Abstract
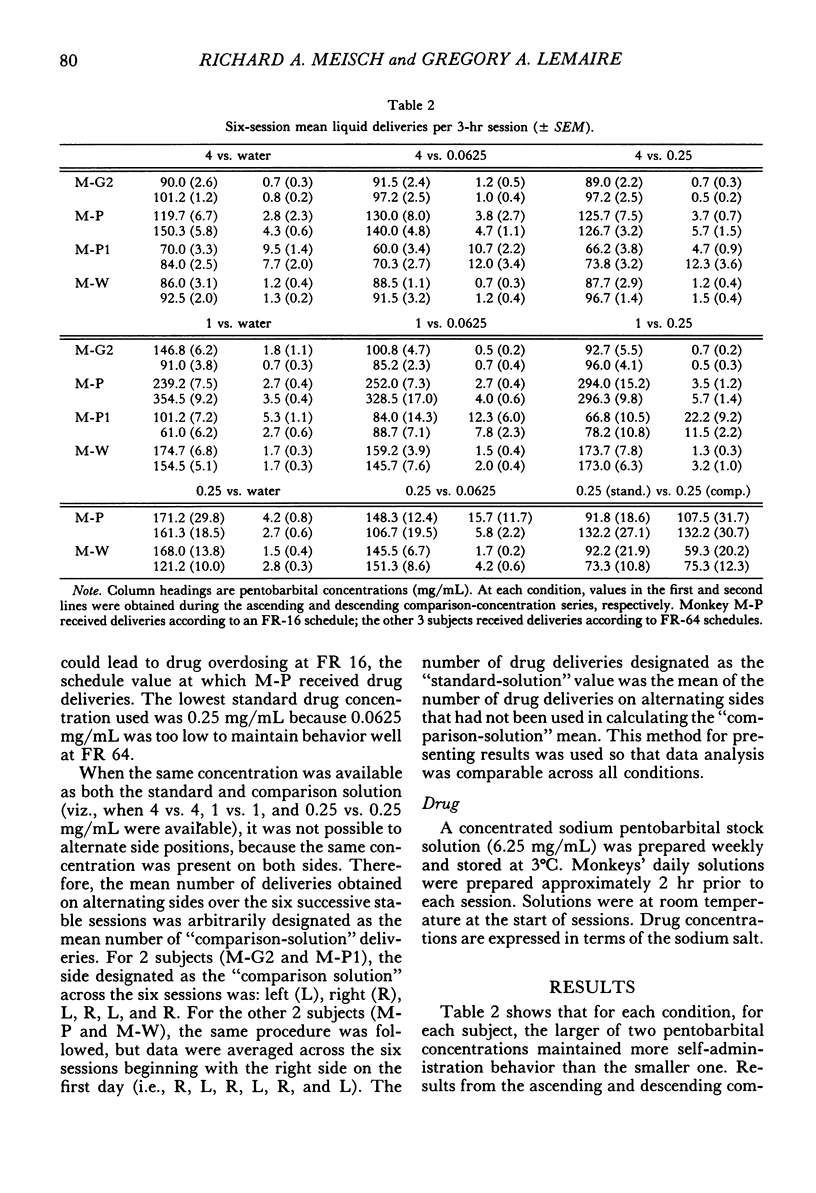
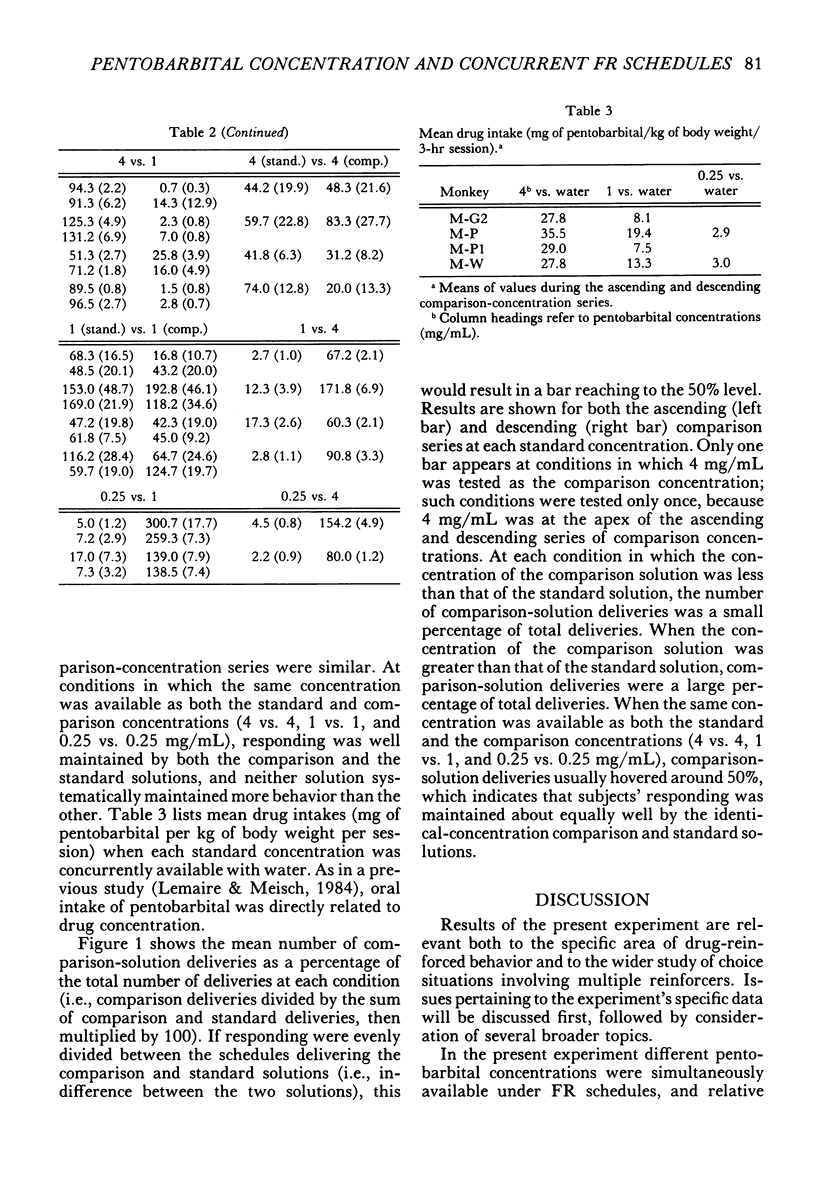
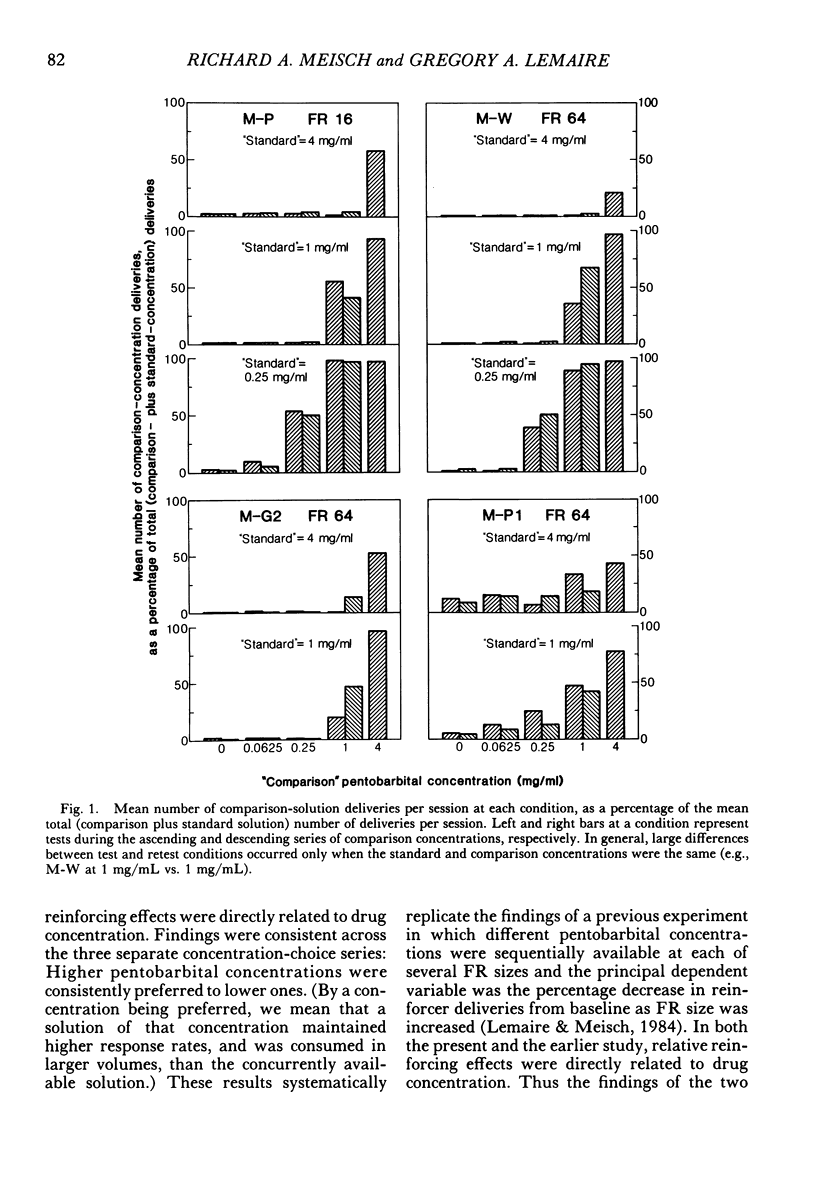
During daily 3-hr sessions, orally delivered pentobarbital solutions and water, or two separate pentobarbital solutions, were concurrently available to rhesus monkeys according to fixed-ratio schedules of mouth contacts with a spout. First water, and then each of four "comparison-concentration" pentobarbital solutions (0.0625, 0.25, 1, and 4 mg/mL), was successively available from one spout for a block of sessions under a fixed-ratio-64 (three monkeys) or fixed-ratio-16 (one monkey) schedule. Under an identically sized fixed-ratio schedule, deliveries of a "standard-concentration" pentobarbital solution were concurrently available from a second spout. The concentration of the standard solution remained unchanged throughout testing of the series of comparison solutions. Each of three pentobarbital concentrations (4, 1, and 0.25 mg/mL) in turn served as the standard concentration. Within each pair of concurrently available solutions, the higher drug concentration maintained more behavior than the lower concentration. Thus when monkeys were provided with concurrent access to different pentobarbital concentrations, relative reinforcing effects were directly related to drug concentration. Further, the amount of behavior maintained by a particular drug concentration was dependent on the concentration of the concurrently available drug solution. Thus, the relative effectiveness of a reinforcer in maintaining behavior is a function of both the reinforcer's magnitude and the availability of alternative reinforcers in the environment.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. E. Concurrent access to two concentrations of orally delivered phencyclidine: effects of feeding conditions. J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 May;47(3):347–362. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.47-347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. E. Concurrent phencyclidine and saccharin access: presentation of an alternative reinforcer reduces drug intake. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 Jan;43(1):131–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. E., Stotz D. C., Kliner D. J., Meisch R. A. Self-administration of orally-delivered methohexital in rhesus monkeys with phencyclidine or pentobarbital histories: effects of food deprivation and satiation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984 Jan;20(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(84)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essock S. M., Reese E. P. Preference for and effects of variable-as opposed to fixed-reinforcer duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):89–97. