Abstract
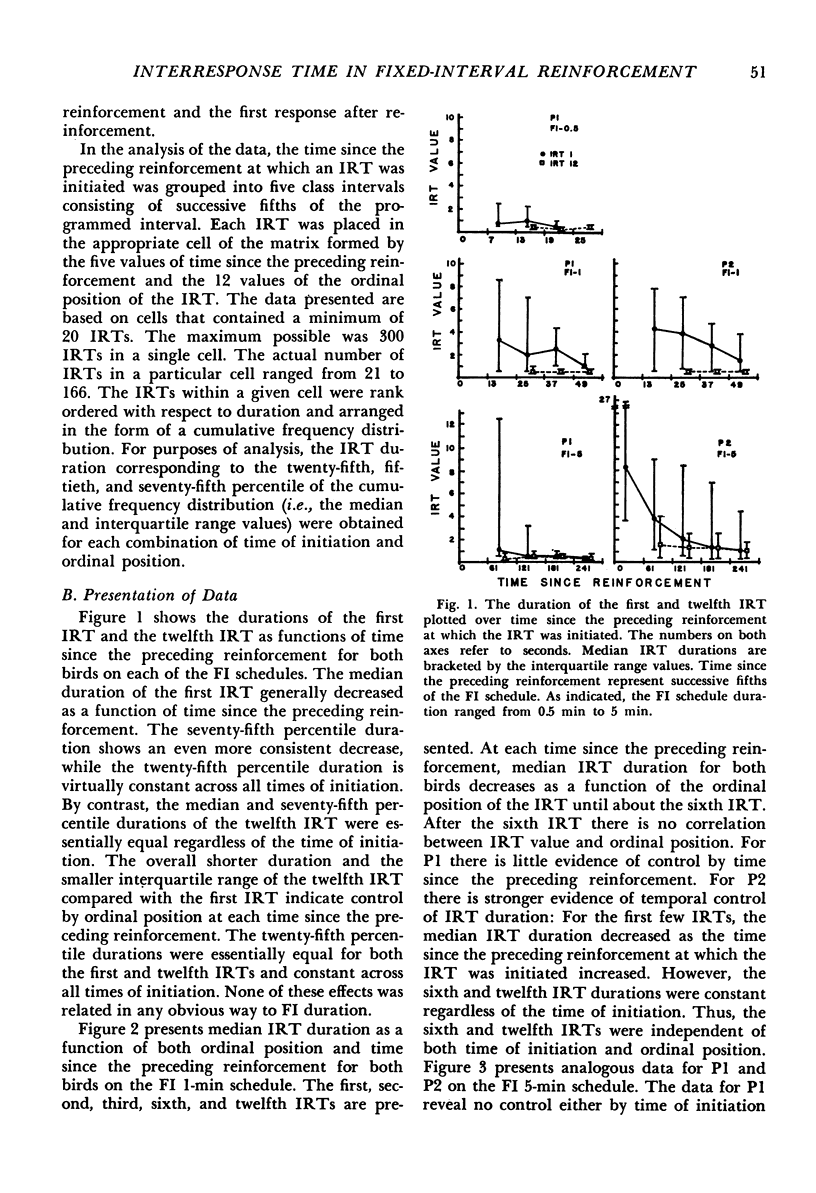
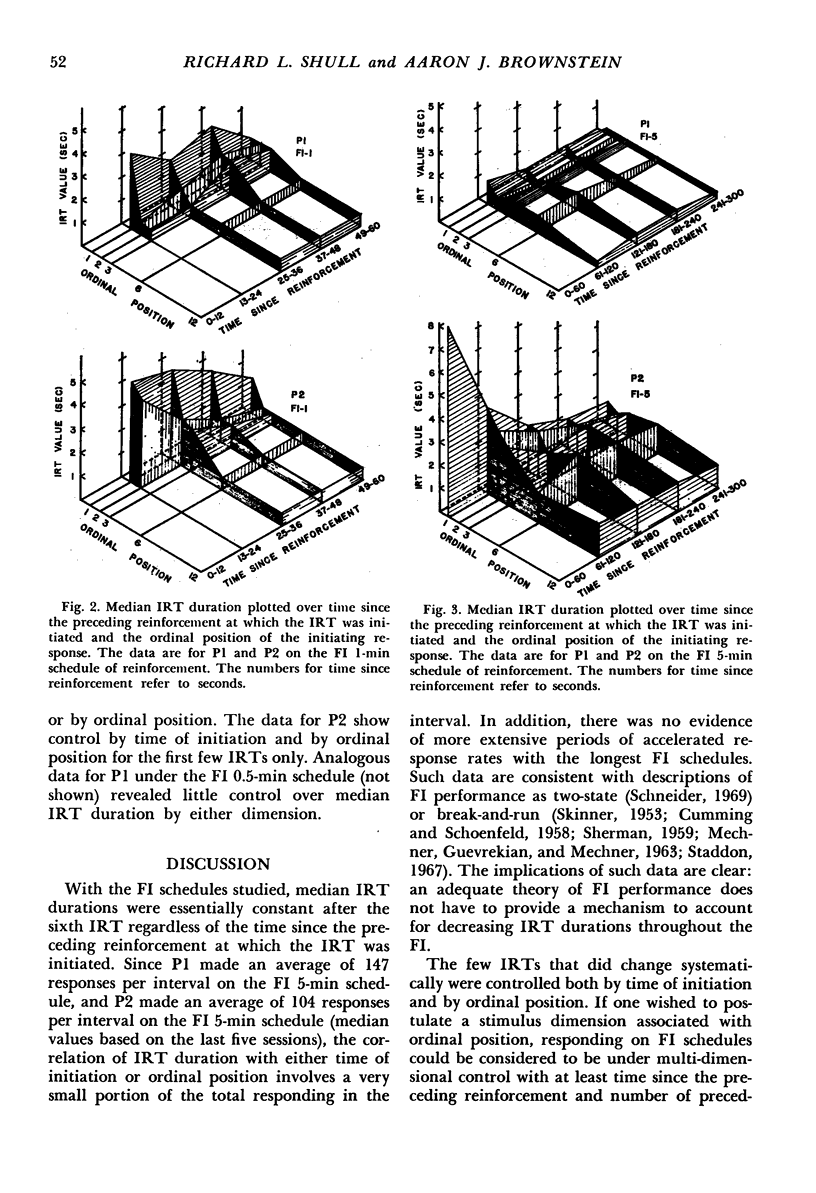
The times between each of the first thirteen responses after reinforcement (the first twelve interresponse times) were determined for two pigeons whose pecking was reinforced on fixed-interval schedules of food reinforcement ranging from 0.5 min to 5 min. These interresponse times were classified with respect to their ordinal position in the sequence of responses and with respect to the time since the preceding reinforcement at which the initiating response occurred. The median interresponse time durations were essentially constant after the sixth response after reinforcement regardless of the time at which the interresponse time was initiated. The durations of the first few interresponse times after reinforcement decreased as the number of preceding responses increased and as the time since the preceding reinforcement increased.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blough D. S. Interresponse time as a function of continuous variables: a new method and some data. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6(2):237–246. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming W. W., Schoenfeld W. N. Behavior under extended exposure to a high-value fixed interval reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Aug;1(3):245–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. The effect of multiple S delta periods on responding on a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jul;5:369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINTSCH W. FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION OF INTERRESPONSE TIMES DURING VI AND VR REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Sep;8:347–352. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MECHNER F., GUEVREKIAN L., MECHNER V. A fixed interval schedule in which the interval is initiated by a response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:323–330. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechner F. Probability Relations within Response Sequences under Ratio Reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):109–121. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliskoff S. S., Goldiamond I. Some discriminative properties of fixed ratio performance in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jan;9(1):1–9. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILLING M., MCDIARMID C. SIGNAL DETECTION IN FIXED-RATIO SCHEDULES. Science. 1965 Apr 23;148(3669):526–527. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3669.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling M. Number of responses as a stimulus in fixed interval and fixed ratio schedules. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Feb;63(1):60–65. doi: 10.1037/h0024164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Attention and temporal discrimination: factors controlling responding under a cyclic-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jul;10(4):349–359. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


