Abstract
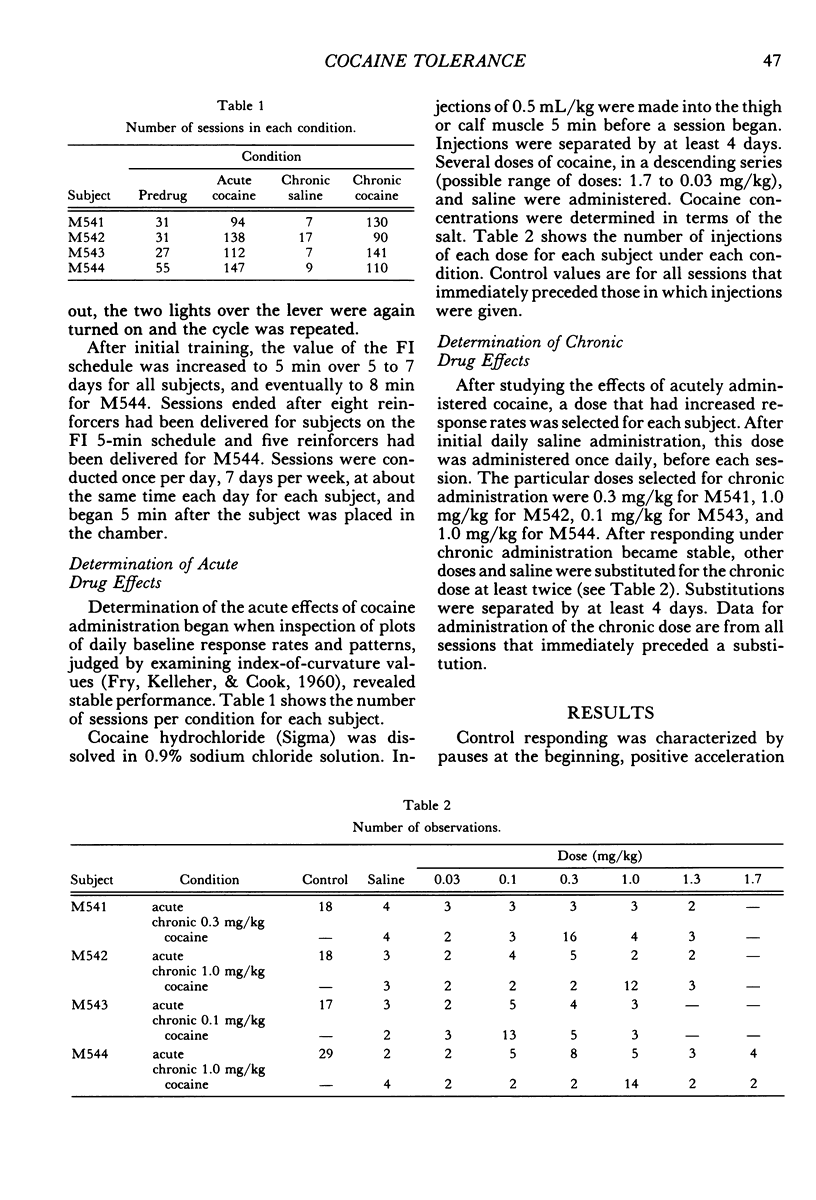
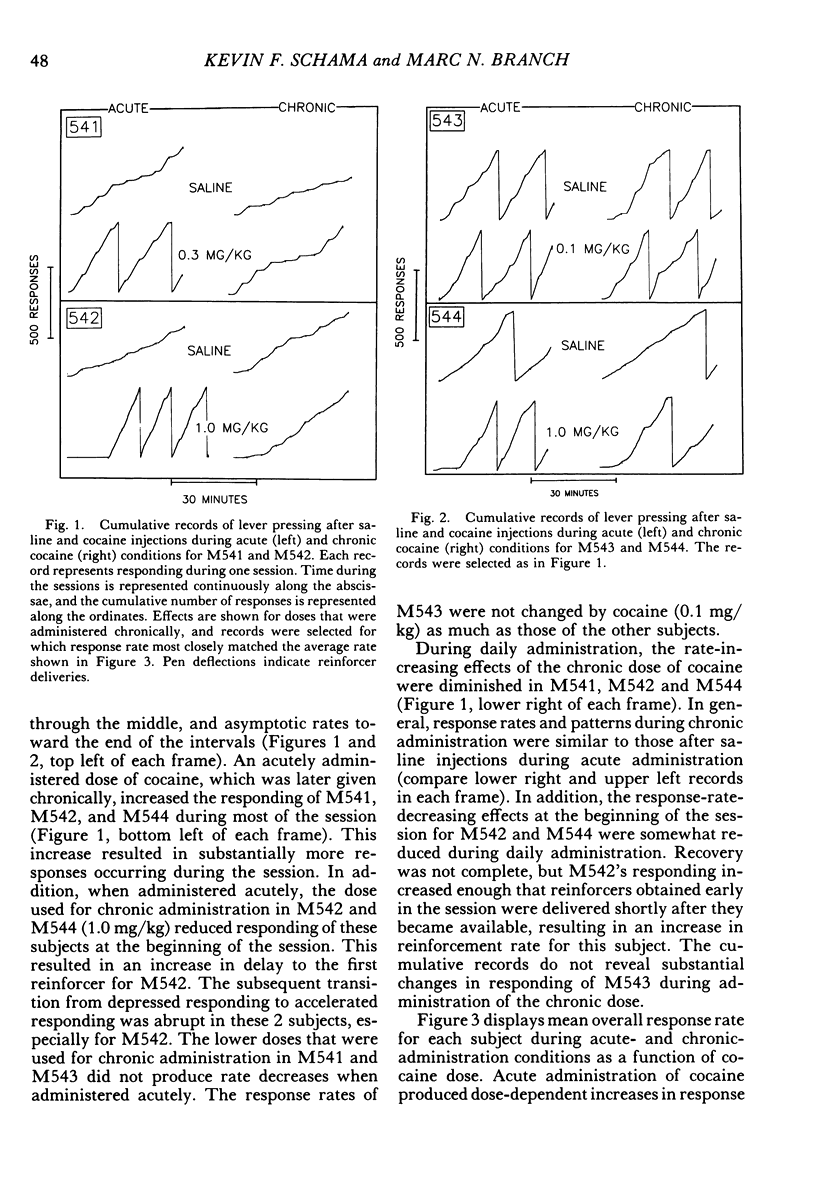
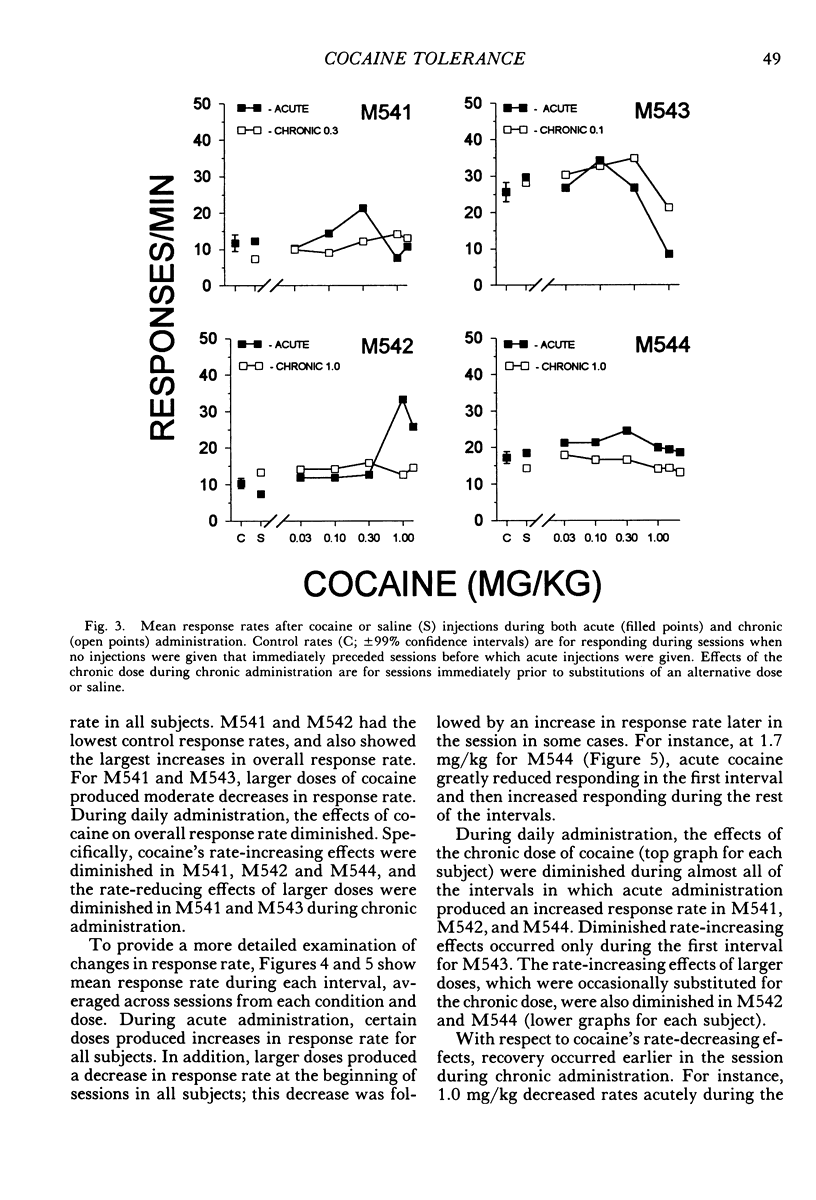
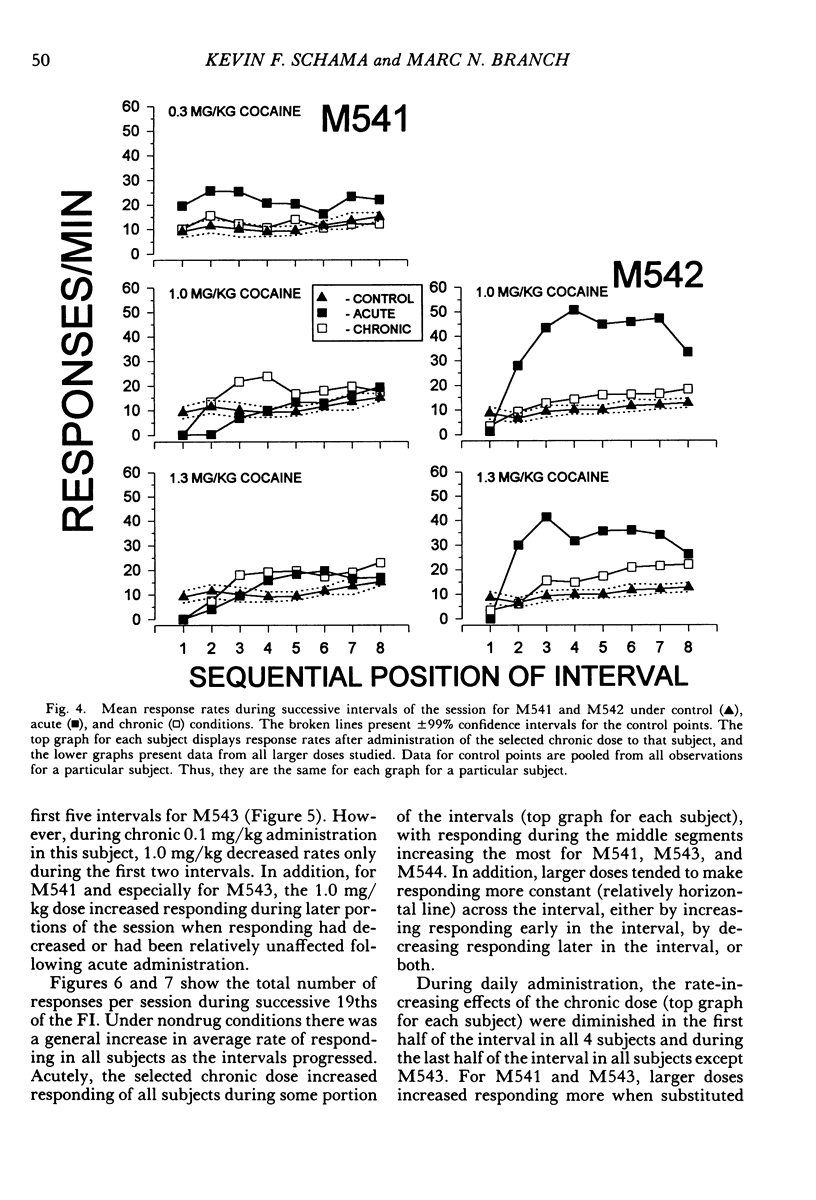
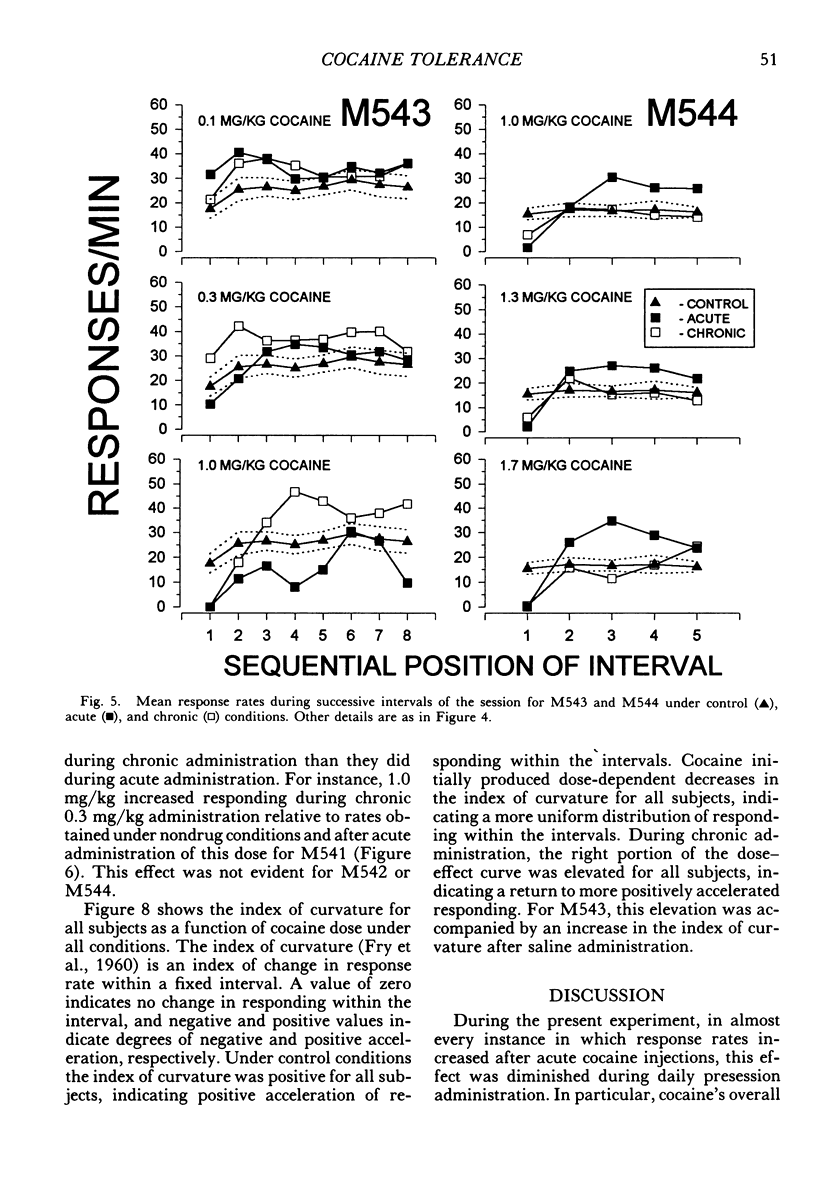
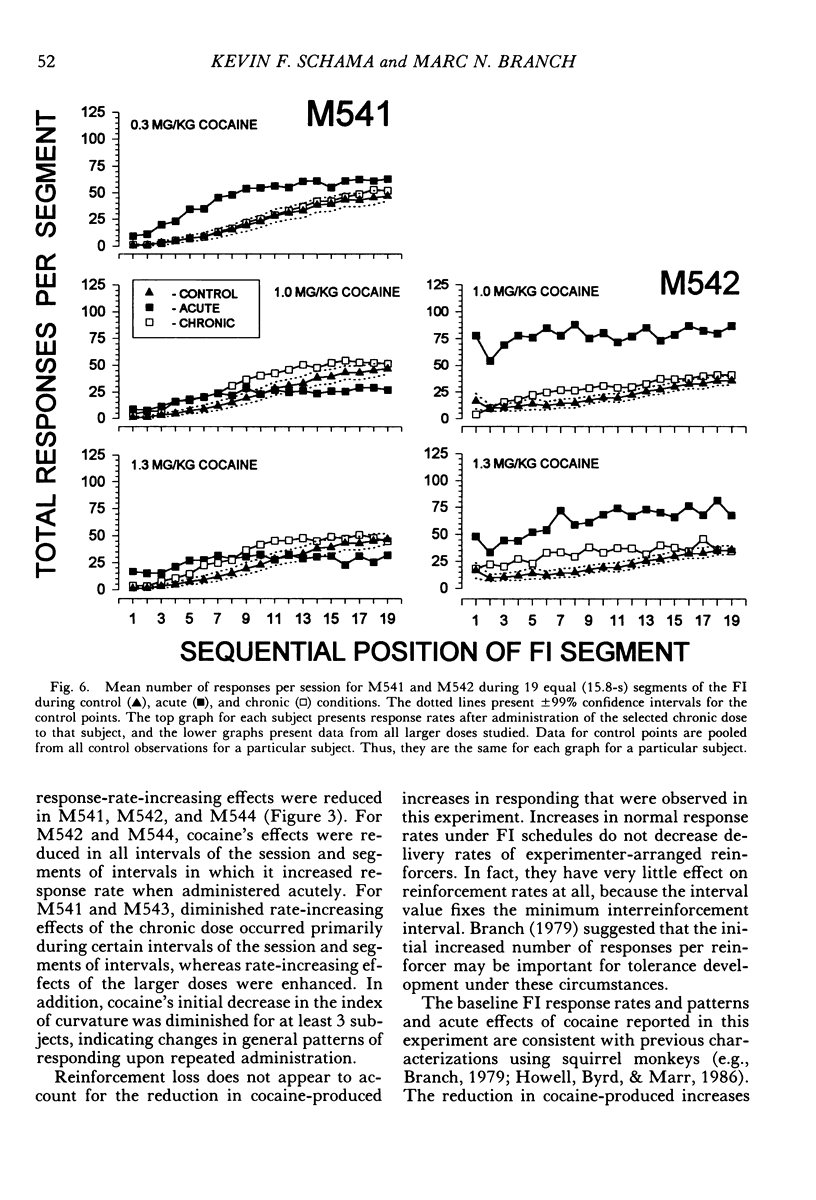
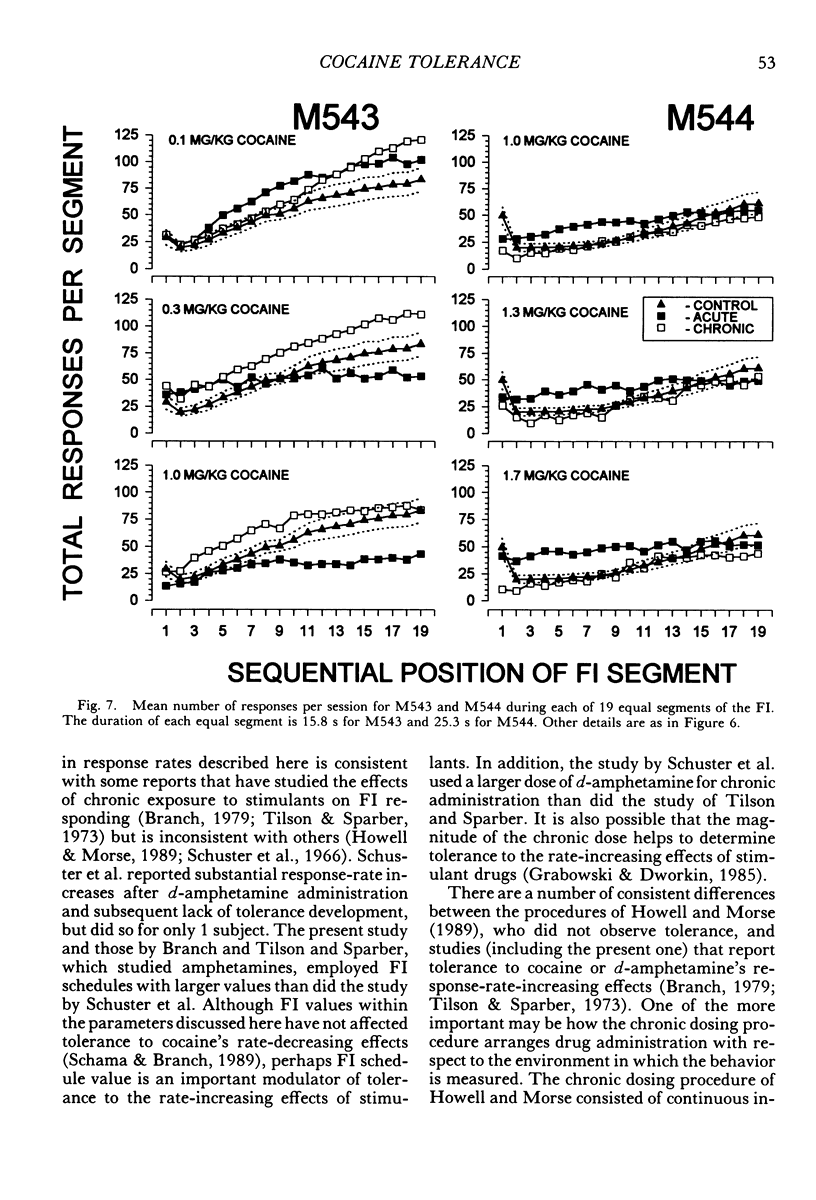
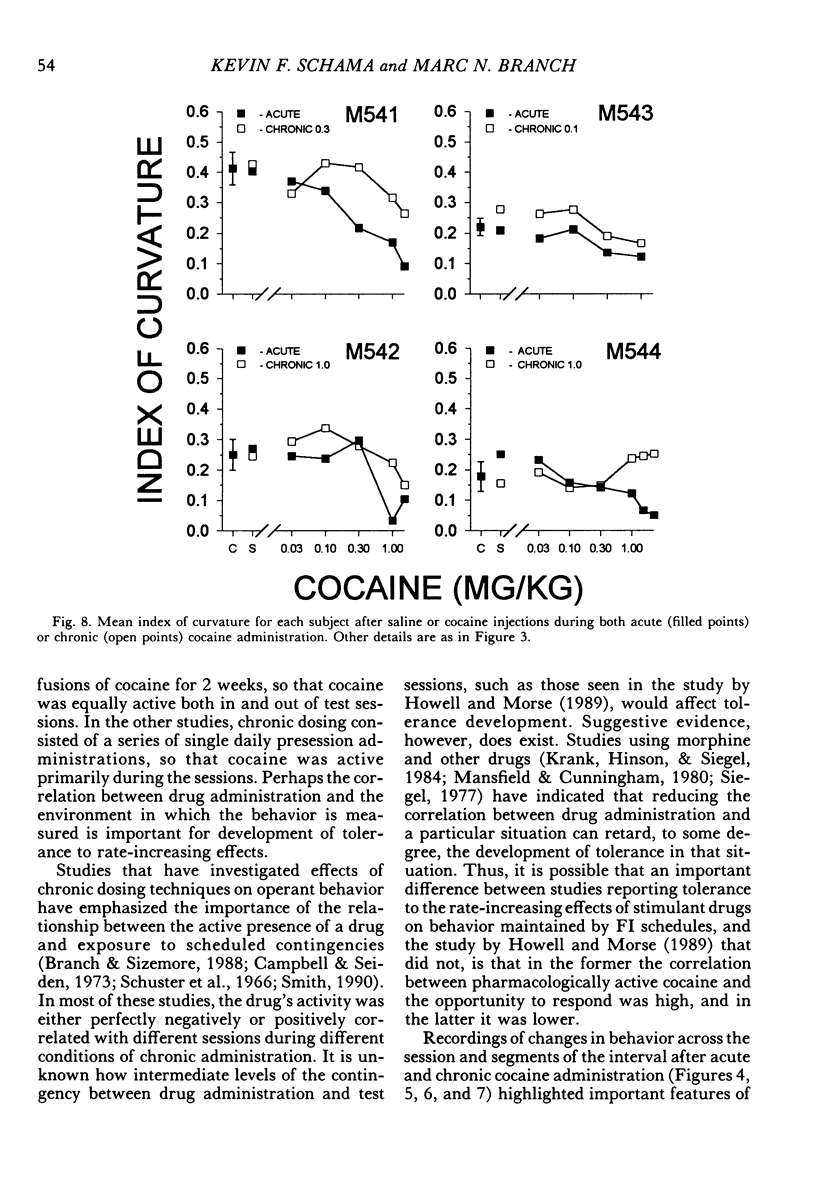
Four squirrel monkeys responded daily under a fixed-interval 5-min or 8-min schedule of food-pellet delivery. Cocaine (0.03 to 1.7 mg/kg) and saline were injected before occasional daily sessions (acute administration). Some doses of cocaine produced substantial overall increases in response rate for 3 of the subjects; effects were less substantial for the remaining subject, who exhibited modest increases in response rate early in the session and during the middle portion of the intervals. A dose that increased response rate when administered acutely was then administered before each session (chronic administration). Chronic