Abstract
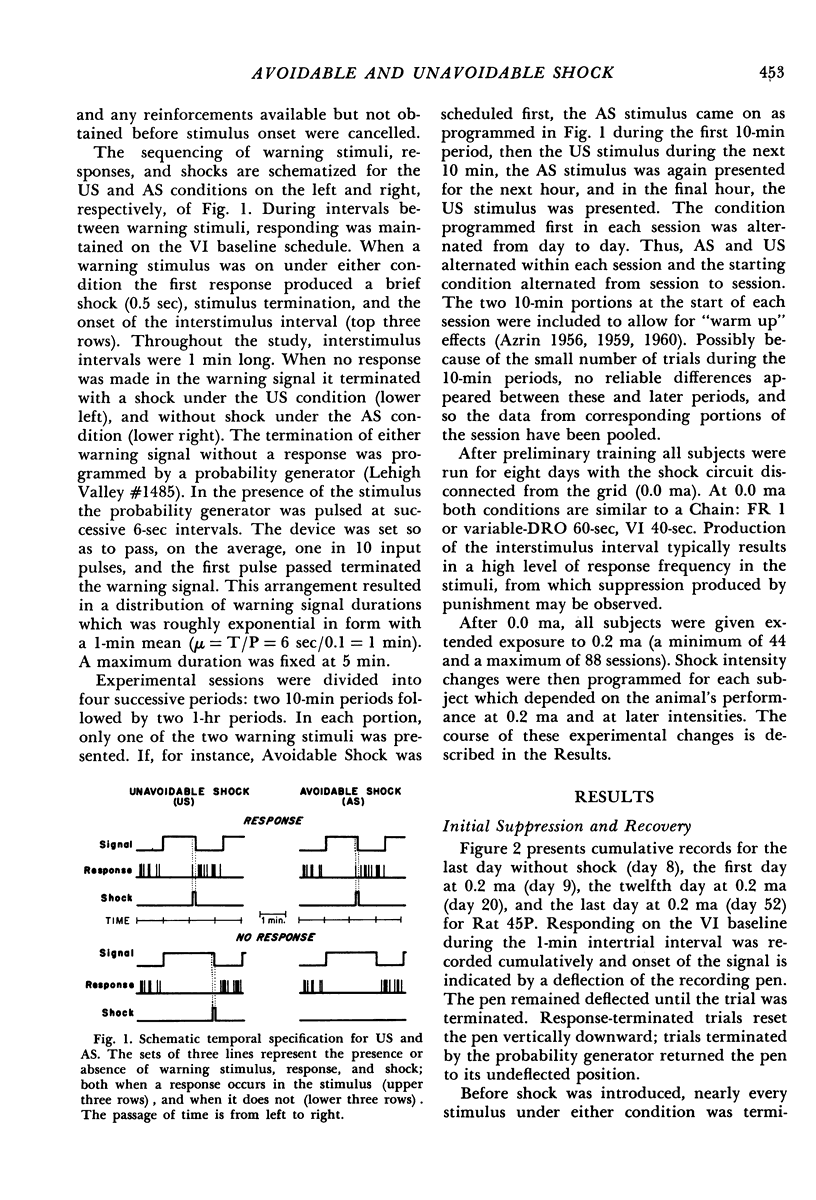
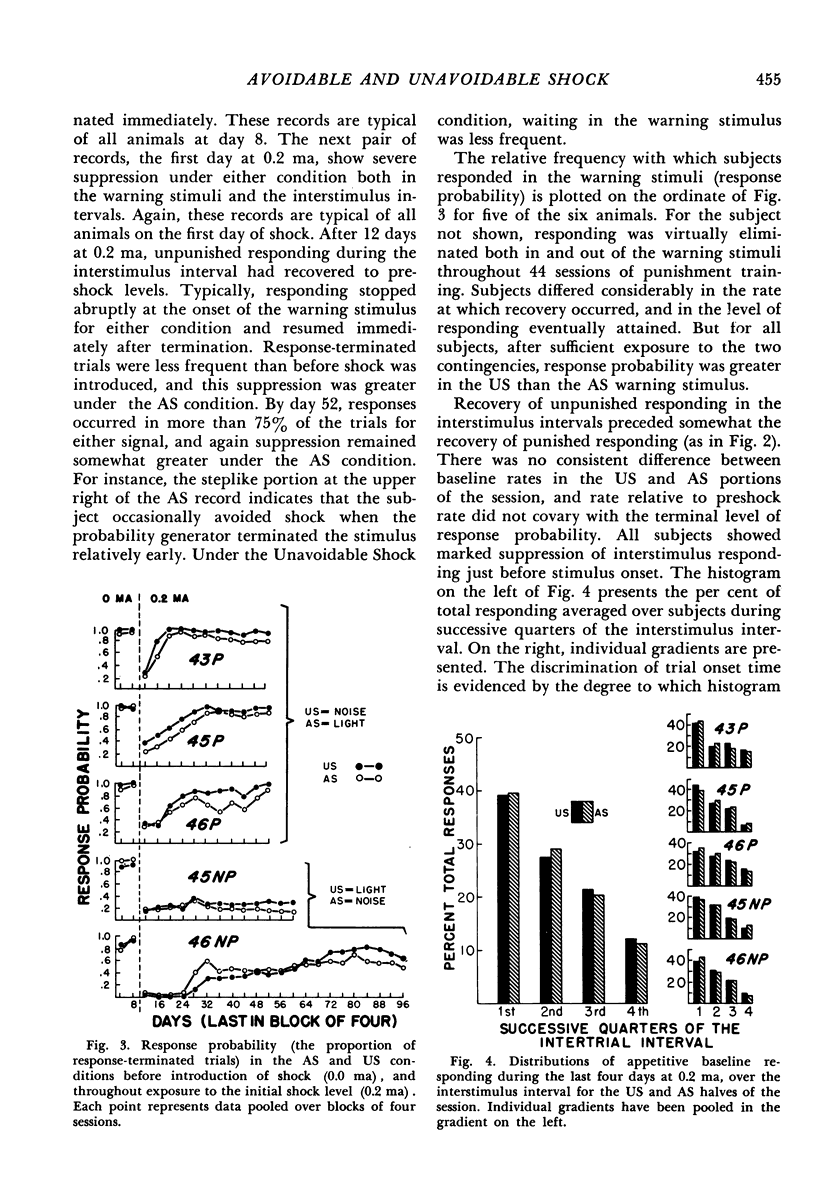
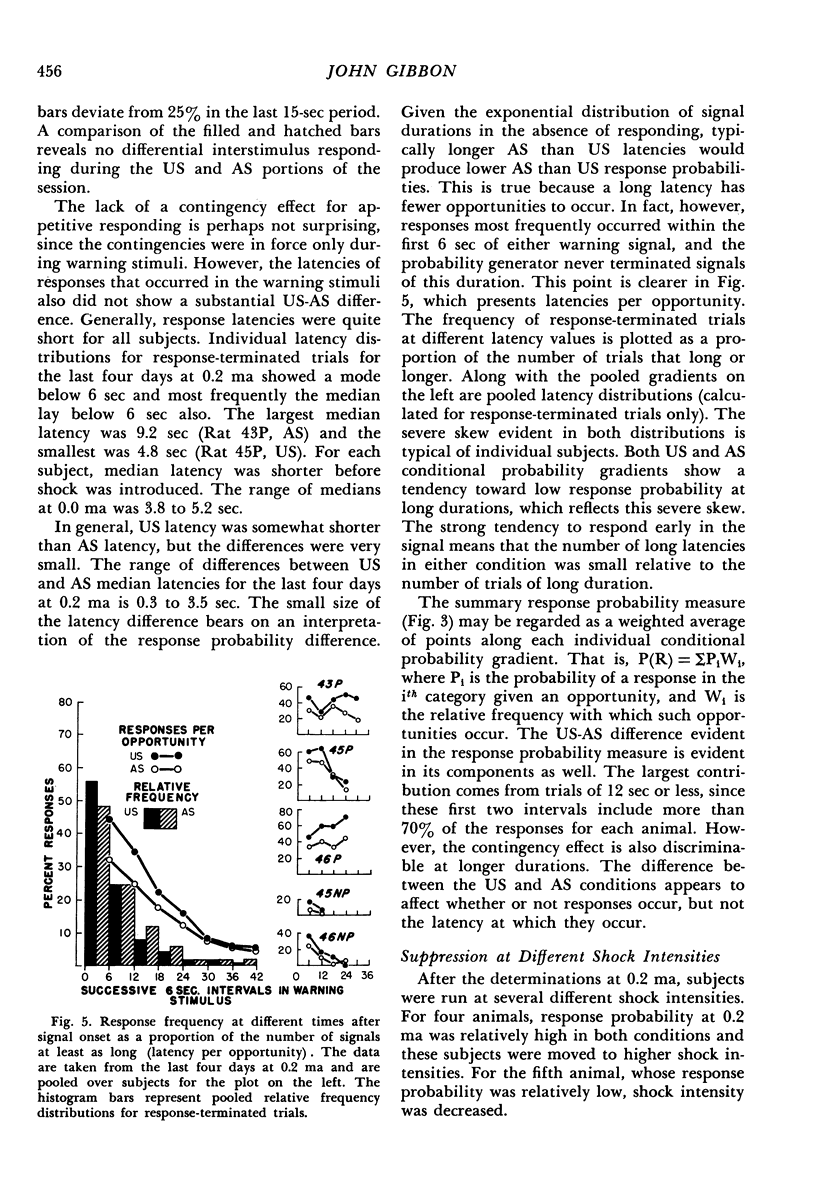
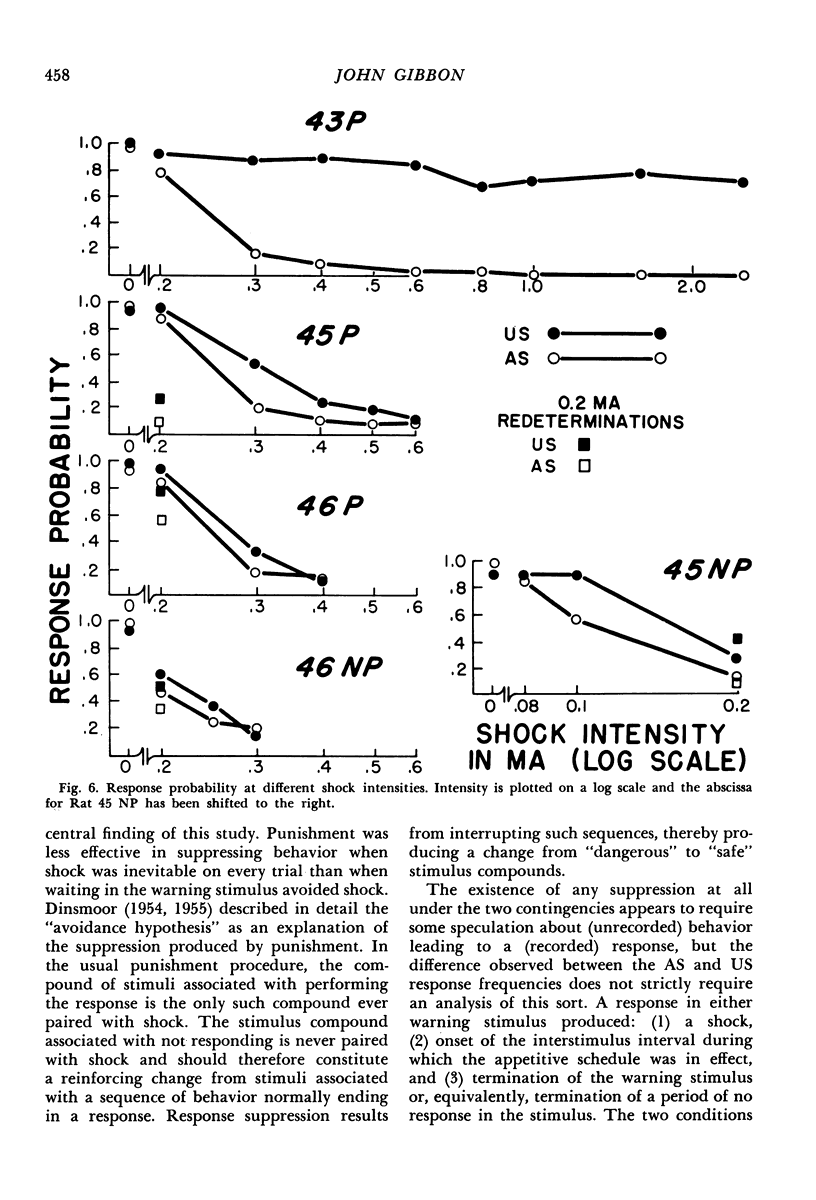
Warning stimuli for two punishment conditions were alternated with periods of appetitive responding by rats. In either warning stimulus, the first response produced a brief shock, terminated the stimulus, and started an interval during which the baseline appetitive schedule was in effect. Not responding resulted in stimuli of random duration, which terminated with a shock under one condition and without a shock under the other. Each subject was exposed to several shock intensities, with trials for the two conditions programmed during alternate portions of the session. In general, response frequency in the warning signal for either condition decreased with increasing intensity; however, at a given intensity, responding was more frequent in the stimulus invariably terminating with shock than in the stimulus terminating without shock when no response was made. The frequency difference was greatest at intensities intermediate between those producing minimal and maximal suppression.