Abstract
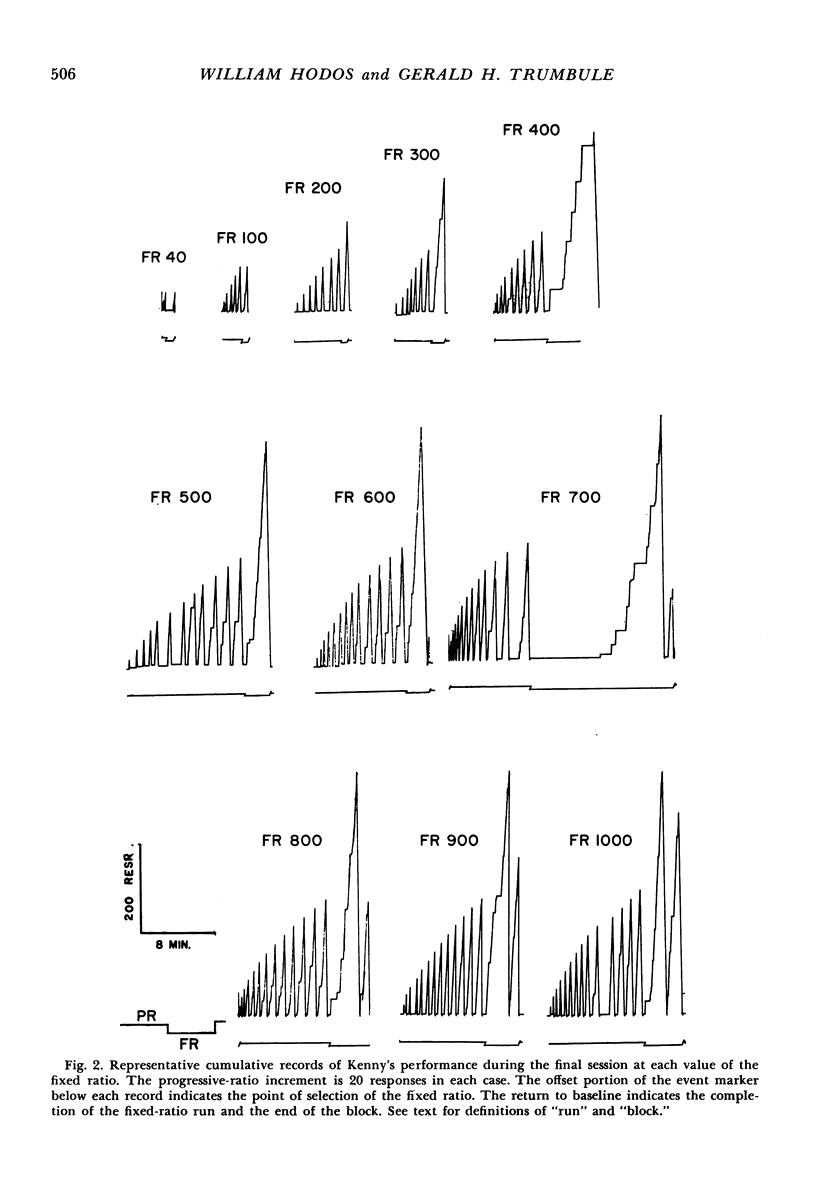
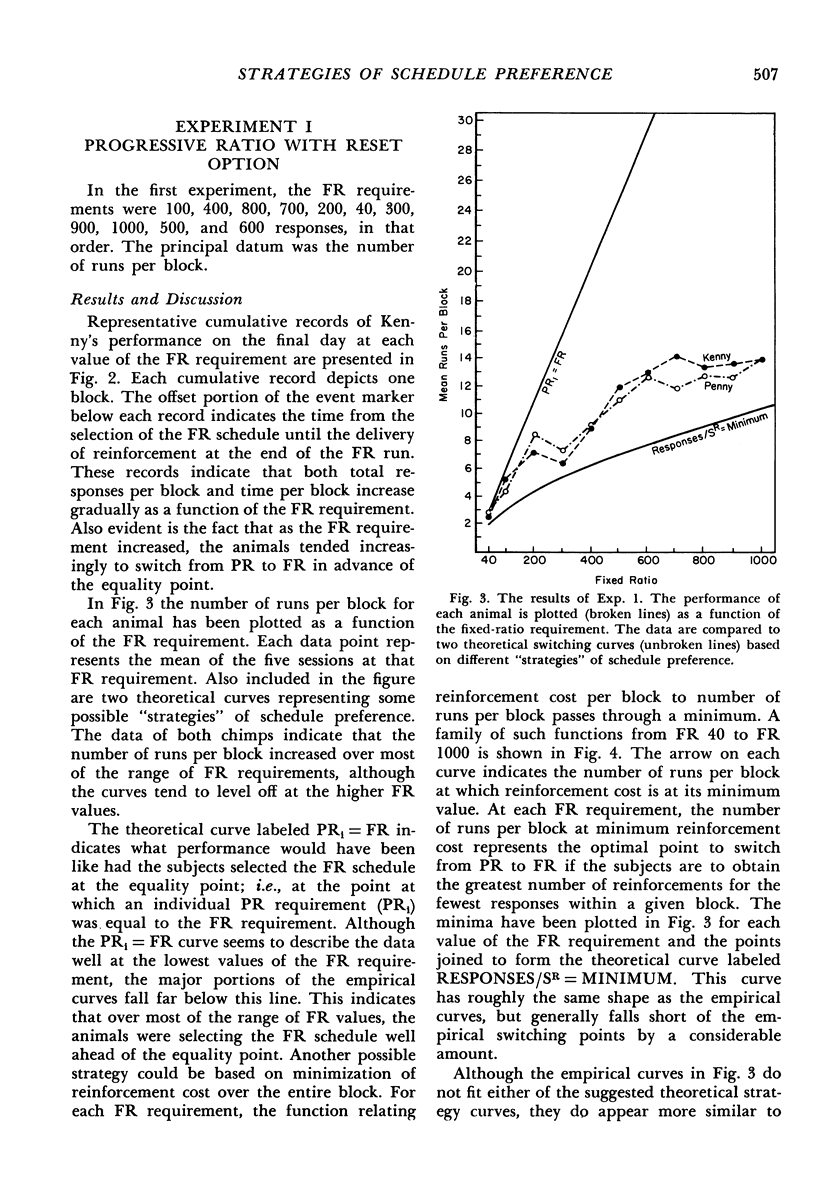
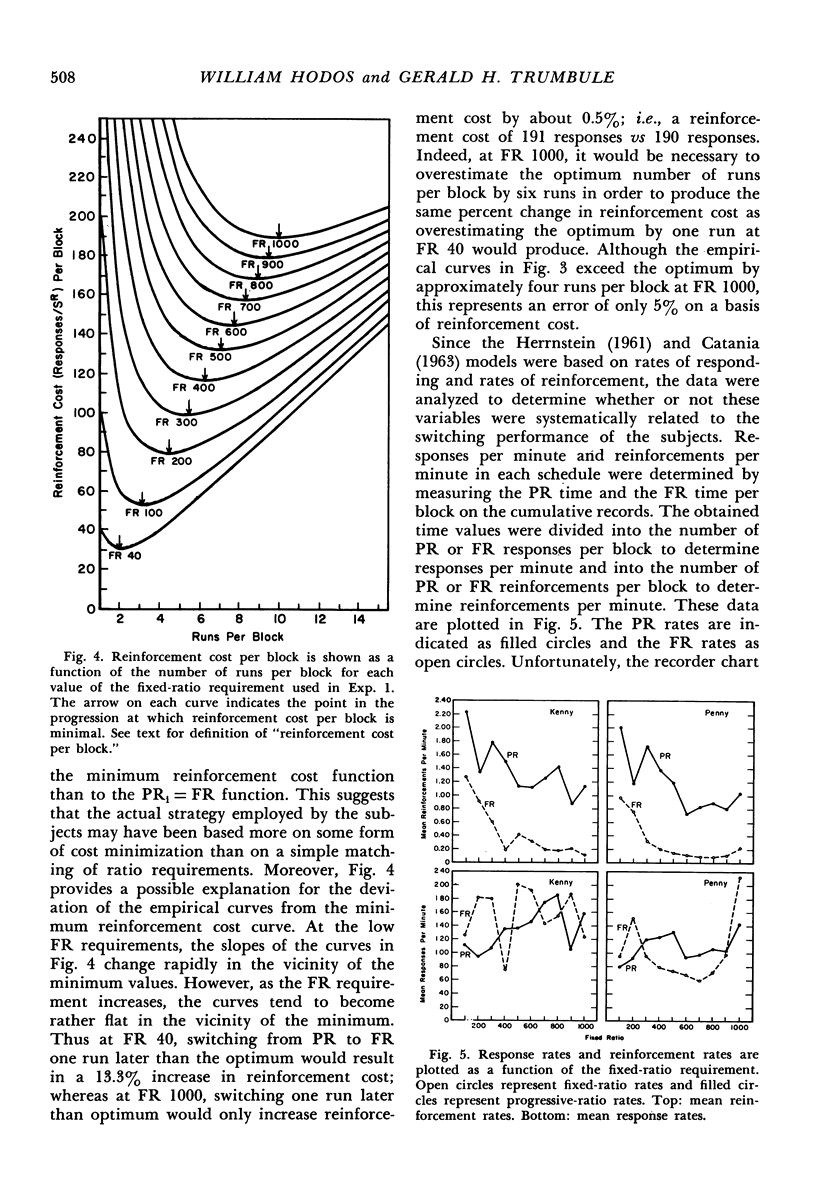
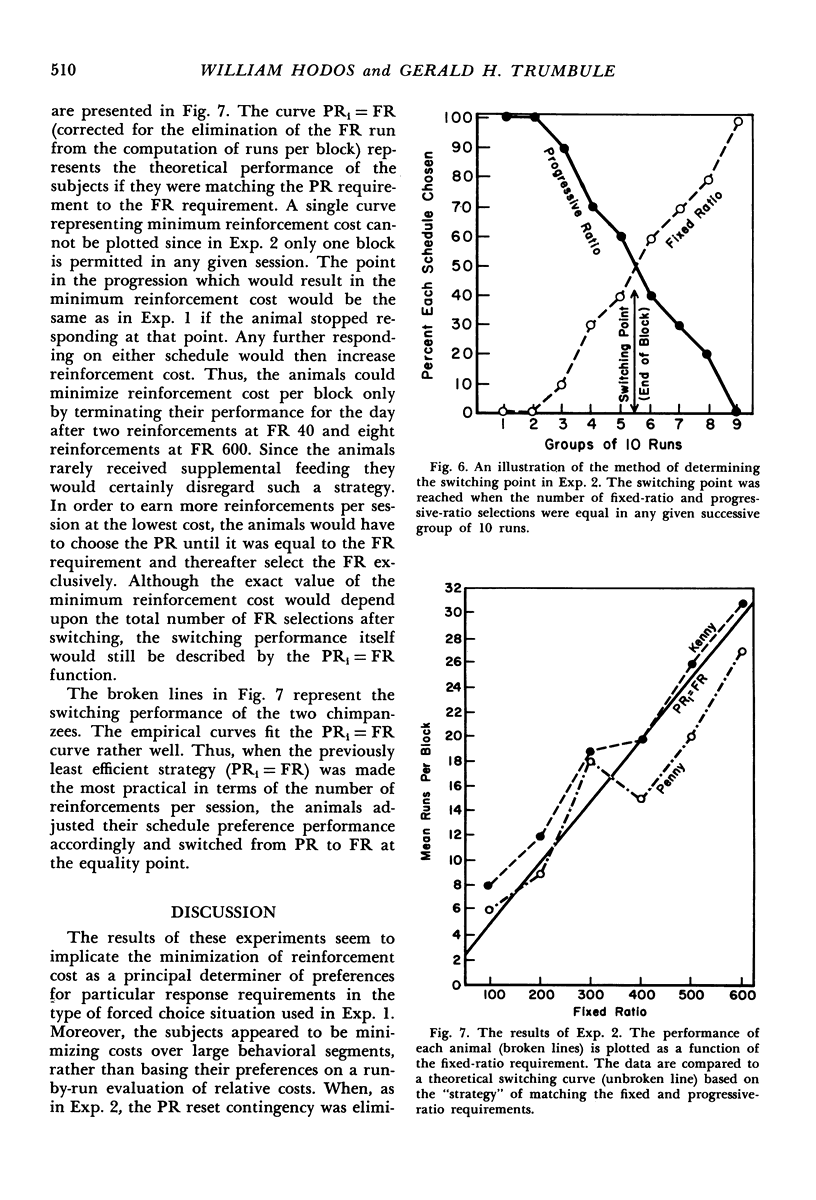
Two chimpanzees were required to choose between a fixed-ratio schedule and a progressive-ratio schedule which increased in response requirement by 20 responses each time it was chosen. Each choice of the fixed ratio reset the progressive