administration resulted in a reduction in the increases in response rate seen under acute administration for all subjects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branch M. N. Consequent events as determinants of drug effects on schedule-controlled behavior: modification of effects of cocaine and d-amphetamine following chronic amphetamine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Sep;210(3):354–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch M. N., Sizemore G. M. Behavioral tolerance to cocaine in squirrel monkeys: acute and chronic effects on complex operant behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Jul;30(3):737–748. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. C., Seiden L. S. Performance influence on the development of tolerance to amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1973 Nov-Dec;1(6):703–708. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(73)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY W., KELLEHER R. T., COOK L. A mathematical index of performance on fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:193–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski J., Dworkin S. I. Cocaine: an overview of current issues. Int J Addict. 1985 Jun-Jul;20(6-7):1065–1088. doi: 10.3109/10826088509047765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKE D. F., AZRIN N. H. An apparatus for delivering pain shock to monkevs. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:297–298. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell L. L., Byrd L. D., Marr M. J. Similarities in the rate-altering effects of white noise and cocaine. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Nov;46(3):381–394. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.46-381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell L. L., Morse W. H. Behavioral effects of chronically administered cocaine in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1989;97(1):12–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00443405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson C. E., Fischman M. W. The pharmacology of cocaine related to its abuse. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Mar;41(1):3–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., MORSE W. H. ESCAPE BEHAVIOR AND PUNISHED BEHAVIOR. Fed Proc. 1964 Jul-Aug;23:808–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krank M. D., Hinson R. E., Siegel S. Effect of partial reinforcement on tolerance to morphine-induced analgesia and weight loss in the rat. Behav Neurosci. 1984 Feb;98(1):72–78. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.98.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. G., Cunningham C. L. Conditioning and extinction of tolerance to the hypothermic effect of ethanol in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1980 Oct;94(5):962–969. doi: 