Abstract
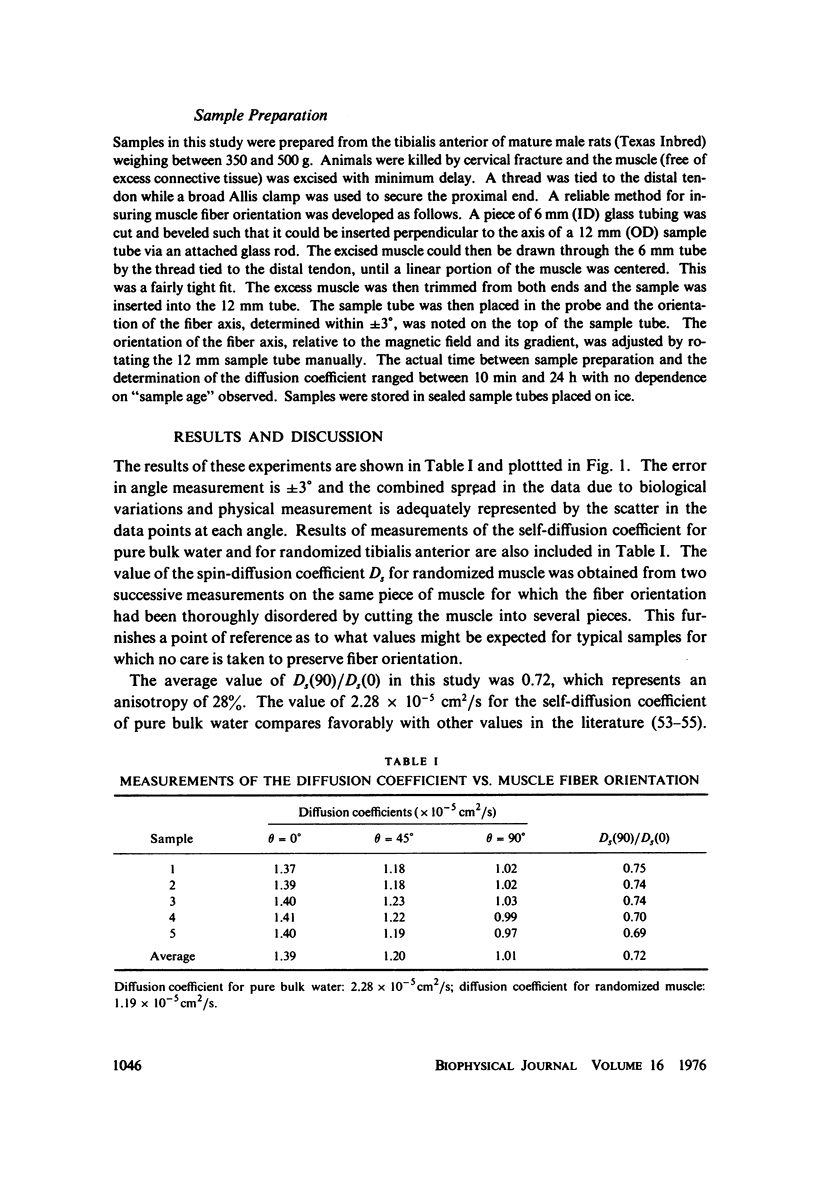
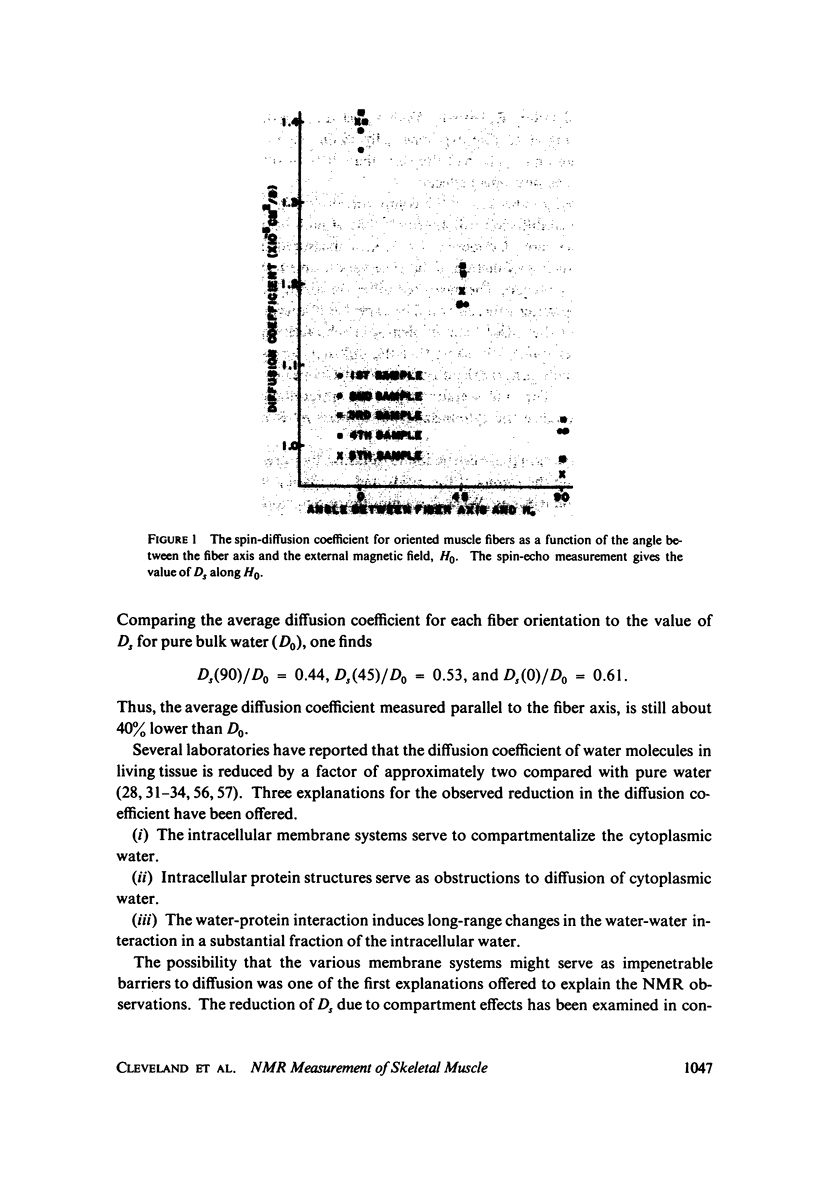
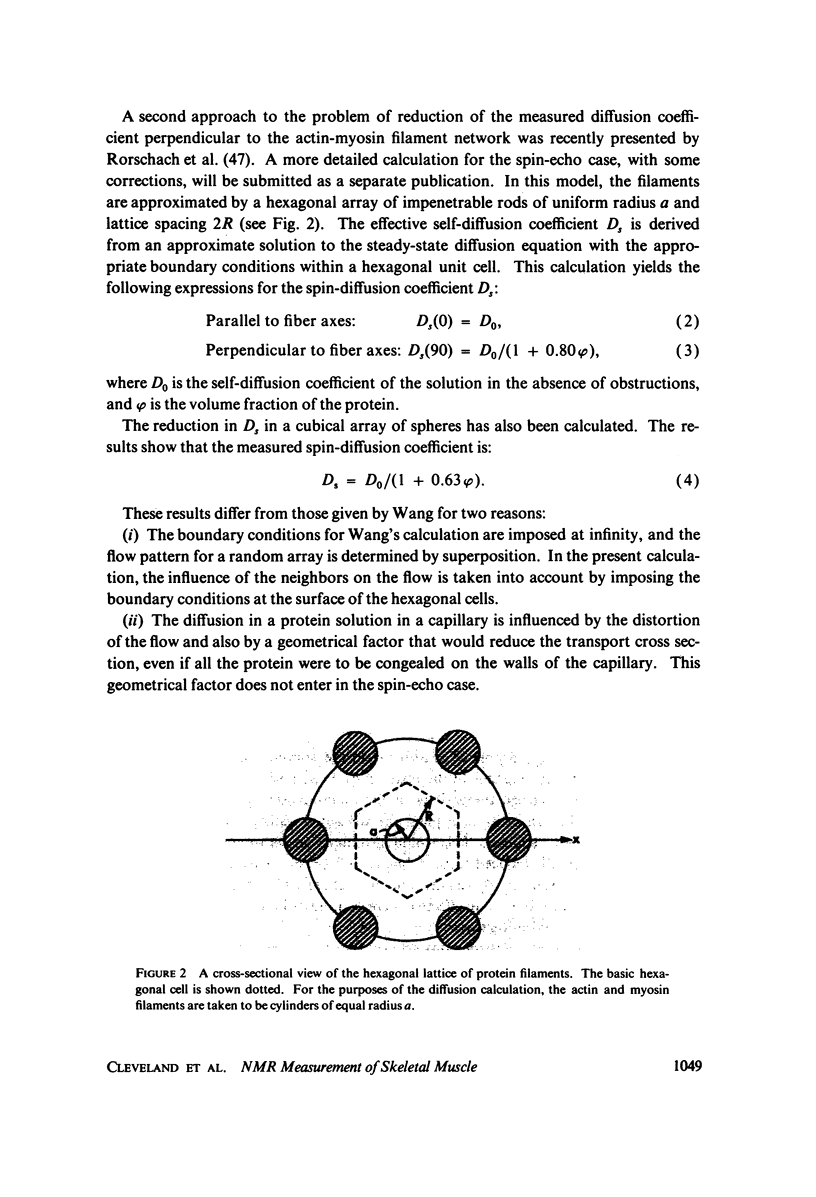
The anisotropy of the spin-diffusion coefficient Ds of water protons in skeletal muscle has been studied by pulsed NMR methods. The mid-portion of the tibialis anterior muscle of mature male rats was placed in a special sample holder by means of which the muscle fiber orientation theta relative to the diffusion direction could be varied over the range 0 degrees less than or equal to theta less than or equal to 90 degrees. The value of Ds(theta) was determined for theta = 0 degrees, 45 degrees, and 90 degrees. The measured anisotropy Ds(0)/Ds(90) was 1.39, and the value of Ds(0) was 1.39 X 10(-5) cm2/s. These results are interpreted within the framework of a model calculation in which the diffusion equation is solved for a regular hexagonal network similar to the actin-myosin filament network. The large anisotropy, and the large reduction in the value of Ds measured parallel to the filament axes lead to two major conclusions: (a) interpretations in which the reduction in Ds is ascribed to the effect of geometrical obstructions on the diffusion of "free" water are ruled out; and, (b) there is a large fraction of the cellular water associated with the proteins in such a way that its diffusion coefficient is substantially reduced.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRATTON C. B., HOPKINS A. L., WEINBERG J. W. NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF LIVING MUSCLE. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):738–739. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillé J. P., Hinke J. A. The volume available to diffusion in the muscle fiber. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;52(4):814–828. doi: 10.1139/y74-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. C. Factors governing movement and distribution of inorganic ions in nerve and muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jan;48(1):1–64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Hazlewood C. F., Nichols B. L., Rorschach H. E. Spin echo studies on cellular water. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):170–171. doi: 10.1038/235170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Rorschach H. E., Nichols B. L., Hazlewood C. F. Implications of diffusion coefficient measurements for the structure of cellular water. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:434–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman G., McLauchlan K. A. Oriented water in the sciatic nerve of rabbit. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):391–392. doi: 10.1038/215391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Shporer M. 17 O nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of H 2 17 O in frog striated muscle. Biophys J. 1972 Apr;12(4):404–413. