Abstract
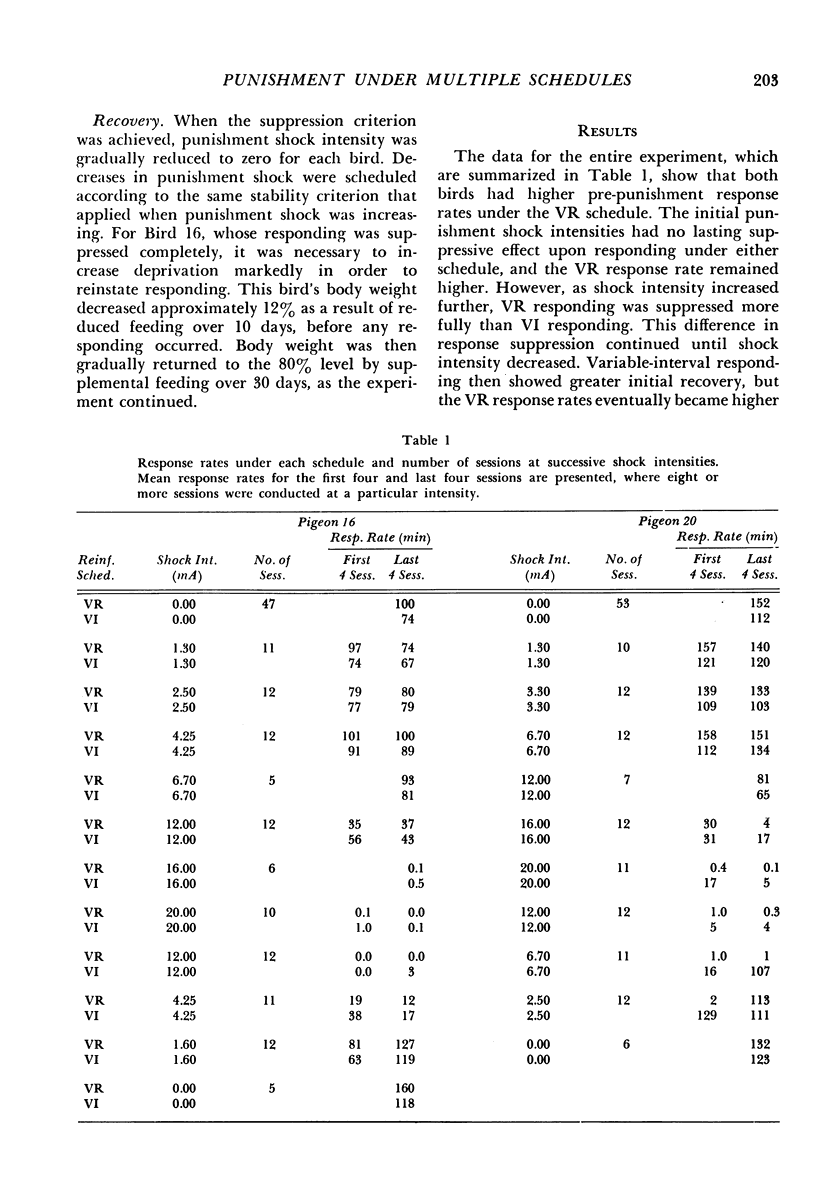
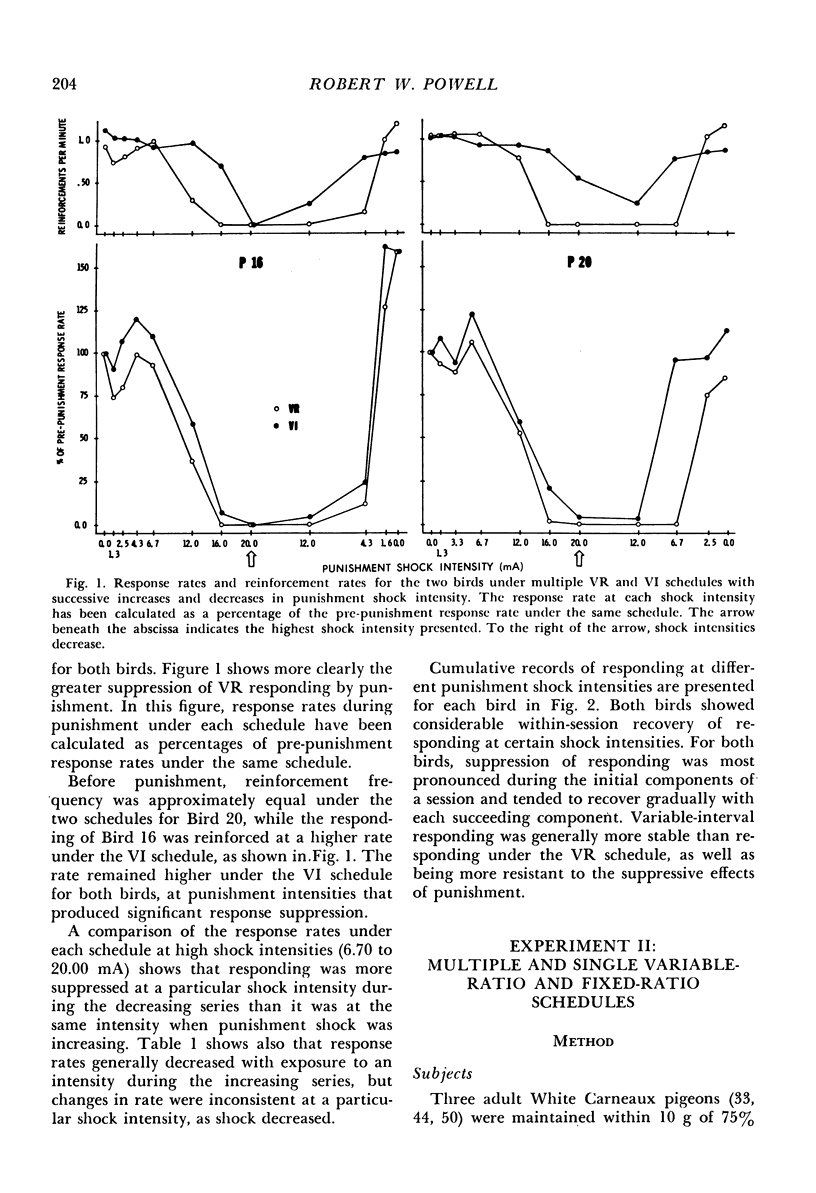
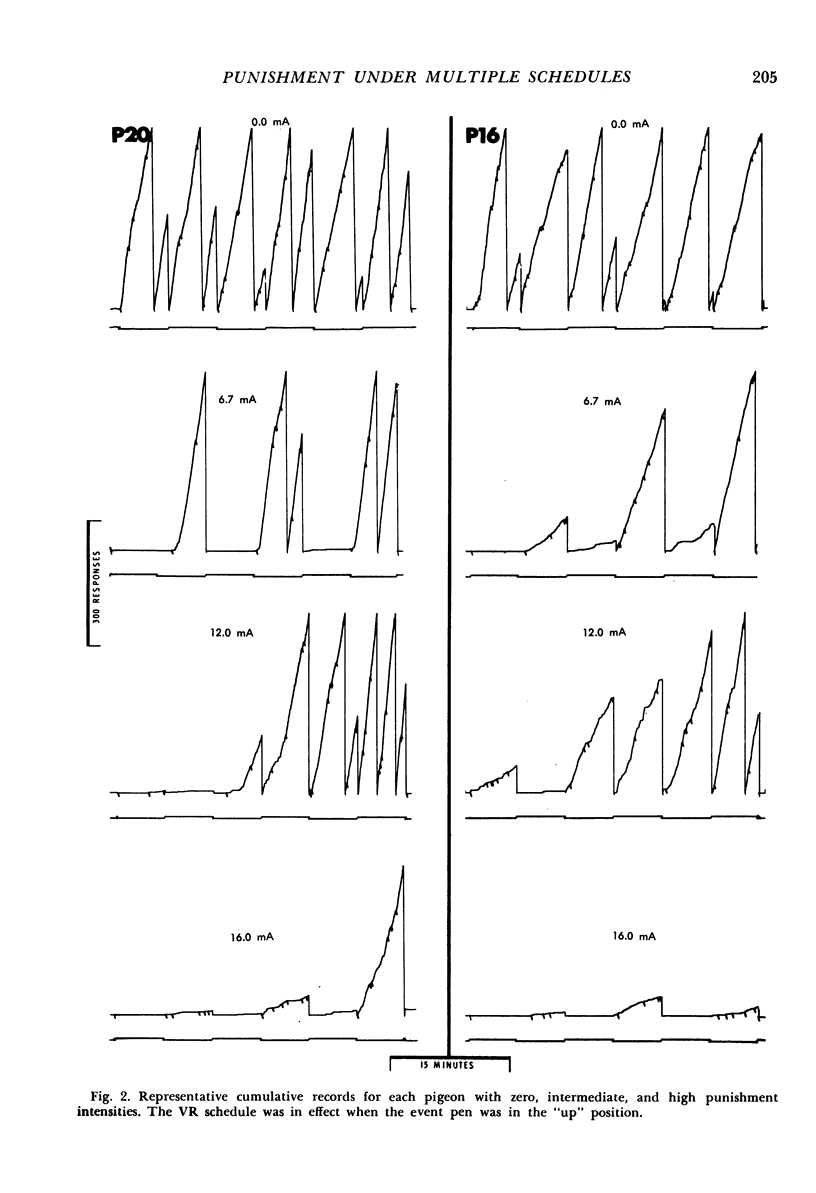
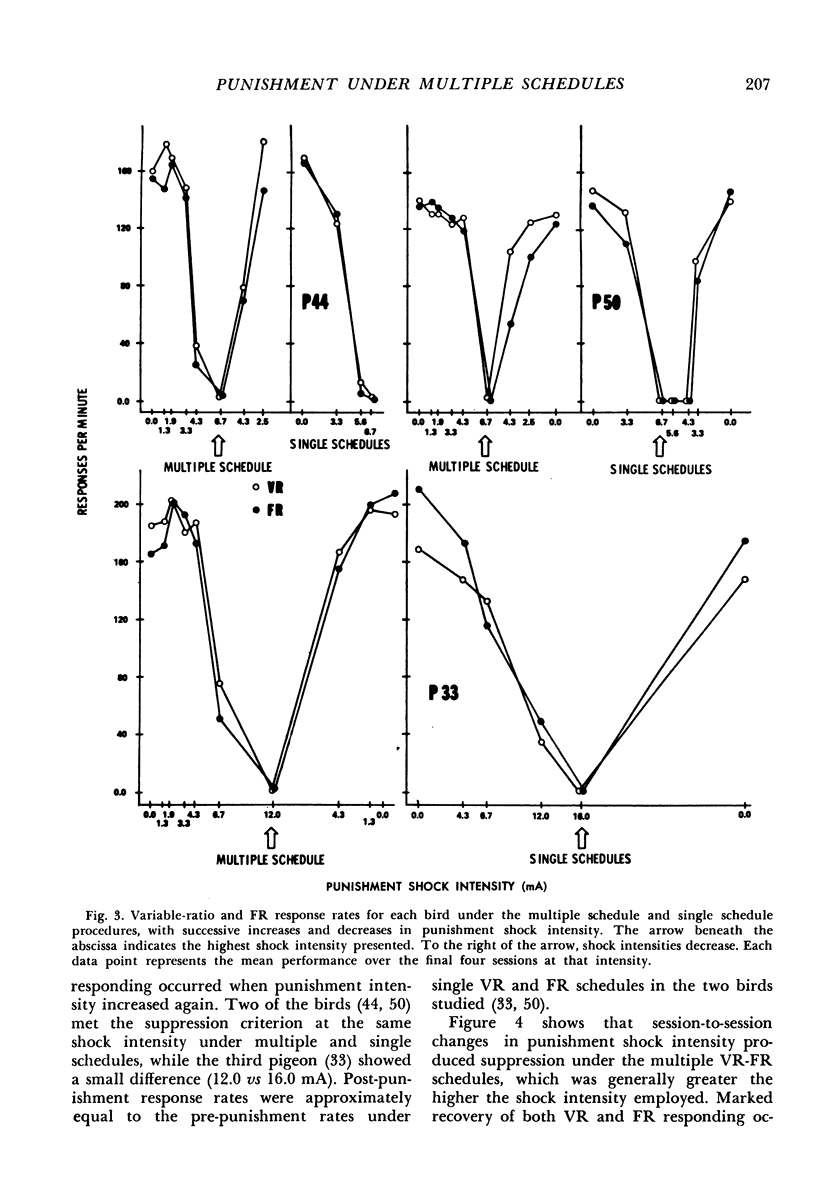
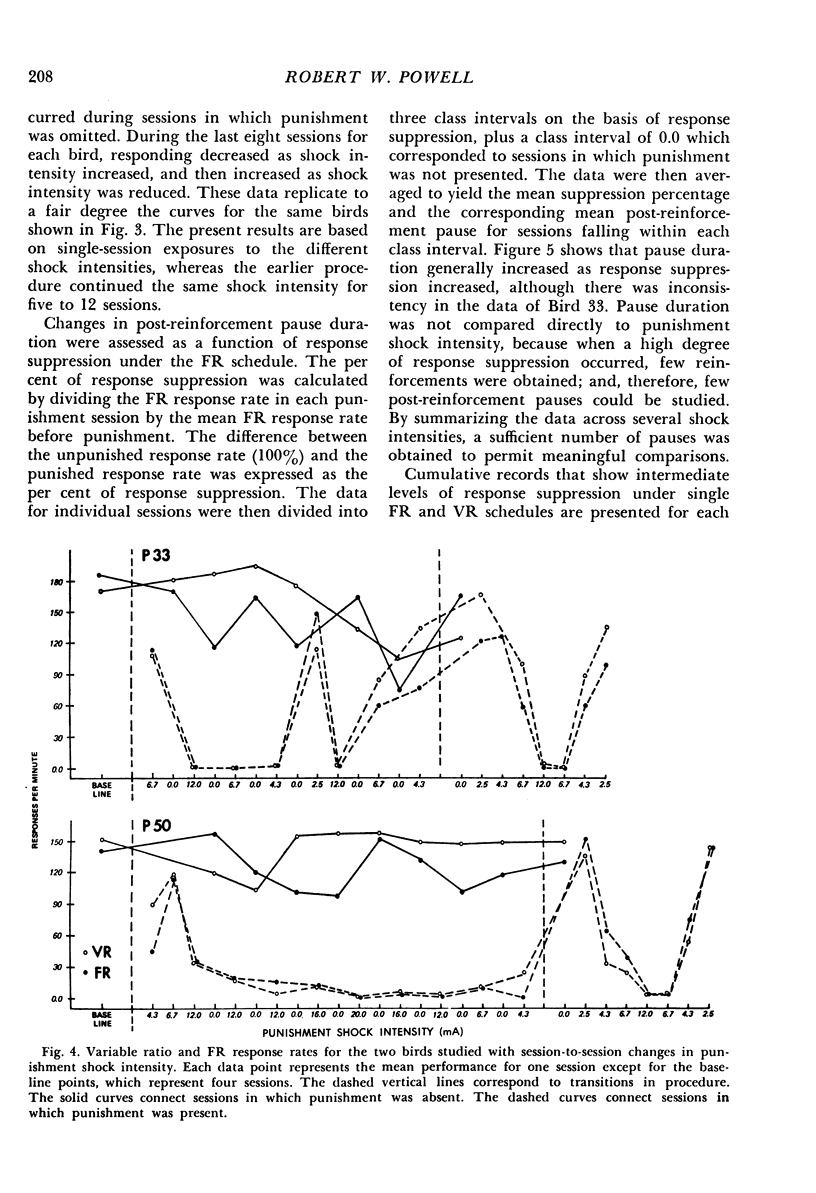
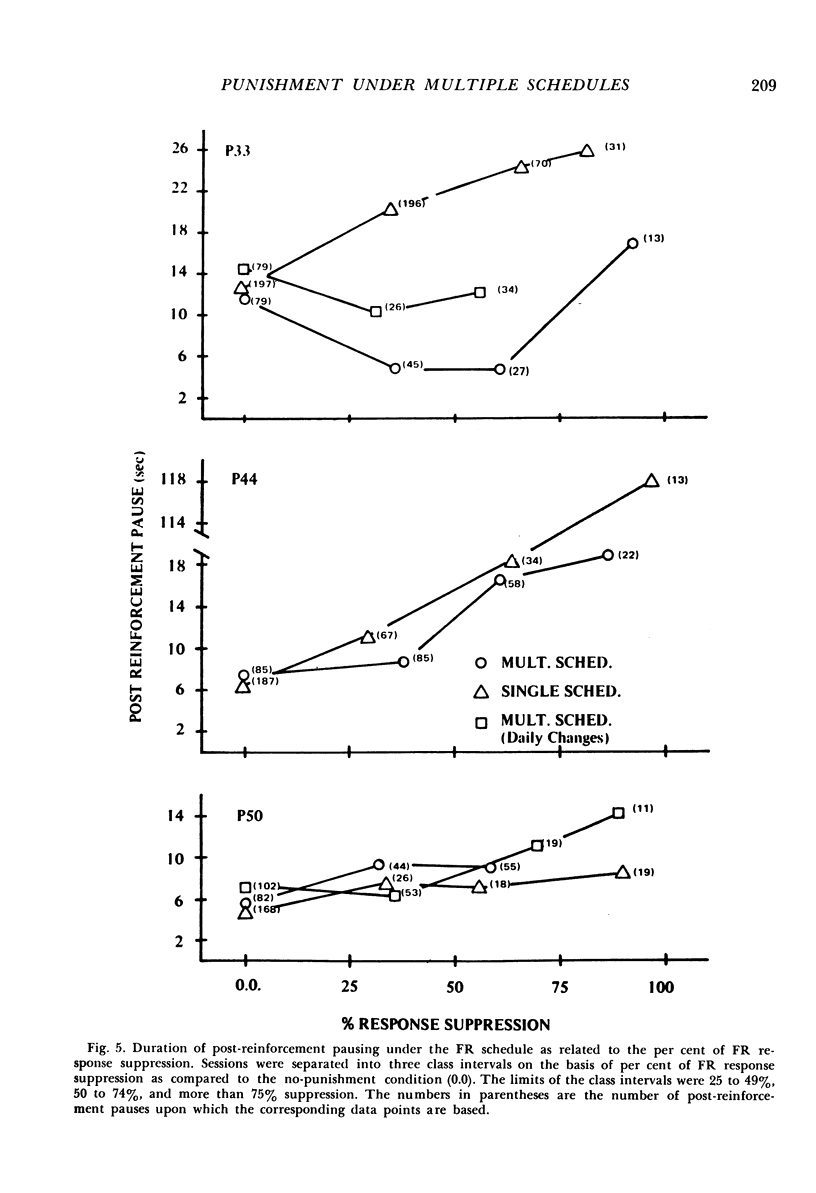
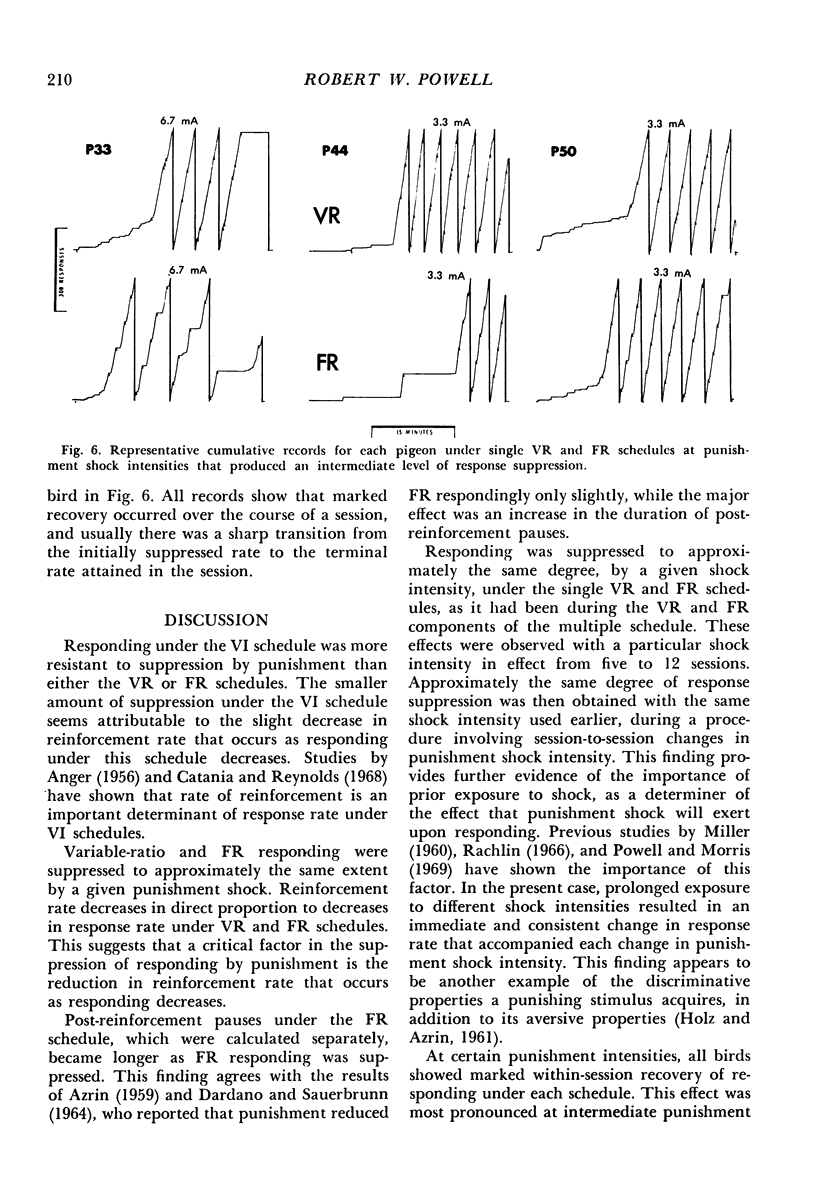
In the first of two experiments, responses of two pigeons were maintained by multiple variable-interval, variable-ratio schedules of food reinforcement. Concurrent punishment was introduced, which consisted of a brief electric shock after each tenth response. The initial punishment intensities had no lasting effect upon responding. Then, as shock