Abstract
We investigated the possibility that human-like fixed-interval performances would appear in rats given a variable-ratio history (Wanchisen, Tatham, & Mooney, 1989). Nine rats were trained under single or compound variable-ratio schedules and then under a fixed-interval 30-s schedule. The histories produced high fixed-interval rates that declined slowly over 90 sessions; differences as a function of the particular history were absent. Nine control animals given only fixed-interval training responded at lower levels initially, but rates increased with training. Despite differences in absolute rates, rates within the intervals and postreinforcement pauses indicated equivalent development of the accelerated response patterns suggestive of sensitivity to fixed-interval contingencies. The finding that the histories elevated rates without retarding development of differentiated patterns suggests that the effective response unit was a burst of several lever presses and that the fixed-interval contingencies acted on these units in the same way as for single responses. Regardless of history, the rats did not manifest the persistent, undifferentiated responding reported for humans under comparable schedules. We concluded that the shortcomings of animal models of human fixed-interval performances cannot be easily remedied by including a variable-ratio conditioning history within the model.
Full text
PDF


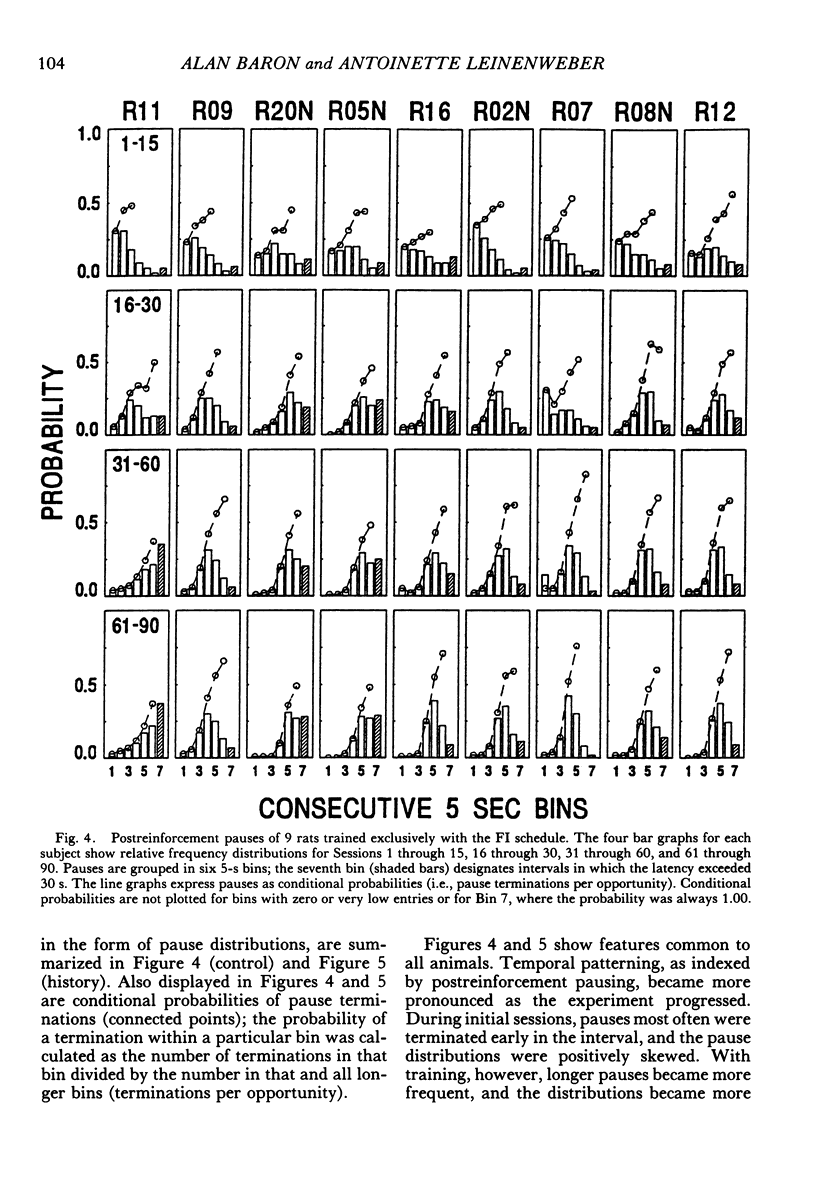
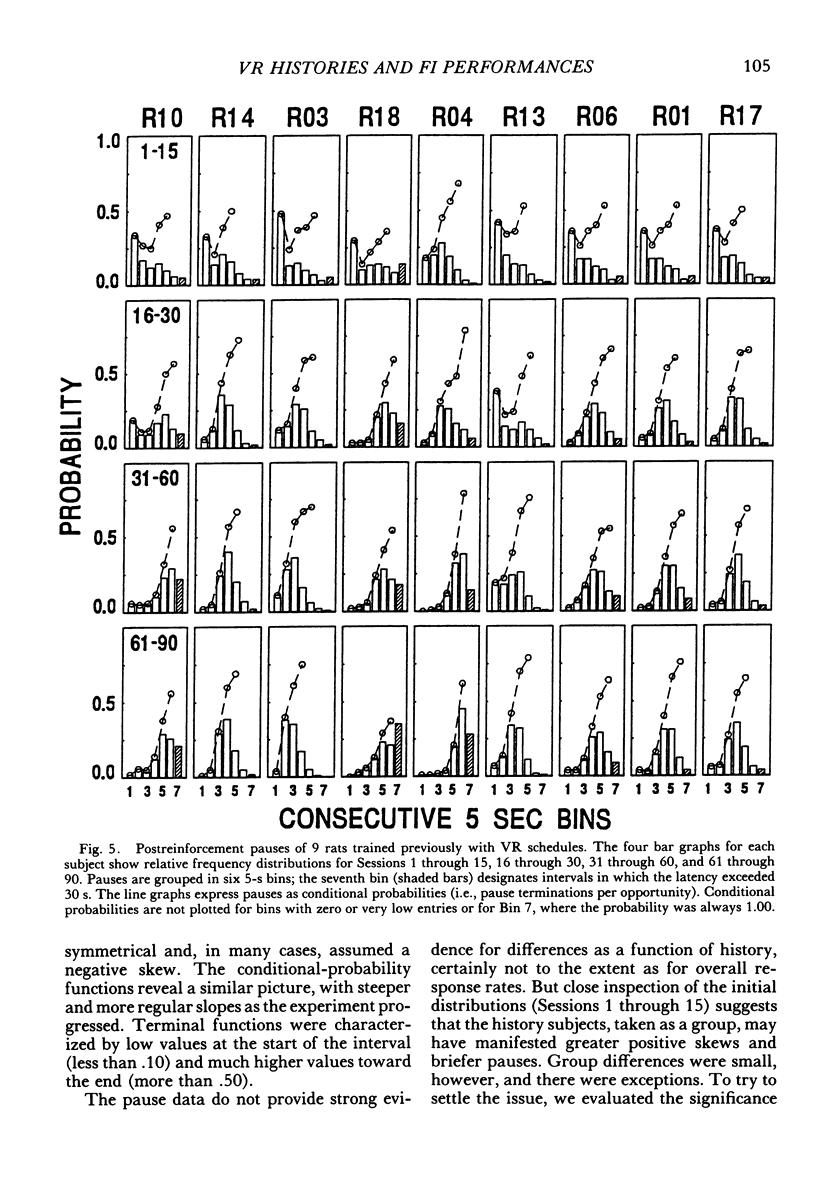
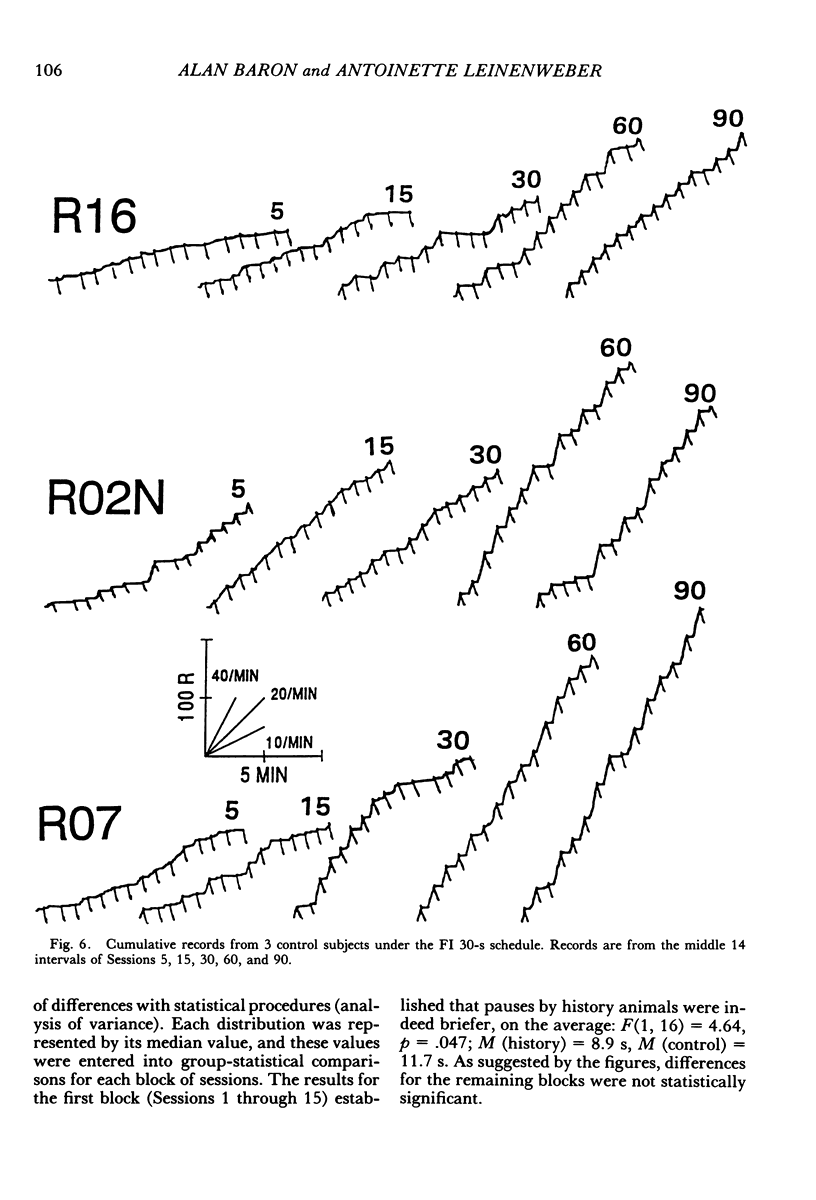
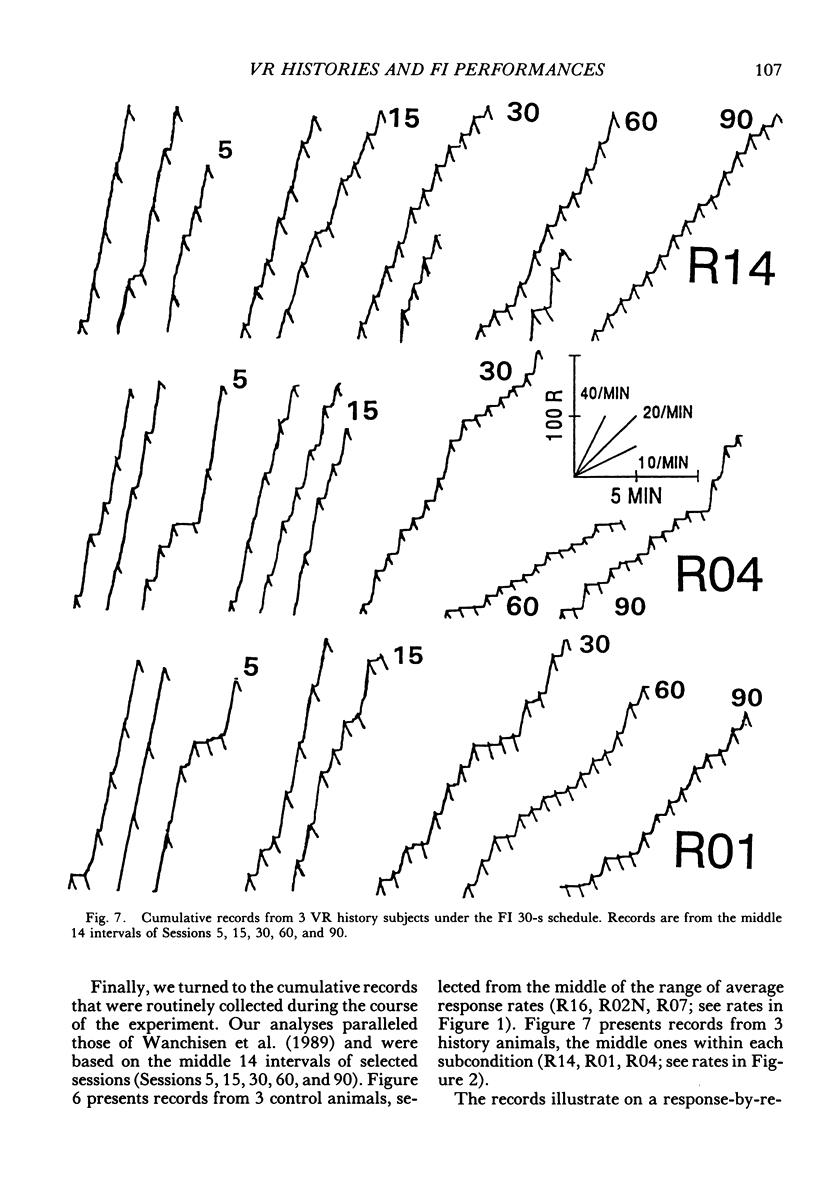



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron A., Leinenweber A. Molecular and molar analyses of fixed-interval performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1994 Jan;61(1):11–18. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1994.61-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY W., KELLEHER R. T., COOK L. A mathematical index of performance on fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:193–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman T. J., Lattal K. A. Stimulus control of behavioral history. J Exp Anal Behav. 1992 Jan;57(1):5–15. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1992.57-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz H. M., Davis H. Depriving rats of food: A reappraisal of two techniques. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Sep;40(2):211–213. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbain C., Poling A., Millam J., Thompson T. d-amphetamine and fixed-interval performance: effects of operant history. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 May;29(3):385–392. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. CONDITIONING HISTORY AND HUMAN FIXED-INTERVAL PERFORMANCE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Sep;7:383–385. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanchisen B. A., Tatham T. A., Mooney S. E. Variable-ratio conditioning history produces high- and low-rate fixed-interval performance in rats. J Exp Anal Behav. 1989 Sep;52(2):167–179. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1989.52-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. Controlling human fixed-interval performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):349–373. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