10.1037/h0077824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Thompson D. M. Acute and chronic effects of cocaine on extinction-induced aggression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Mar;29(2):309–318. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. M., Rose H. Increasing effects of repetitive cocaine administration in the rat. Nature. 1976 Apr 22;260(5553):731–732. doi: 10.1038/260731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schama K. F., Branch M. N. Tolerance to effects of cocaine on schedule-controlled behavior: effects of fixed-interval schedule parameter. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989 Jan;32(1):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(89)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster C. R., Dockens W. S., Woods J. H. Behavioral variables affecting the development of amphetamine tolerance. Psychopharmacologia. 1966;9(2):170–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00404721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., McKearney J. W. Changes in the rate-increasing effects of d-amphetamine and pentobarbital by response consequences. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1977 Jul 18;53(2):151–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00426485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spealman R. D., Goldberg S. R., Kelleher R. T., Goldberg D. M., Charlton J. P. Some effects of cocaine and two cocaine analogs on schedule-controlled behavior of squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Sep;202(3):500–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilson H. A., Sparber S. B. The effects of d- and l- amphetamine on fixed-interval and fixed-ratio behavior in tolerant and nontolerant rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Nov;187(2):372–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolverton W. L., Kandel D., Schuster C. R. Effects of repeated administration of cocaine on schedule-controlled behavior of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1978 Sep;9(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(78)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolverton W. L., Kandel D., Schuster C. R. Tolerance and cross-tolerance to cocaine and d-amphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Jun;205(3):525–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolverton W. L., Kleven M. S. Evidence for cocaine dependence in monkeys following a prolonged period of exposure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;94(2):288–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00176861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haaren F. Differential effects of cocaine on high and low response rates maintained with and without rate requirements. Behav Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;3(5):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


