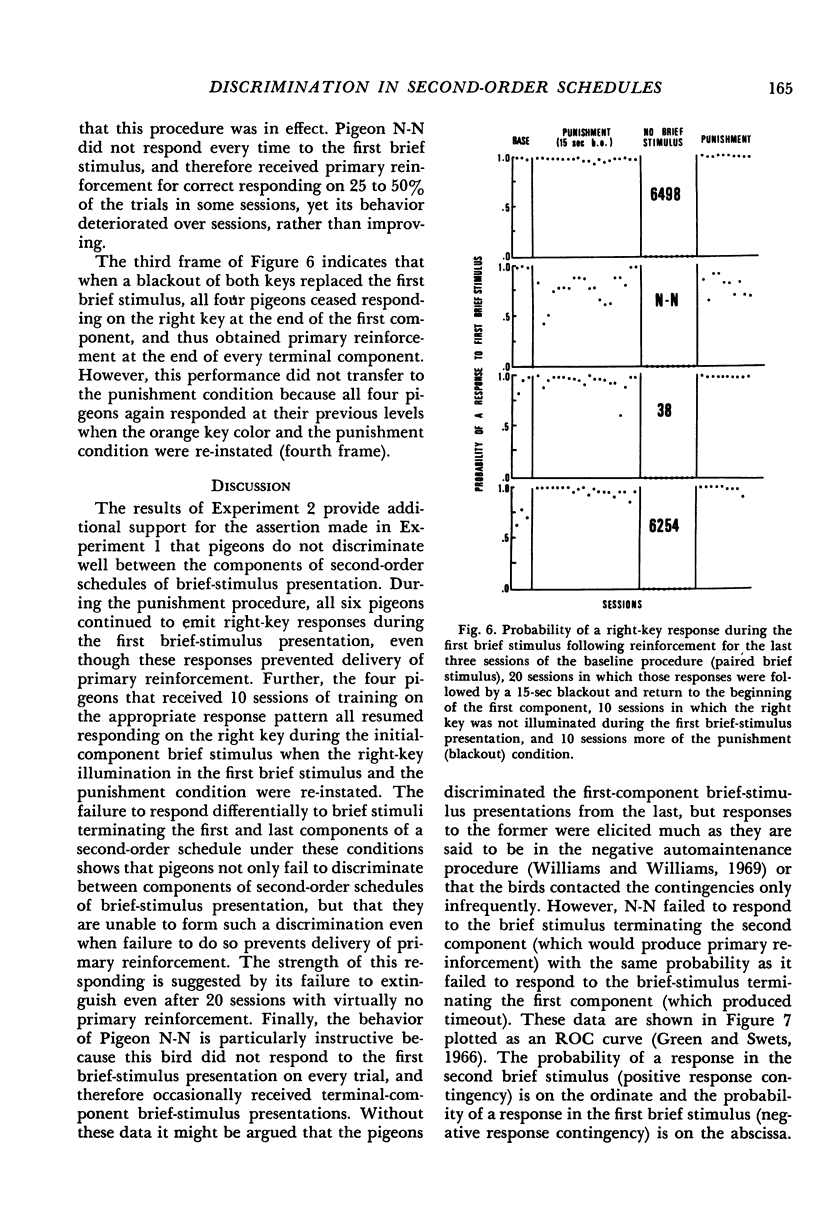
Pigeons were exposed to a series of second-order schedules in which the completion of a fixed number of fixed-interval components produced food. In Experiment 1, brief (2 sec) stimulus presentations occurred as each fixed-interval component was completed. During the brief-stimulus presentation terminating the last fixed-interval component, a response was required on a second key, the brief-stimulus key, to produce food. Responses on the brief-stimulus key before the last brief-stimulus presentation had no scheduled consequences, but served as a measure of the extent to which the final component was discriminated from preceding components. Whether there were one, two, four, or eight fixed-interval components, responses on the brief-stimulus key occurred during virtually every brief-stimulus presentation. In Experiment 2, an attempt was made to punish unnecessary responses on the brief-stimulus key, i.e., responses on the brief-stimulus key that occurred before the last component. None of the pigeons learned to withhold these responses, even though they produced a 15-sec timeout and loss of primary reinforcement. In Experiment 3, different key colors were associated with each component of a second-order schedule (a chain schedule). In contrast to Experiment 1, brief-stimulus key responses were confined to the last component. It was concluded that pigeons do not discriminate well between components of second-order schedules unless a unique exteroceptive cue is provided for each component. The relative discriminability of the components may account for the observed differences in initial-component response rates between comparable brief-stimulus, tandem, and chain schedules.
Keywords: second-order schedule, brief-stimulus presentations, chain schedule, conditioned reinforcement, temporal discrimination, fixed-interval schedule, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMSEL A., ROUSSEL J. Motivational properties of frustration. I. Effect on a running response of the addition of frustration to the motivational complex. J Exp Psychol. 1952 May;43(5):363–366. doi: 10.1037/h0059393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd L. D., Marr M. J. Relations between patterns of responding and the presentation of stimuli under second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):713–722. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. E. Cognition and conditioning: effects of masking the CS-UCS contingency on human GSR classical conditioning. J Exp Psychol. 1970 Sep;85(3):389–396. doi: 10.1037/h0029715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. E., Grings W. W. Comparison of classical conditioning and relational learning. J Exp Psychol. 1968 Feb;76(2):227–231. doi: 10.1037/h0025369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINGS W. W., LOCKHART R. A. EFFECTS OF ''ANXIETY-LESSENING'' INSTRUCTIONS AND DIFFERENTIAL SET OF DEVELOPMENT ON THE EXTINCTION OF GSR. J Exp Psychol. 1963 Sep;66:292–299. doi: 10.1037/h0045094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E. R., Williams D. R. Associative factors underlying the pigeon's key pecking in auto-shaping procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Mar;19(2):225–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E., Schwartz B. The maintenance of key pecking by stimulus-contingent and response-independent food presentation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jan;19(1):65–72. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E., Williams D. R. Classical conditioning of a complex skeletal response. Science. 1971 Mar 5;171(3974):923–925. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3974.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jwaideh A. R. Responding under chained and tandem fixed-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Mar;19(2):259–267. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., FRY W. T. Stimulus functions in chained fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:167–173. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagodi E. F., Deweese J., Johnston J. M. Second-order schedules: a comparison of chained, brief-stimulus, and tandem procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):447–460. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Chung S. H. Quasi-reinforcement: control of responding by a percentage-reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):45–54. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs A. Contiguity of briefly presented stimuli with food reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):271–278. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A. Second-order schedules and the problem of conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):289–313. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J. R. MULTIPLE BASELINE INVESTIGATION OF STIMULUS FUNCTIONS IN AN FR CHAINED SCHEDULE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 May;7:241–245. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. R., Williams H. Auto-maintenance in the pigeon: sustained pecking despite contingent non-reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jul;12(4):511–520. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J., Hanford P. V. Sustaining behavior with conditioned reinforcement as the only response-produced consequence. Psychol Rep. 1966 Oct;19(2):391–401. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1966.19.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