intensity increased, variable-ratio response rates were suppressed more quickly than variable-interval response rates. When shock intensity decreased, variable-interval responding recovered more quickly, but the rates under both schedules eventually returned to their pre-punishment levels. In the second experiment, the following conditions were studied in three additional pigeons: (1) With each shock intensity in effect for a number of sessions, punishment shock intensity was gradually increased and decreased and responding was maintained by multiple variable-ratio, fixed-ratio schedules of food reinforcement; (2) Changes in punishment shock intensity as described above with responding maintained by either a variable-ratio or a fixed-ratio schedule, which were presented on alternate days; (3) Session-to-session changes in shock intensity with responding maintained by multiple variable-ratio, fixed-ratio schedules. Responding under the two schedules was suppressed to approximately the same extent by a particular shock intensity. Also, post-reinforcement pauses under the fixed-ratio schedule increased as response suppression increased.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPEL J. B., PETERSON N. J. PUNISHMENT: EFFECTS OF SHOCK INTENSITY ON RESPONSE SUPPRESSION. Psychol Rep. 1965 Jun;16:721–730. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1965.16.3.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Effects of punishment intensity during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:123–142. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C. Punishment during fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:343–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARDANO J. F., SAUERBRUNN D. SELECTIVE PUNISHMENT OF FIXED-RATIO PERFORMANCE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 May;7:255–260. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H. Discriminative properties of punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:225–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake D. F., Azrin N. H., Oxford R. The effects of punishment intensity on squirrel monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):95–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON D. O. Frequency of reinforcement as a parameter of conditioned suppression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:95–98. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon D. O., Felton M. Conditioned suppression and variable ratio reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):245–248. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER N. E. Learning resistance to pain and fear: effects of overlearning, exposure, and rewarded expsure in context. J Exp Psychol. 1960 Sep;60:137–145. doi: 10.1037/h0043321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R. W., Morris G. Continuous punishment of free-operant avoidance in the rat. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):149–157. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. Recovery of responses during mild punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):251–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


