Full text
PDF


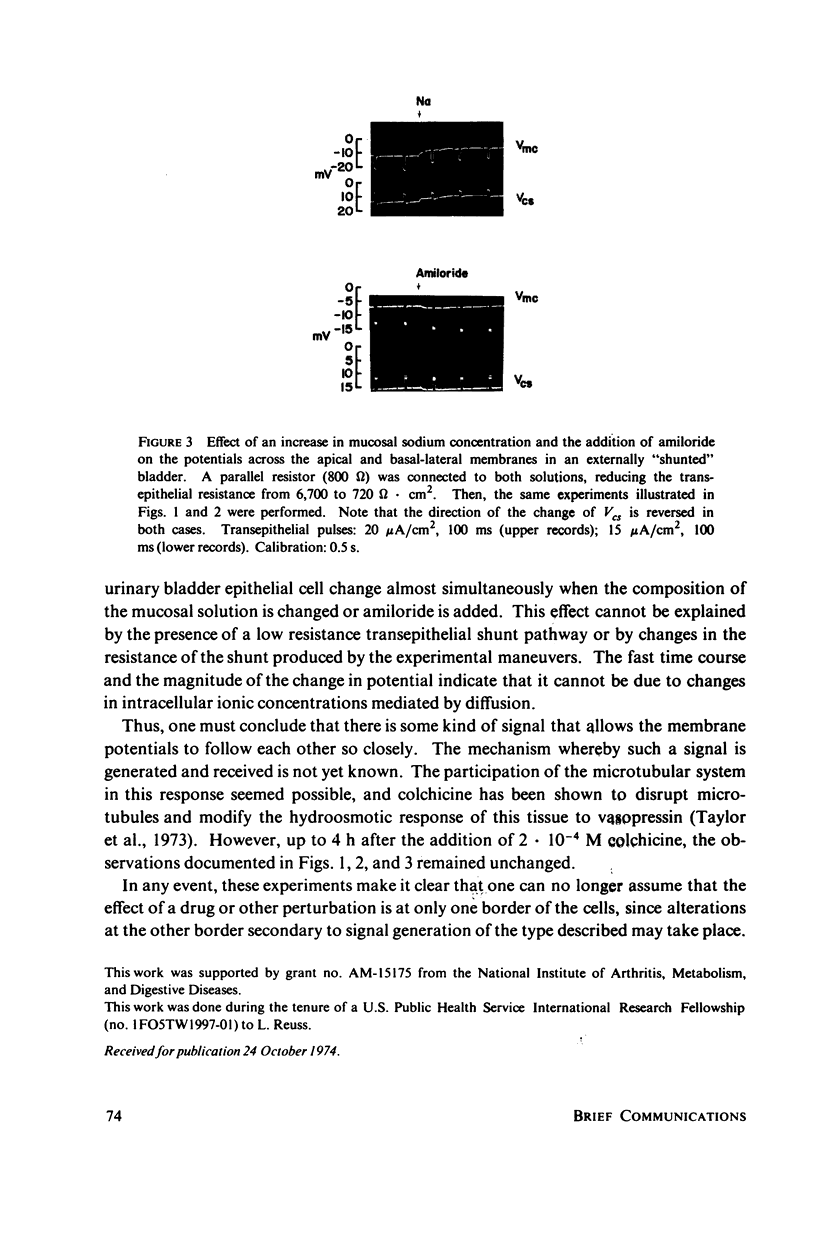

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CEREIJIDO M., CURRAN P. F. INTRACELLULAR ELECTRICAL POTENTIALS IN FROG SKIN. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Mar;48:543–557. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn A. L., Hutton S. A. Absence of edge damage in toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1974 Oct;227(4):950–953. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.4.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GATZY J. T., CLARKSON T. W. THE EFFECT OF MUCOSAL AND SEROSAL SOLUTION CATIONS ON BIOELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF THE ISOLATED TOAD BLADDER. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Mar;48:647–671. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.4.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jun 2;42(3-4):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEB D. E., HOSHIKO T., LINDLEY B. D., DUGAN J. A. EFFECT OF ALKALI METAL CATIONS ON THE POTENTIAL ACROSS TOAD AND BULLFROG URINARY BLADDER. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jan;48:527–540. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss L., Finn A. L. Passive electrical properties of toad urinary bladder epithelium. Intercellular electrical coupling and transepithelial cellular and shunt conductances. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):1–25. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G. Electrical potential differences and electromotive forces in epithelial tissues. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):794–798. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Mamelak M., Reaven E., Maffly R. Vasopressin: possible role of microtubules and microfilaments in its action. Science. 1973 Jul 27;181(4097):347–350. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4097.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]