Abstract
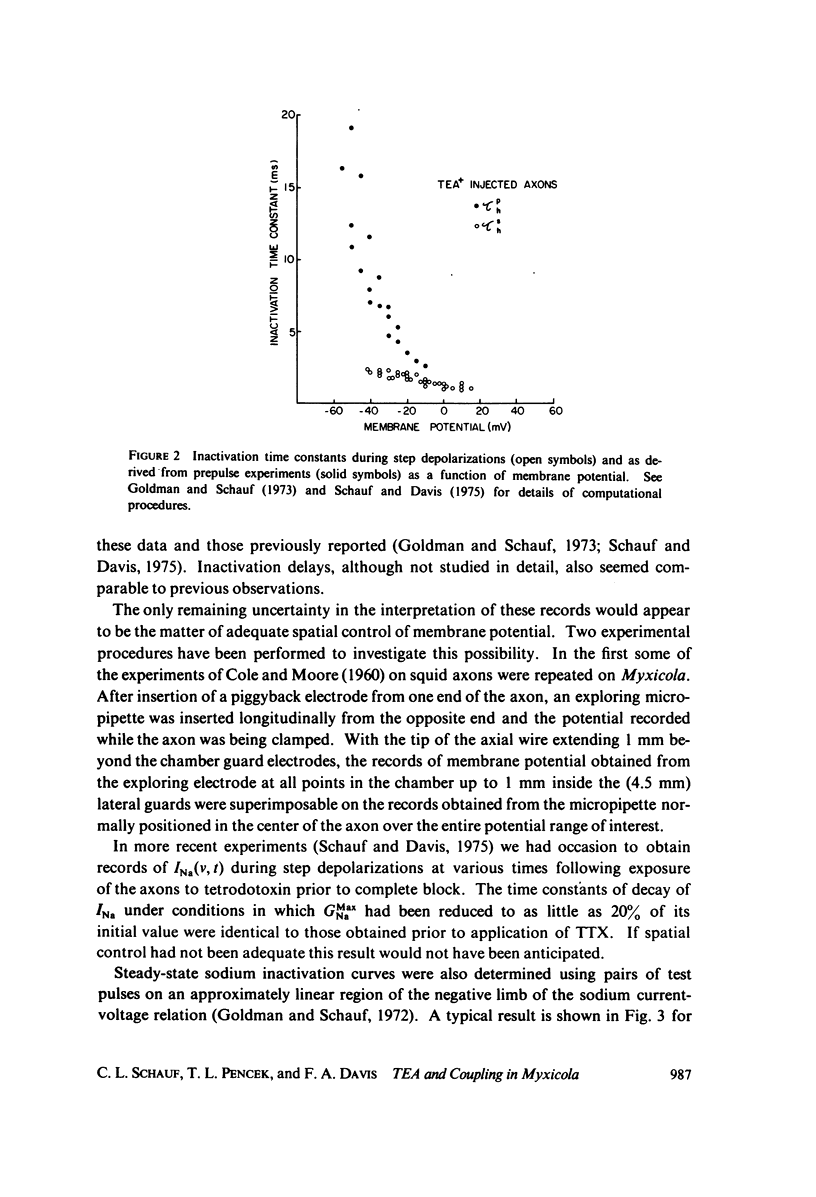
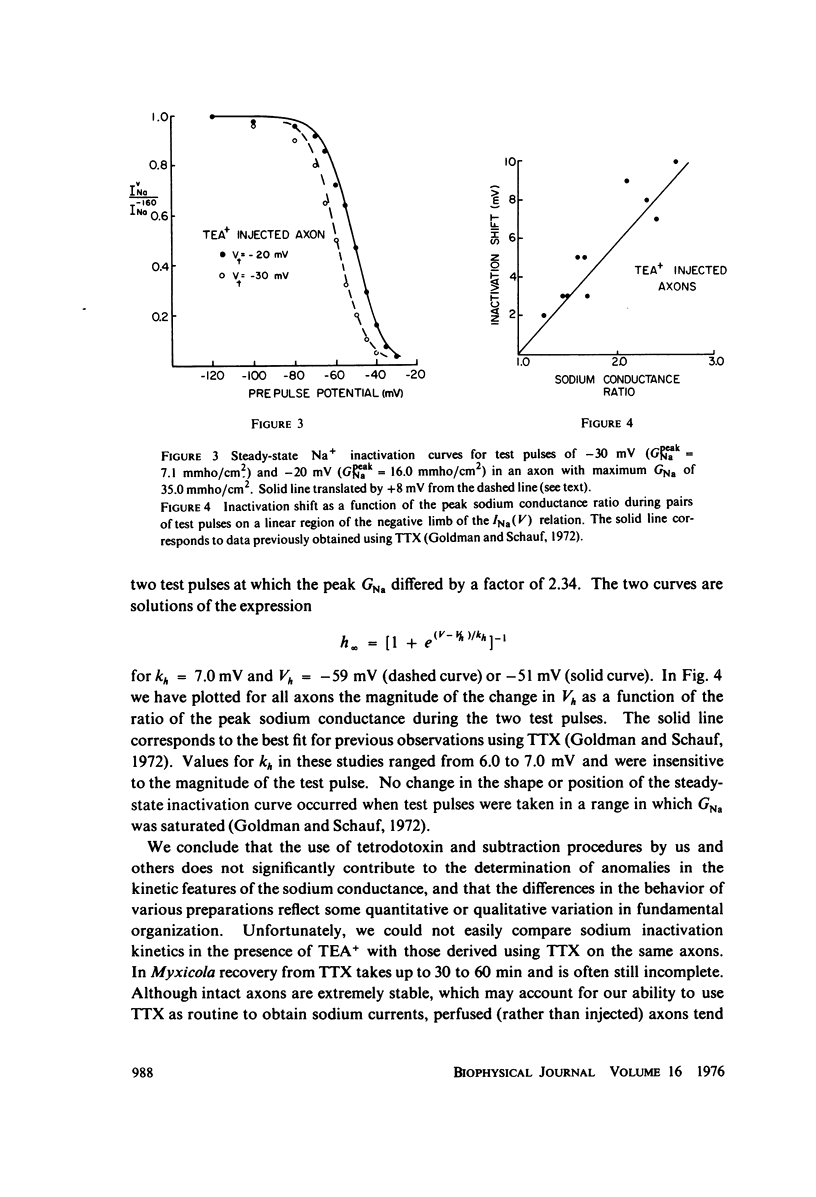
Myxicola giant axons internally injected with tetraethylammonium chloride to block potassium currents were examined under voltage clamp. The sodium inactivation time constants obtained from the decline in INa during step depolarizations were substantially smaller than those obtained using conditioning prepulses to the same potentials and the ratios agreed with previous observations using TTX. Inactivation shifts were also measured and found to be comparable to previous results.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Ionic current measurements in the squid giant axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:123–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Inactivation of the sodium current in Myxicola giant axons. Evidence for coupling to the activation process. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):659–675. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Quantitative description of sodium and potassium currents and computed action potentials in Myxicola giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):361–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt R. C., Adelman W. J., Jr Sodium inactivation. Experimental test of two models. Biophys J. 1970 Jul;10(7):610–617. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86323-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Pooler J. P. Selective modification of sodium channel gating in lobster axons by 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol: Evidence for two inactivation mechanisms. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Dec;66(6):765–779. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.6.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Colton C. A., Colton J. S., Davis F. A. Aminopyridines and sparteine as inhibitors of membrane potassium conductance: effects on Myxicola giant axons and the lobster neuromuscular junction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):414–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. Comparison of two-pulse sodium inactivation with reactivation in Myxicola giant axons. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):245–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85684-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Davis F. A. Further studies of activation-inactivation coupling in Myxicola axons. Insensitivity to changes in calcium concentration. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1111–1116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85887-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. Sodium currents in Myxicola axons. Nonexponential recovery from the inactive state. Biophys J. 1974 Feb;14(2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)70006-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


