Abstract
In Myxicola axons subjected to moderate depolarizations the sodium inactivation time constants obtained from the decay of sodium current during a maintained depolarizatin (TSh) are substantially smaller than inactivation time constants determined at the same potential from the effect of changes in the duration of conditioning prepulses (Tph). This report extends these observations to positive membrane potentials and demonstrates that for sufficiently large depolarizations TSh and Tph become comparable. The ratio of inactivation time constants, Tph/TSh, is unaffected by changes in [Ca++] provided total divalent cation concentration is maintained constant, while changes in total divalent ion concentrations produce simple voltage shifts comparable to those obtained from measurement of membrane sodium or potassium conductances. Sodium inactivation delay was quantitatively determined as a function of membrane potential, and found to be similarly unaffected by changes in [Ca++] at constant total divalent ion concentration. Inactivation delay is, however, directly proportional to the activation rate constant over a wide range of potentials.
Full text
PDF

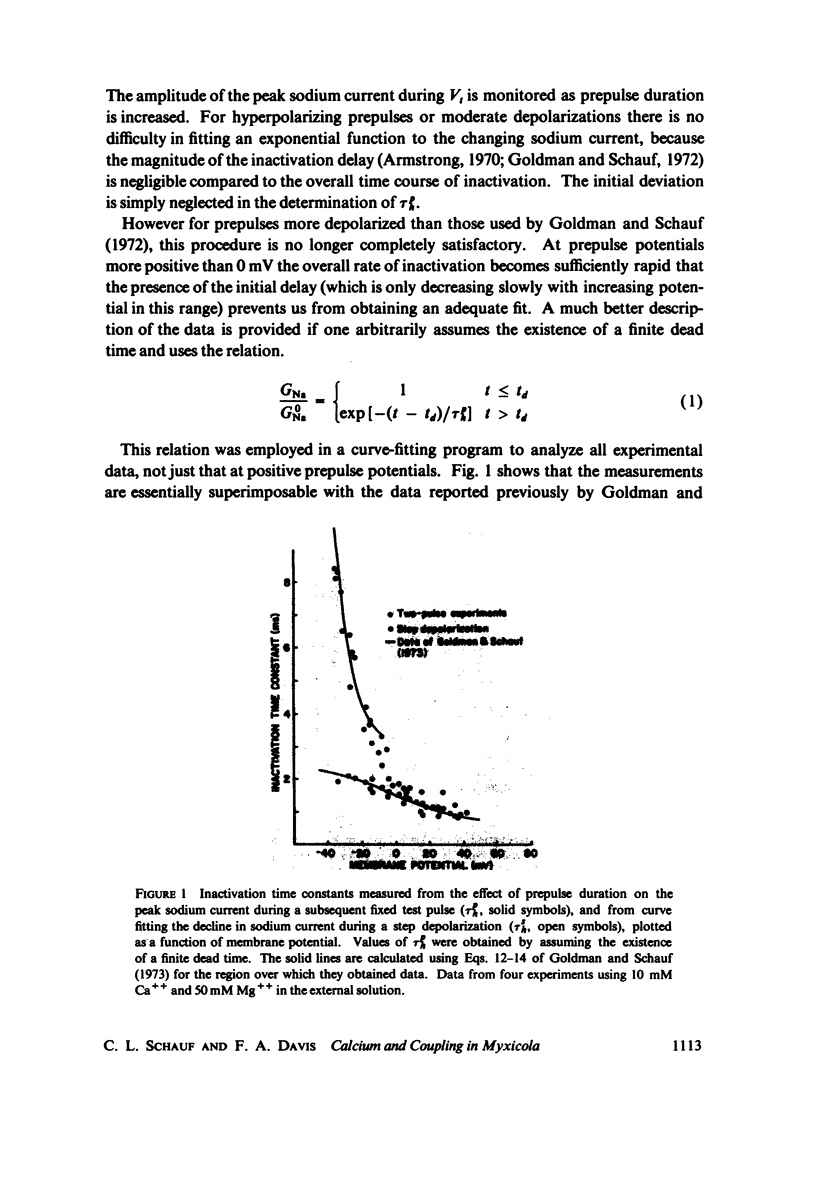


Selected References
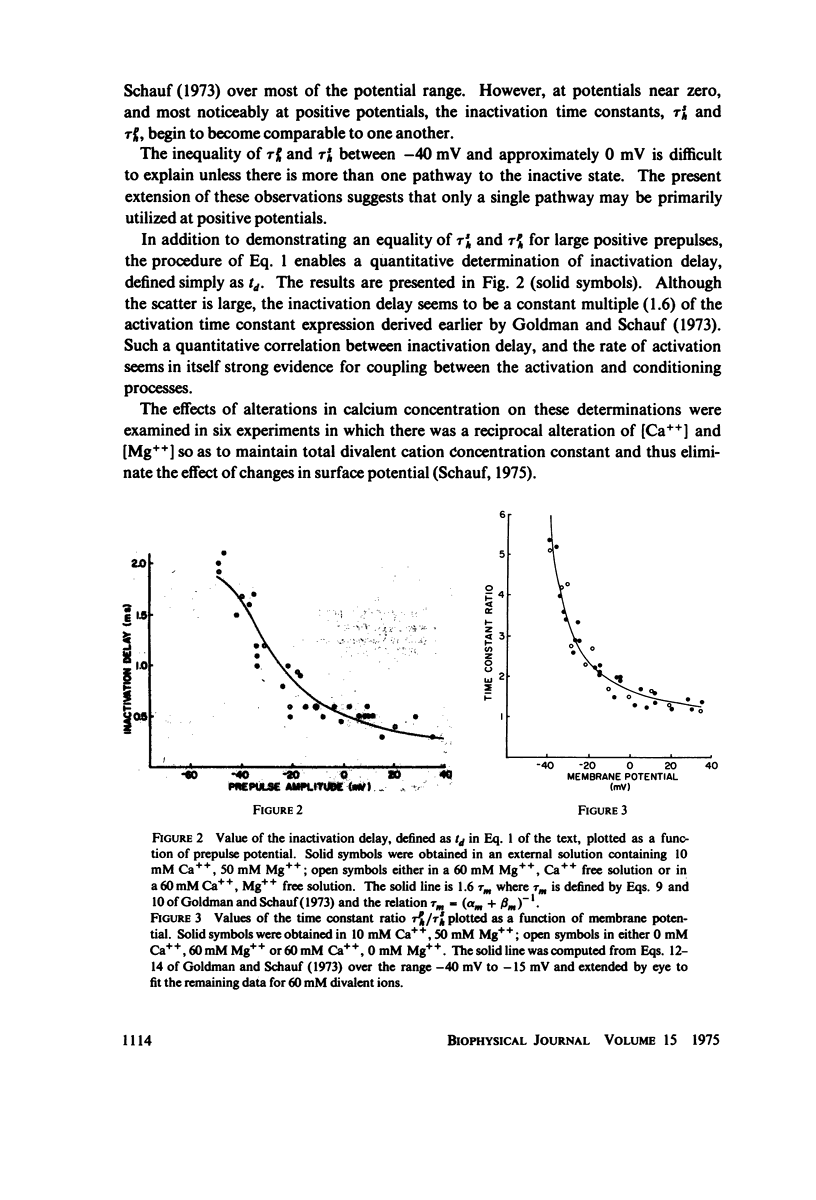
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binstock L., Goldman L. Current- and voltage-clamped studies on Myxicola giant axons. Effect of tetrodotoxin. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Dec;54(6):730–740. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.6.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman S. N., Chodorov B. I., Volkenstein M. V. Molecular mechanisms of membrane ionic permeability changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 5;225(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMANN D. E. A MOLECULAR STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR THE EXCITATION PROPERTIES OF AXONS. Biophys J. 1964 May;4:167–188. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86776-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L. Quantitative description of the sodium conductance of the giant axon of Myxicola in terms of a generalized second-order variable. Biophys J. 1975 Feb;15(2 Pt 1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(75)85796-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Inactivation of the sodium current in Myxicola giant axons. Evidence for coupling to the activation process. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):659–675. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Quantitative description of sodium and potassium currents and computed action potentials in Myxicola giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):361–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Jakobsson E. Interpretation of the sodium permeability changes of myelinated nerve in terms of linear relaxation theory. J Theor Biol. 1971 Oct;33(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offner F. F. Kinetics of excitable membranes. Voltage amplification in a diffusion regime. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):272–296. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. Sodium currents in Myxicola axons. Nonexponential recovery from the inactive state. Biophys J. 1974 Feb;14(2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)70006-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. Temperature dependence of the ionic current kinetics of Myxicola giant axons. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):197–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. The interactions of calcium with mpyxicola giant axons and a description in terms of a simple surface charge model. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;248(3):613–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