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86092-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Shporer M. Pulsed NMR studies of 17O from H2 17O in frog striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 22;343(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Shporer M. Pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance study of 17-O, 2-D, and 1-H of water in frog striated muscle. Biophys J. 1975 Apr;15(4):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85820-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Wien R. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of intracellular water protons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:197–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Wien R. The state of water in muscle tissue as determined by proton nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1971 Dec;11(12):1002–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86274-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. L., Chang D. B., Young A. C., Martin C. J., Ancker-Johnson D. Restricted diffusion in biophysical systems. Experiment. Biophys J. 1974 Mar;14(3):161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(74)85904-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence using D2O for structured water in muscle and brain. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):303–319. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86388-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. W. Supramolecular biology: a solid state physical approach to ion and electron transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:416–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICK D. A. Osmotic properties of living cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1959;8:387–448. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62736-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Biological ion exchanger resins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:211–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. D., Harmon J. F., Muller B. H. Pulsed NMR measurements of the diffusion constant of water in muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz O. G., Jr, Swift T. J. The state of water in polarized and depolarized frog nerves a proton magnetic resonance study. Biophys J. 2008 Dec 31;7(6):675–687. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86616-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M., McGaughy T. W. The state of water in muscle as studied by pulsed NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 24;343(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. R. Pulsed NMR study of water mobility in muscle and brain tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971;230(3):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelwood C. F., Chang D. C., Medina D., Cleveland G., Nichols B. L. Distinction between the preneoplastic and neoplastic state of murine mammary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1478–1480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F. Accumulation and exclusion of ions in contractile tissue of developing animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:593–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Rorschach H. E. Interaction of water molecules with macromolecular structures in cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1971 Mar;2(1):51–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(71)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation times of water protons in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):583–606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85937-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Cleveland G., Medina D. Relationship between hydration and proton nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation times in tissues of tumor-bearing and non-tumor-bearing mice: implications for cancer detection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Nichols B. L., Chamberlain N. F. Evidence for the existence of a minimum of two phases of ordered water in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1969 May 24;222(5195):747–750. doi: 10.1038/222747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. A., Woessner D. E. A simple single-coil probe for pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance. J Sci Instrum. 1966 Nov;43(11):838–840. doi: 10.1088/0950-7671/43/11/417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. C., Paterson C. A., Rae J. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies and water "ordering" in the crystalline lens. Science. 1974 Jun 7;184(4141):1072–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4141.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outhred R. K., George E. P. Water and ions in muscles and model systems. Biopolymers. 1973 Feb;13(2):97–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisin I. L., Ling G. N. Exchange of 3HHO in intact isolated muscle fiber of the giant barnacle. Physiol Chem Phys. 1973;5(3):183–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J. A., Hope A. B. Nuclear magnetic resonance and the state of water in cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1971;23:1–20. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(71)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