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. T., Kelleher R. T. Behavior controlled by scheduled injections of cocaine in squirrel and rhesus monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jan;25(1):93–104. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Bigelow G. E., Liebson I., Kaliszak J. E. Drug preference in humans: double-blind choice comparison of pentobarbital, diazepam and placebo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Dec;215(3):649–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Brady J. V., Snell J. D. Progressive-ratio performance maintained by drug infusions: comparison of cocaine, diethylpropion, chlorphentermine, and fenfluramine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Jan 31;56(1):5–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00571401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Findley J. D., Brady J. V., Dolan-Gutcher K., Robinson W. W. Comparison of progressive-ratio performance maintained by cocaine, methylphenidate and secobarbital. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Jul 23;43(1):81–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00437619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODOS W., KALMAN G. Effects of increment size and reinforcer volume on progressive ratio performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:387–392. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henningfield J. E., Meisch R. A. Drinking device for rhesus monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1976 May;4(5):609–610. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(76)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henningfield J. E., Meisch R. A. Ethanol as a positive reinforcer via the oral route for rhesus monkeys: maintenance of fixed-ratio responding. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1976 Apr;4(4):473–475. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(76)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henningfield J. E., Meisch R. A. Ethanol drinking by rhesus monkeys with concurrent access to water. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 May;10(5):777–782. