Abstract
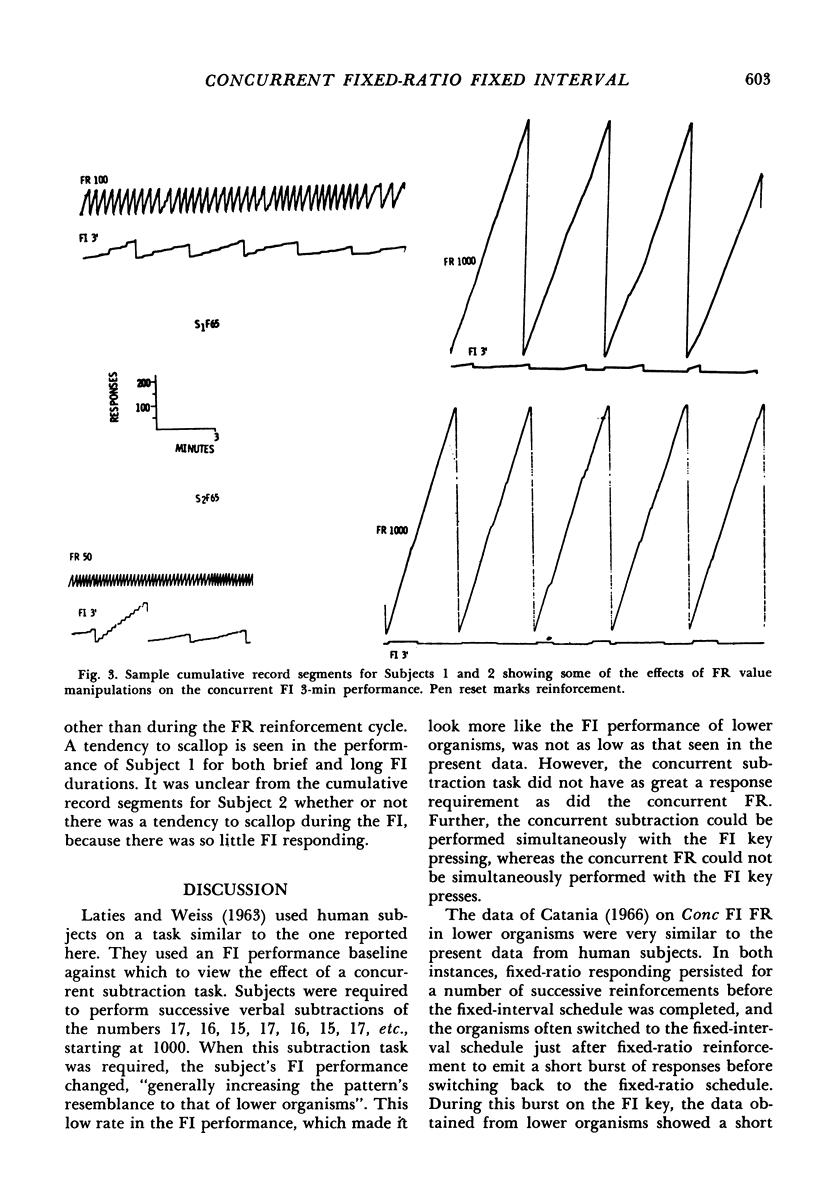
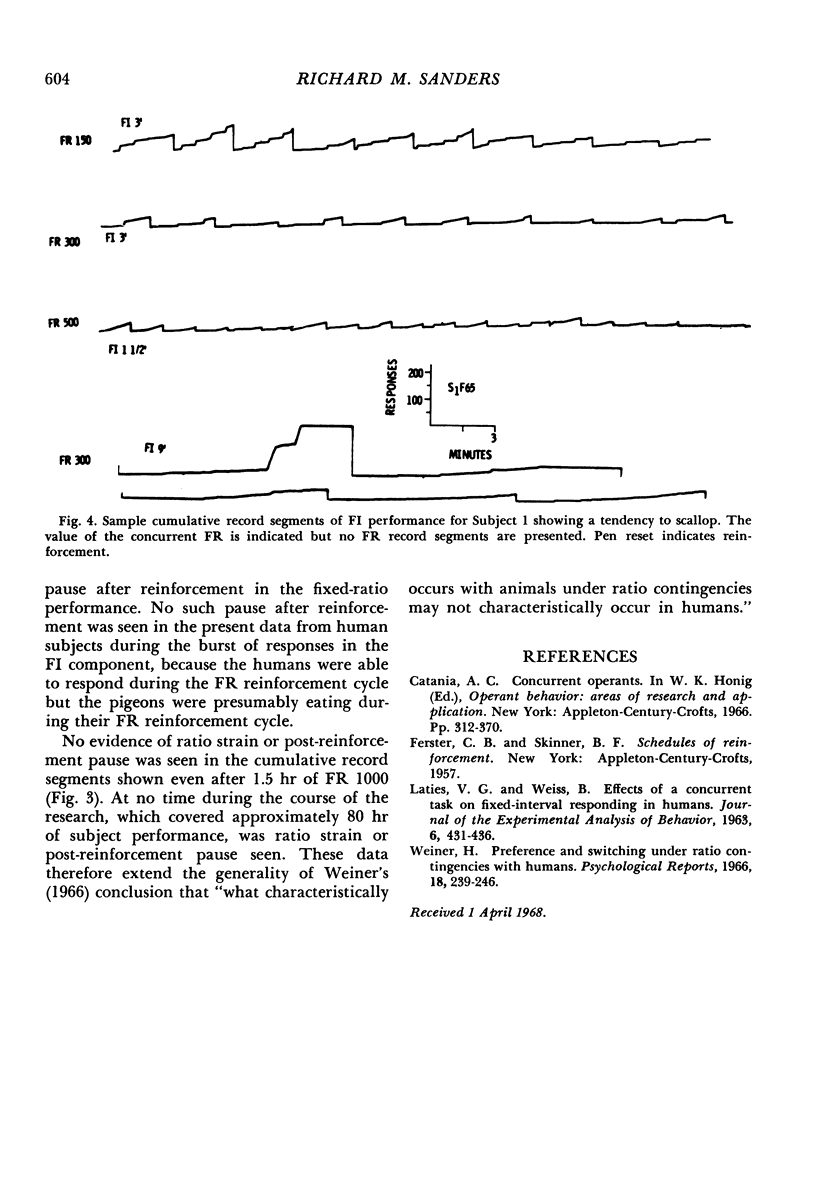
Two undergraduate males worked for money on a button-pressing task associated with concurrent fixed-ratio fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. Manipulations of the fixed-ratio requirement produced an interaction between the various fixed-ratio and fixed-interval performances. When the fixed ratio was small, more fixed-interval responding occurred per interval than when the fixed ratio was large. In general, the data were similar to those obtained with lower organisms except that no post-reinforcement pause or ratio strain was seen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Laties V. G., Weiss B. Effects of a concurrent task on fixed-interval responding in humans. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6(3):431–436. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. Preference and switching under ratio contingencies with humans. Psychol Rep. 1966 Feb;18(1):239–246. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1966.18.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


