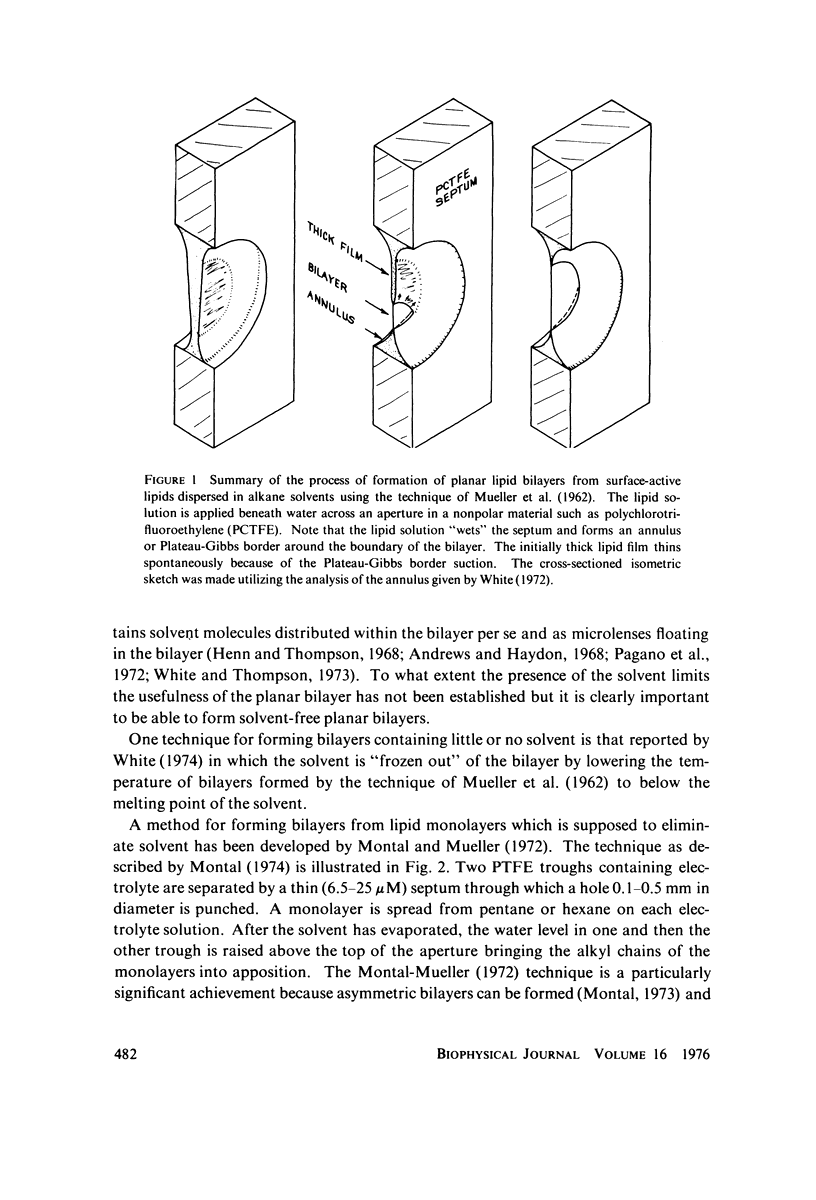
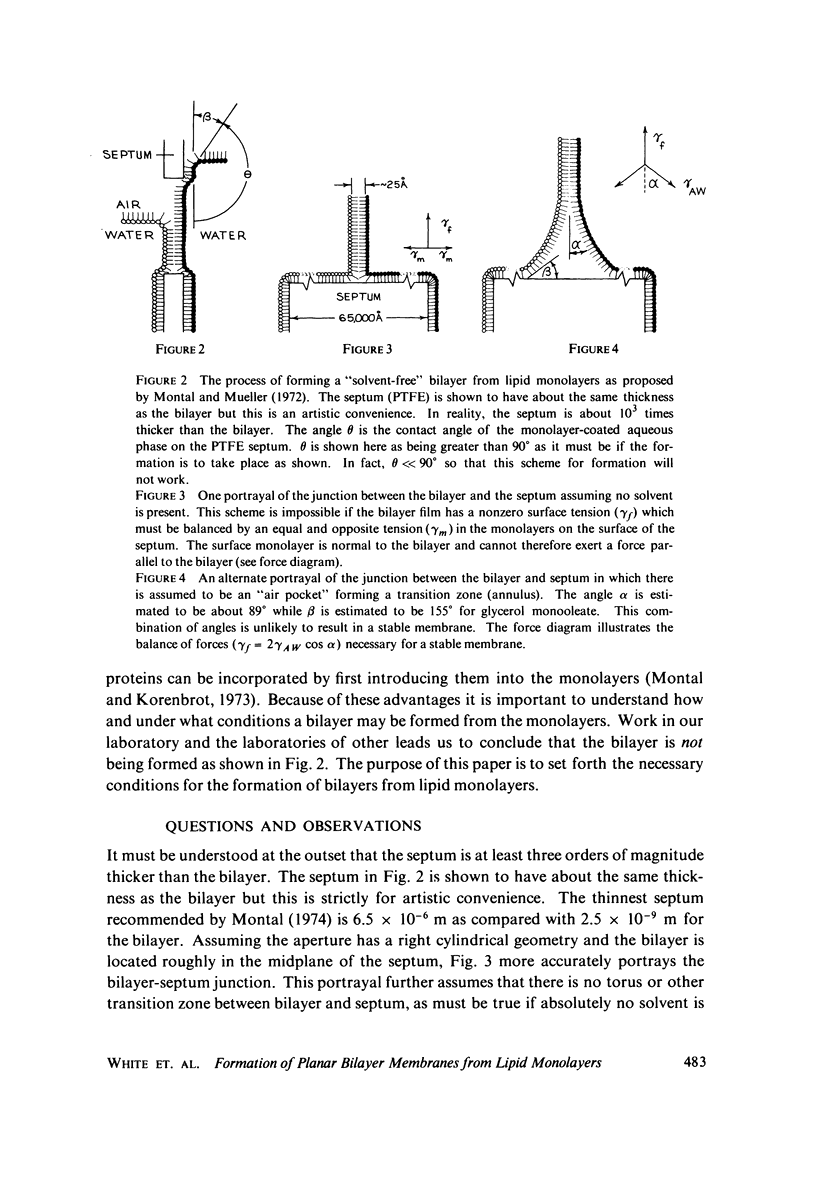
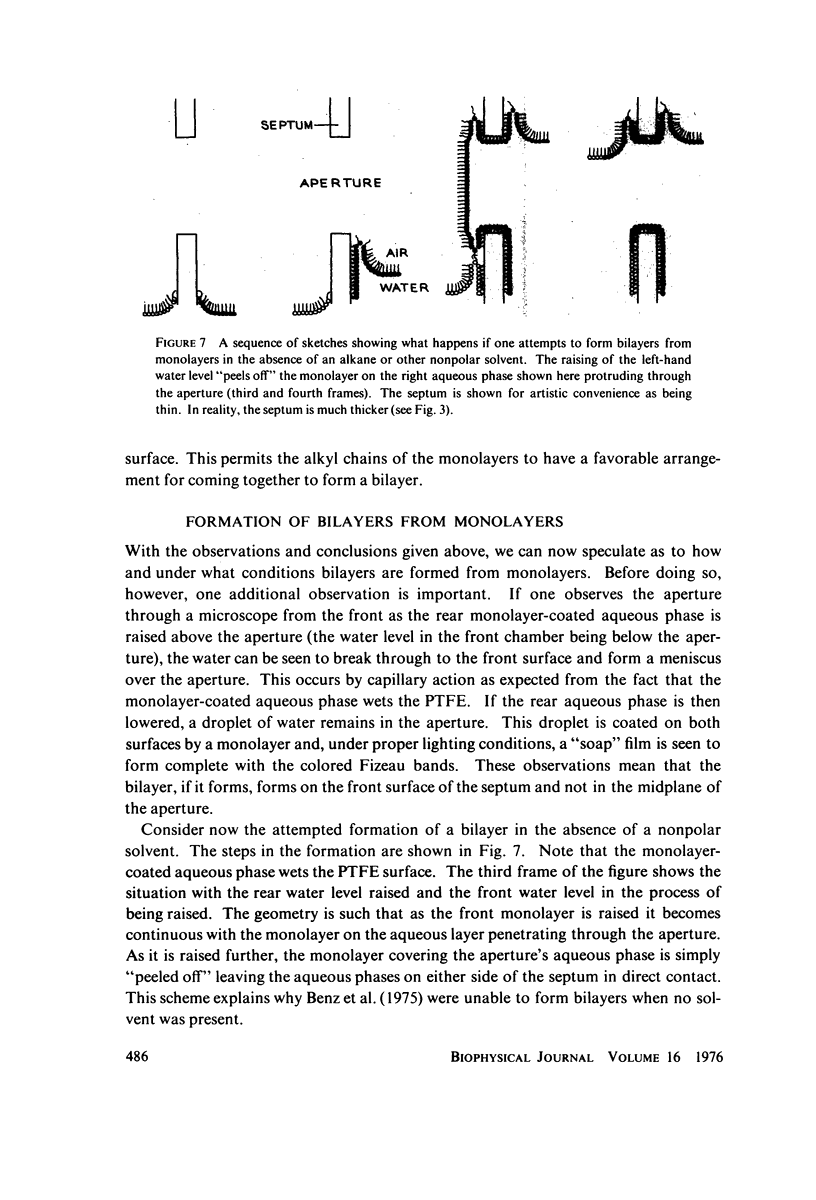
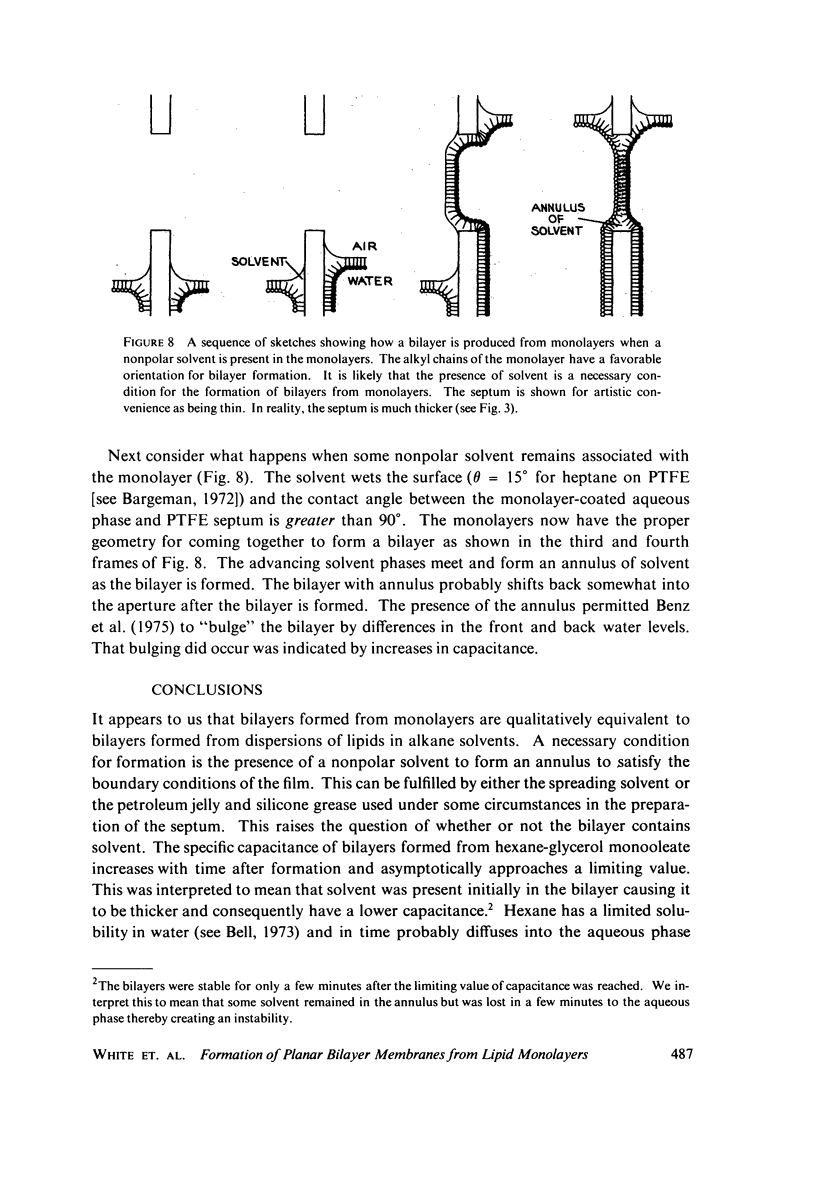
Abstract
The formation of planar bilayer membranes from lipid monolayers as described by Montal and Mueller (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1972. 69:3561) is analyzed. Bilayers absolutely free of alkane solvents or other nonpolar hydrocarbons can be formed on polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) (e.g. Teflon) septa only if certain boundary conditions are satisfied. Measurements have been made of the contact angles between monolayer-coated water and PTFE in the presence and absence of alkane solvents. The measurement suggest that the boundary conditions for formation of stable bilayers can be satisfied only when a nonpolar solvent is present. We conclude that the bilayer must be surrounded by a torus of alkane solvent, petroleum jelly, or silicone grease depending upon the details of technique used to form the bilayer. The non-polar solvent used in the formation of the bilayer may or may not be present in the bilayer depending upon the water solubility and size of the solvent molecule relative to the size of the alkyl chain of the lipid. Detailed sketches describing the formation of bilayers from monolayers are presented.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews D. M., Haydon D. A. Electron microscope studies of lipid bilayer membranes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 28;32(1):149–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Fröhlich O., Läuger P., Montal M. Electrical capacity of black lipid films and of lipid bilayers made from monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Thompson T. E. Properties of lipid bilayer membranes separating two aqueous phases: composition studies. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M. Asymmetric lipid bilayers. Reponse to multivalent ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 29;298(3):750–754. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Korenbrot J. I. Incorporation of rhodopsin proteolipid into bilayer membranes. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):219–221. doi: 10.1038/246219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Ruysschaert J. M., Miller I. R. The molecular composition of some lipid bilayer membranes in aqueous solution. J Membr Biol. 1972;10(1):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01867845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. Analysis of the torus surrounding planar lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1972 Apr;12(4):432–445. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86095-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. Phase transitions in planar bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1975 Feb;15(2 Pt 1):95–117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(75)85795-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. Temperature-dependent structural changes in planar bilayer membranes: solvent "freeze-out". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]