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90332-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J., Loveland D. H. Maximizing and matching on concurrent ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jul;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmeister F. Progressive-ratio performance in the rhesus monkey maintained by opiate infusions. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Apr 11;62(2):181–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00427134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglauer C., Llewellyn M. E., Woods J. H. Concurrent schedules of cocaine injection in rhesus monkeys: dose variations under independent and non-independent variable-interval procedures. Pharmacol Rev. 1975 Sep;27(3):367–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglauer C., Woods J. H. Concurrent performances: reinforcement by different doses of intravenous cocaine in rhesus monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):179–196. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson C. E., Aigner T. Comparison of the reinforcing properties of cocaine and procaine in rhesus monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1981 Jul;15(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(81)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson C. E., Schuster C. R. A choice procedure for drug reinforcers: cocaine and methylphenidate in the rhesus monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 May;193(2):676–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEESEY R. E., KLING J. W. Amount of reinforcement and free-operant responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:125–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliner D. J., Meisch R. A. The effects of food deprivation and satiation on oral pentobarbital self-administration in rhesus monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1982 Apr;16(4):579–584. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(82)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire G. A., Meisch R. A. Oral drug self-administration in rhesus monkeys: interactions between drug amount and fixed-ratio size. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 Nov;44(3):377–389. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.44-377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire G. A., Meisch R. A. Pentobarbital self-administration in rhesus monkeys: drug concentration and fixed-ratio size interactions. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Jul;42(1):37–49. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.42-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn M. E., Iglauer C., Woods J. H. Relative reinforcer magnitude under a nonindependent concurrent schedule of cocaine reinforcement in rhesus monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jan;25(1):81–91. