Abstract
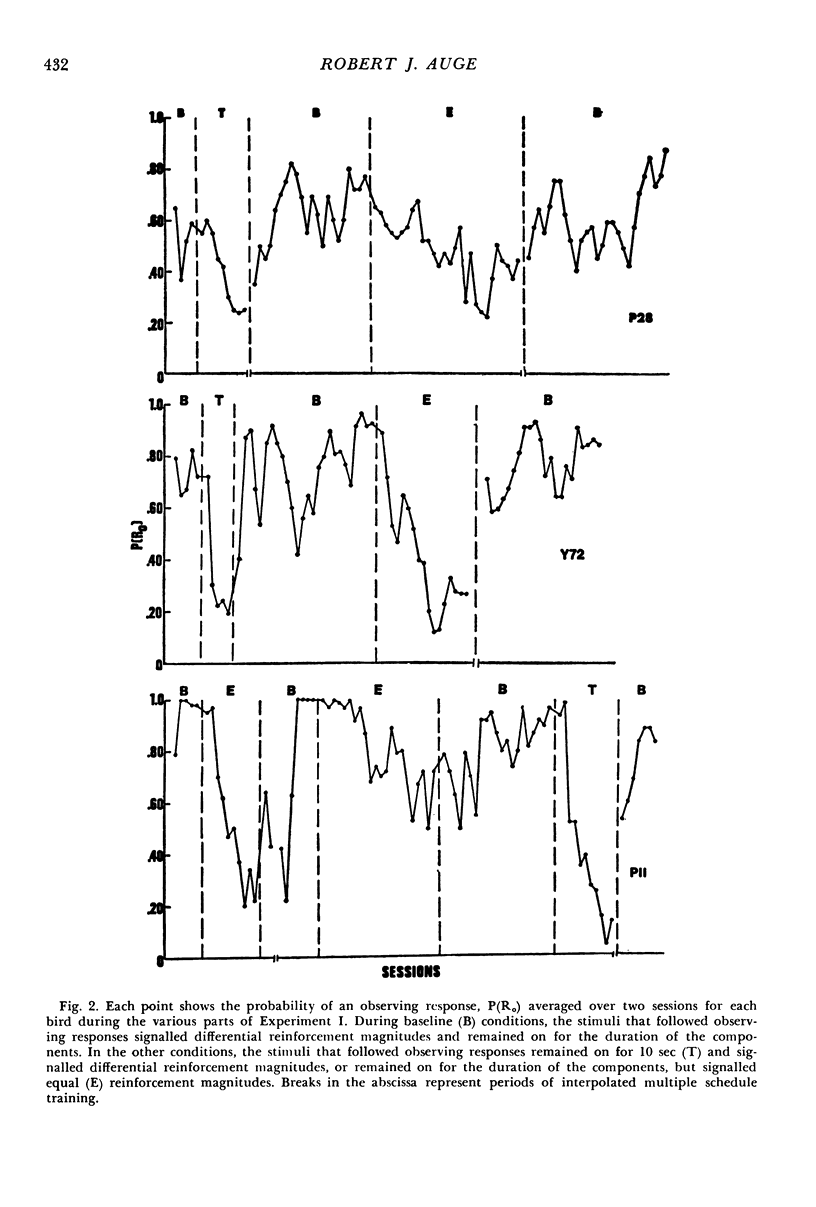
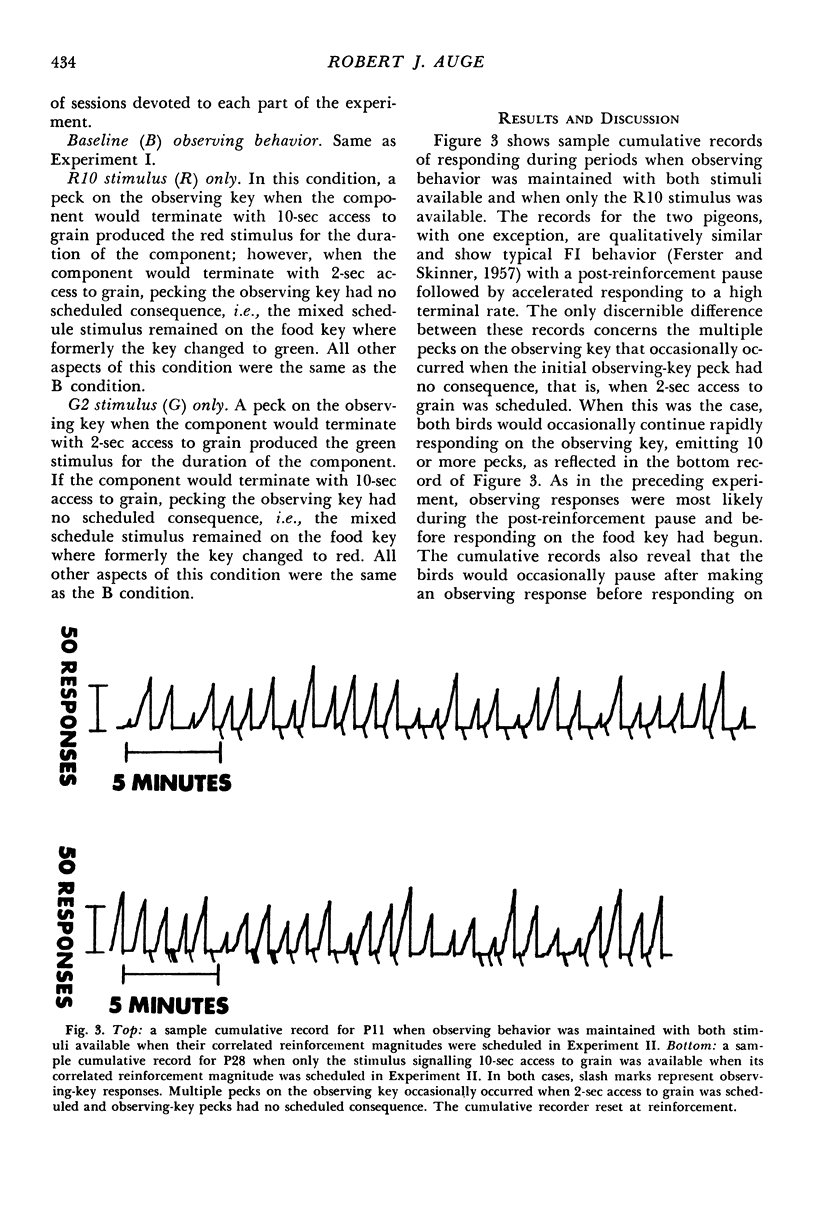
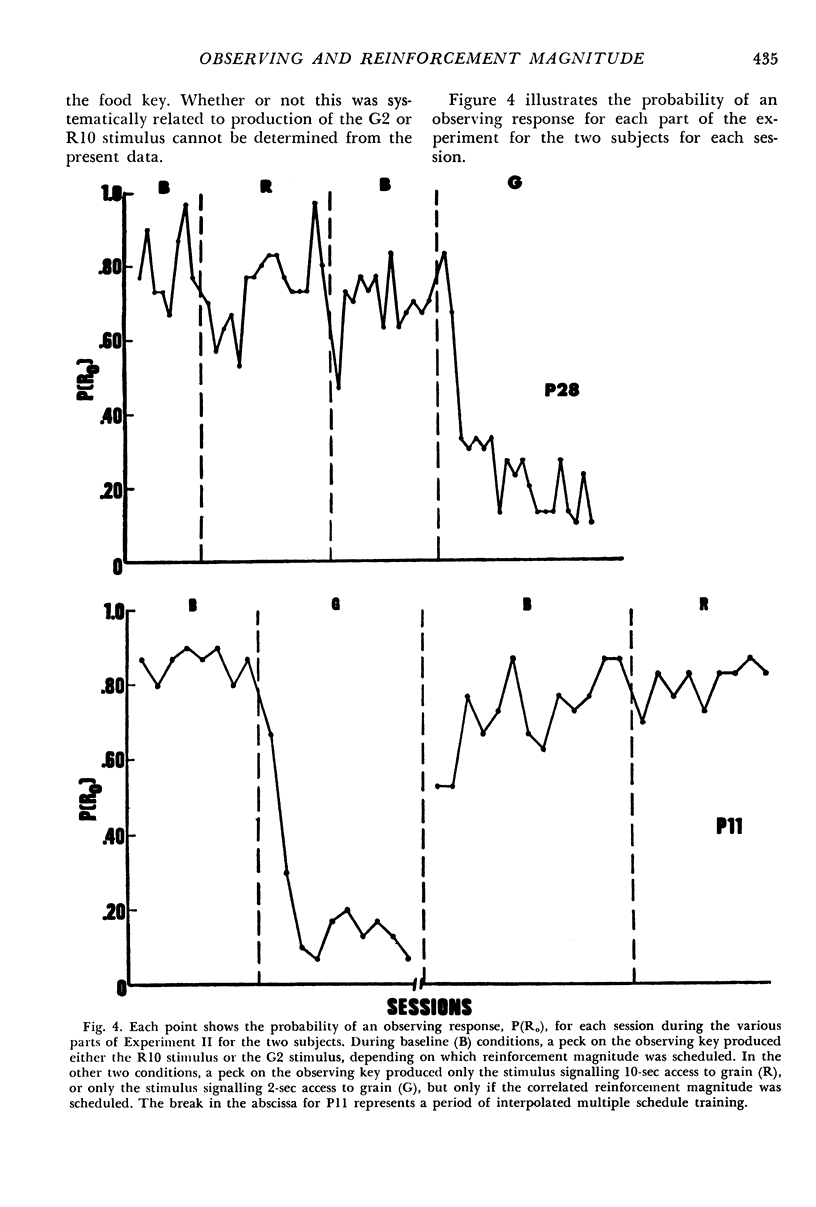
Pigeons made observing responses for stimuli signalling the availability of either 10-sec or 2-sec access to grain on fixed-interval 1-min schedules. If observing responses did not occur, food-producing responses occurred to a stimulus common to both reinforcement magnitudes. When the stimuli remained on for the duration of the components and signalled differential reinforcement magnitudes, observing responses were maintained; however, when the stimuli remained on for 10 sec, observing responses decreased markedly. In addition, it was shown that the occasional presentation of the stimulus signalling 10-sec access to grain was necessary for the maintenance of observing behavior. A control condition demonstrated that when all the available stimuli signalled 6-sec access to grain, observing responses declined. Taken together, the results demonstrated that the occasional presentation of the stimulus that remained on for the duration of the component and signalled the larger reinforcement magnitude was necessary for the maintenance of observing behavior.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownstein A. J. Concurrent schedules of response-independent reinforcement: duration of a reinforcing stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):211–214. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmoor J. A., Browne M. P., Lawrence C. E. A test of the negative discriminative stimulus as a reinforcer of observing. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):79–85. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsmore T. F. Control of responding by stimulus duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jul;16(1):81–87. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEESEY R. E., KLING J. W. Amount of reinforcement and free-operant responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:125–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., RIDDLE W. C., COOK L. Observing responses in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5:3–13. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDALL S. B. THE DISTRIBUTION OF OBSERVING RESPONSES IN A MIXED FI-FR SCHEDULE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Sep;8:305–312. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariner R. W., Thomas D. R. Reinforcement duration and the peak shift in post-discrimination gradients. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):759–766. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Response rate as a function of amount of reinforcement for a signalled concurrent response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):11–16. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHETTLEWORTH S., NEVIN J. A. RELATIVE RATE OF RESPONSE AND RELATIVE MAGNITUDE OF REINFORCEMENT IN MULTIPLE SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jul;8:199–202. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYCKOFF L. B., Jr The role of observing responses in discrimination learning. Psychol Rev. 1952 Nov;59(6):431–442. doi: 10.1037/h0053932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