ratio to its minimum value. The fixed-ratio requirement was varied from 40 to 1000 responses. The subjects' preferences for the progressive-ratio schedule varied as a function of the magnitude of the fixed-ratio requirement. An analysis of the preference data indicated that the animals tended to minimize reinforcement cost rather than match the progressive-ratio requirement to the fixed-ratio requirement. In a second experiment, selection of the fixed ratio did not reset the progressive-ratio requirement to its minimum value. In this case, the animals matched the progressive-ratio requirement to the fixed-ratio requirement. A model based on reinforcement cost is presented which permits accurate prediction of preferences between fixed and progressively increasing ratio schedules.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Independence of concurrent responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:175–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
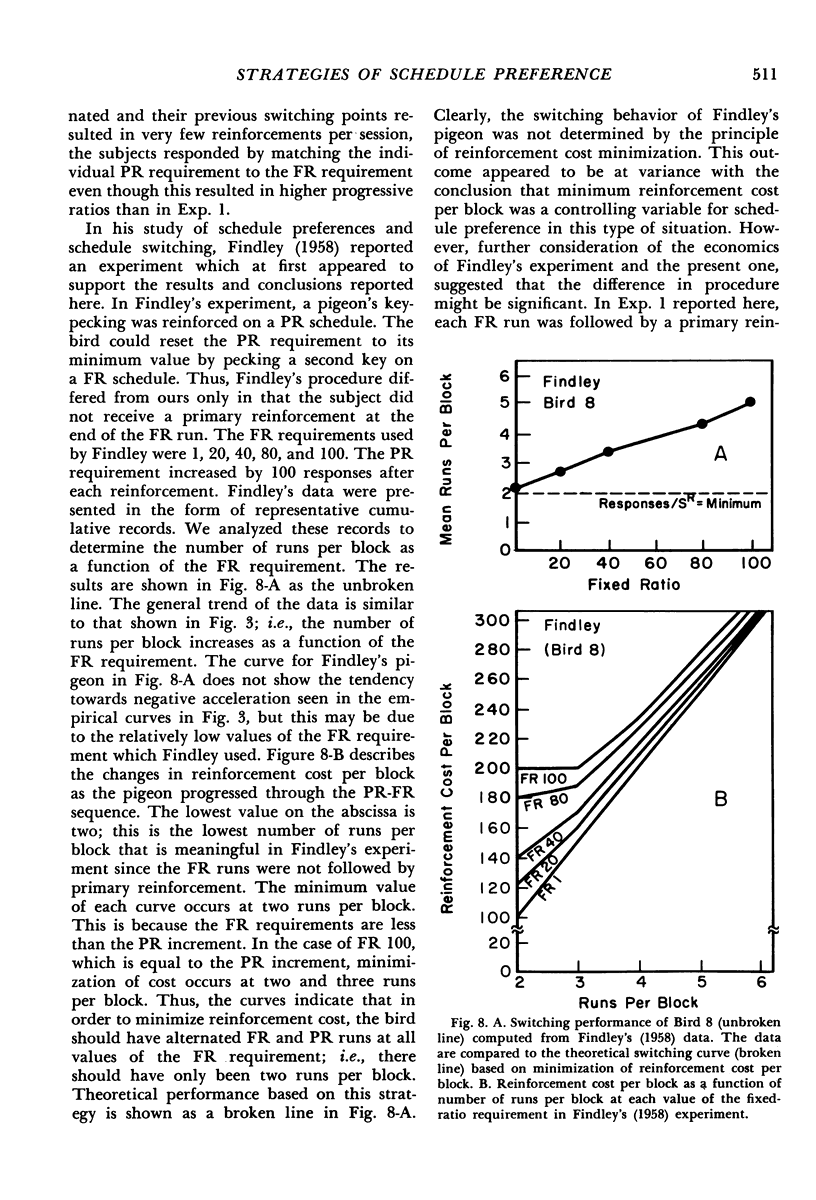
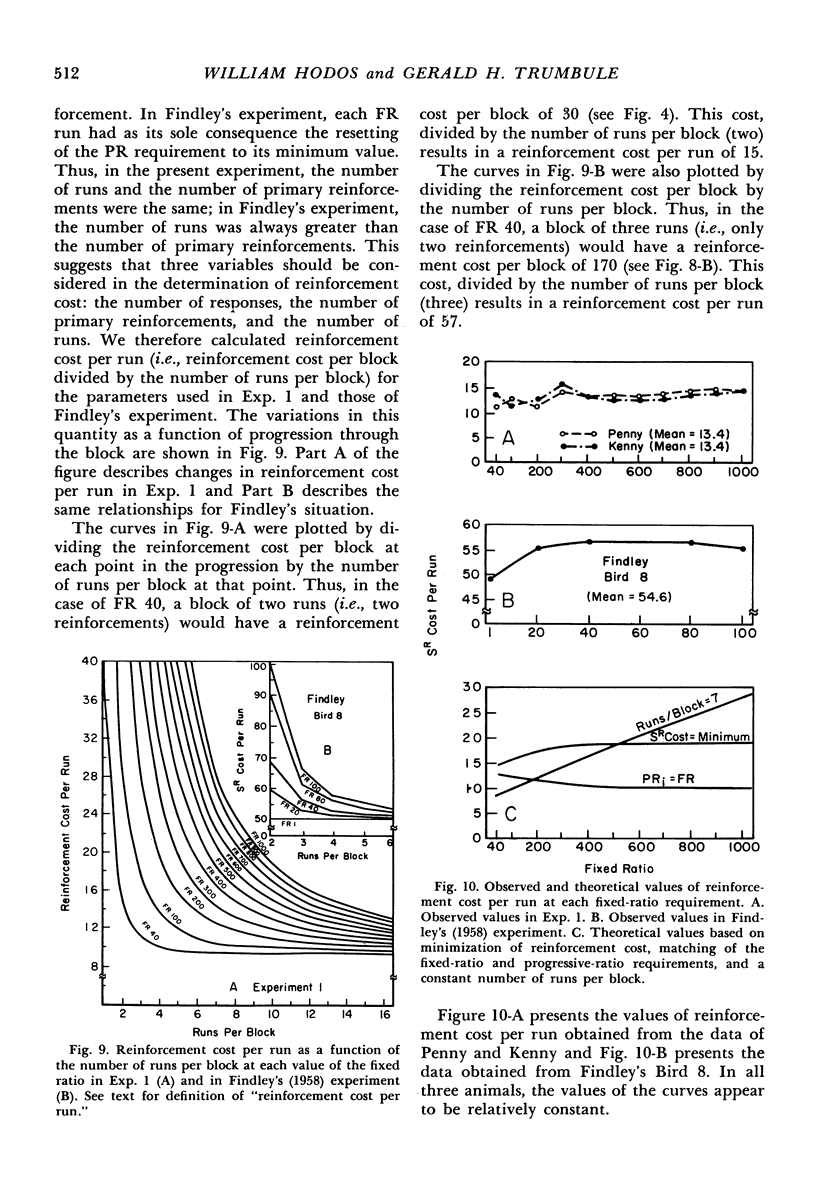
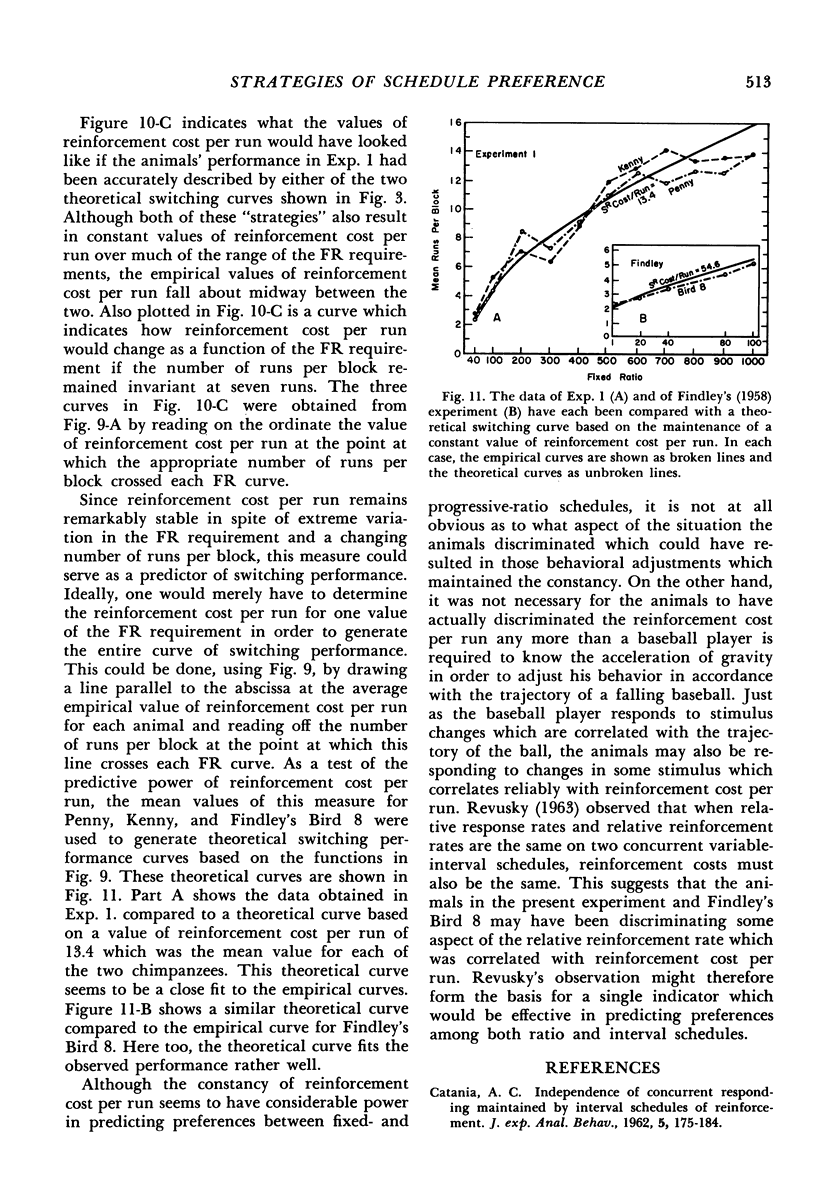
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODOS W., KALMAN G. Effects of increment size and reinforcer volume on progressive ratio performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:387–392. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODOS W. Progressive ratio as a measure of reward strength. Science. 1961 Sep 29;134(3483):943–944. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3483.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVUSKY S. H. A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESPONSES PER REINFORCEMENT AND PREFERENCE DURING CONCURRENT. VI. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:518–518. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinnen M. E., Hodos W. A versatile programmer for ratio and interval schedules using a punched-tape reader. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Nov;10(6):515–516. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