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPEL J. B., PETERSON N. J. PUNISHMENT: EFFECTS OF SHOCK INTENSITY ON RESPONSE SUPPRESSION. Psychol Rep. 1965 Jun;16:721–730. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1965.16.3.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPEL J. B. Punishment and shock intensity. Science. 1963 Aug 9;141(3580):528–529. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3580.528-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPEL J. B. Punishment in the squirrel monkey Saimiri sciurea. Science. 1961 Jan 6;133(3445):36–36. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3445.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Effects of punishment intensity during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:123–142. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Punishment and recovery during fixed-ratio performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Oct;2:301–305. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOREN J. J., SIDMAN M., HERRNSTEIN R. J. Avoidance, escape, and extinction as functions of shock intensity. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1959 Aug;52:420–426. doi: 10.1037/h0042727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURCH R. M. THE VARIED EFFECTS OF PUNISHMENT ON BEHAVIOR. Psychol Rev. 1963 Sep;70:369–402. doi: 10.1037/h0046499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. Punishment. I. The avoidance hypothesis. Psychol Rev. 1954 Jan;61(1):34–46. doi: 10.1037/h0062725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. Punishment. II. An interpretation of empirical findings. Psychol Rev. 1955 Mar;62(2):96–105. doi: 10.1037/h0041258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT H. F., BRADY J. V. Some effects of punishment and intercurrent anxiety on a simple operant. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1955 Aug;48(4):305–310. doi: 10.1037/h0042529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake D. F., Azrin N. H., Oxford R. The effects of punishment intensity on squirrel monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):95–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMIN L. J. The effects of termination of the CS and avoidance of the US on avoidance learning. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Aug;49(4):420–424. doi: 10.1037/h0088011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M., BOREN J. J. The relative aversiveness of warning signal and shock in an avoidance situation. J Abnorm Psychol. 1957 Nov;55(3):339–344. doi: 10.1037/h0043237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Conditioned reinforcing and aversive stimuli in an avoidance situation. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Apr;19(6):534–544. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1957.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