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisch R. A., Kliner D. J., Henningfield J. E. Pentobarbital drinking by rhesus monkeys: establishment and maintenance of pentobarbital-reinforced behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Apr;217(1):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Response strength in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):389–408. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickens R., Muchow D., DeNoble V. Methohexital-reinforced responding in rats: effects of fixed ratio size and injection dose. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Feb;216(2):205–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson H. H., Grant K. A. Chlordiazepoxide effects on ethanol self-administration: dependence on concurrent conditions. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):353–364. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENSTEIN E. S. PROBLEMS OF MEASUREMENT AND INTERPRETATION WITH REINFORCING BRAIN STIMULATION. Psychol Rev. 1964 Nov;71:415–437. doi: 10.1037/h0040694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wauquier A., Niemegeers C. J., Geivers H. A. Intracranial self-stimulation in rats as a function of various stimulus parameters. I. An empirical study with monopolar electrodes in the medial forebrain bundle. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;23(3):238–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00404130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winger G., Stitzer M. L., Woods J. H. Barbiturate-reinforced responding in rhesus monkeys: comparisons of drugs with different durations of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Dec;195(3):505–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolverton W. L., Johanson C. E. Preference in rhesus monkeys given a choice between cocaine and d,l-cathinone. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Jan;41(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.41-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagita T. Some methodological problems in assessing dependence-producing properties of drugs in animals. Pharmacol Rev. 1975 Dec;27(4):503–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. S. Discrete-trial choice in pigeons: Effects of reinforcer magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Jan;35(1):23–29. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


