Abstract
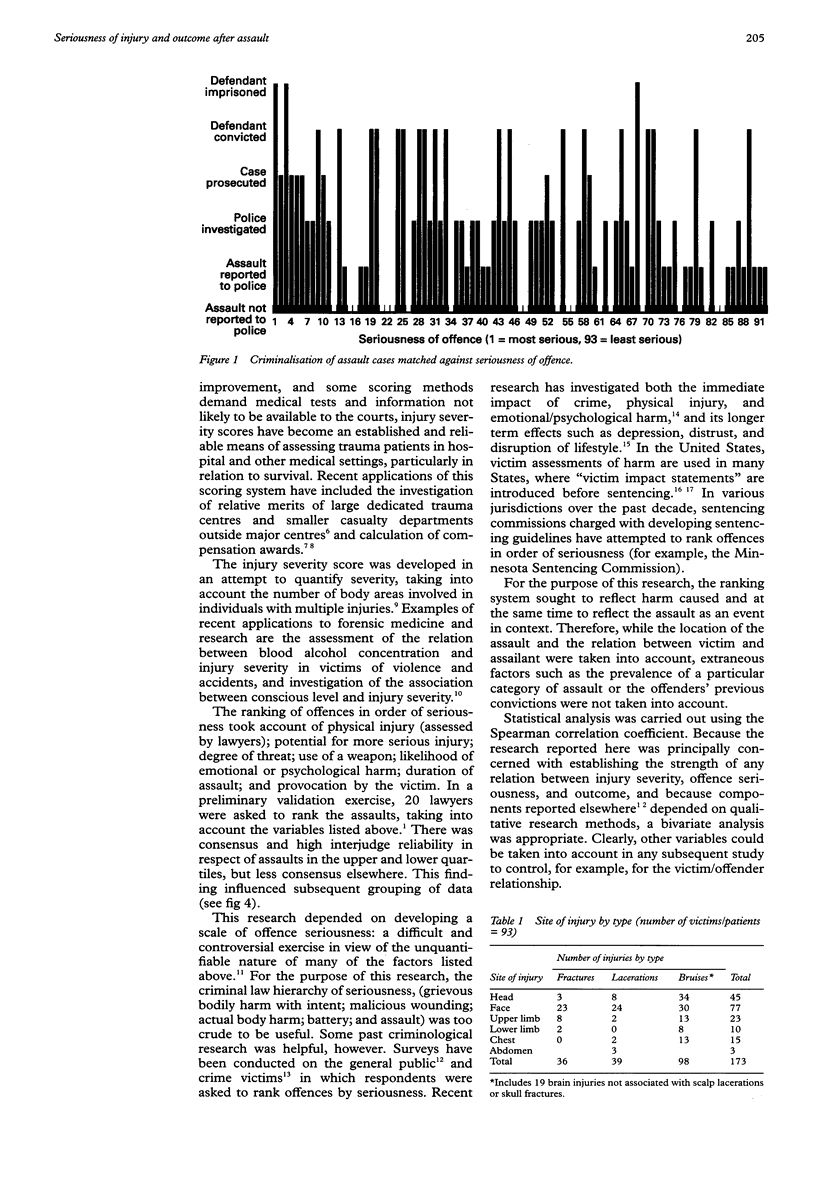
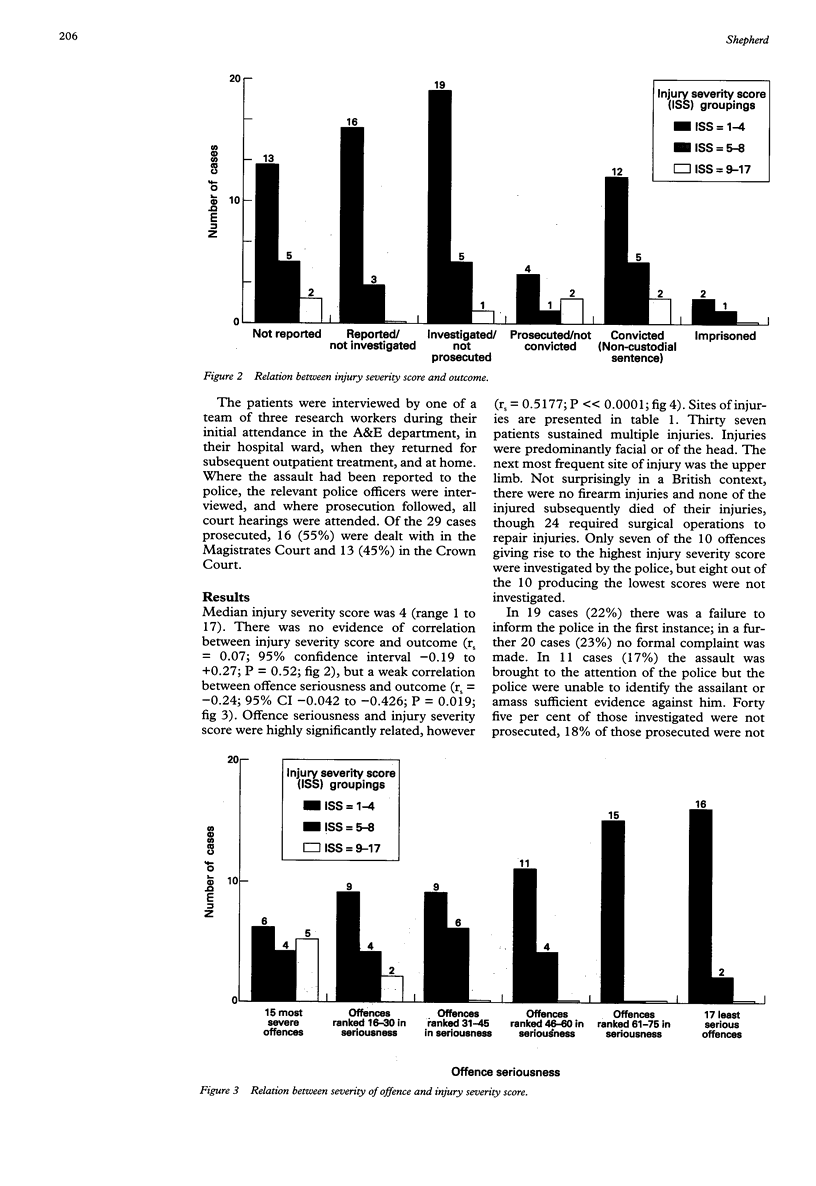
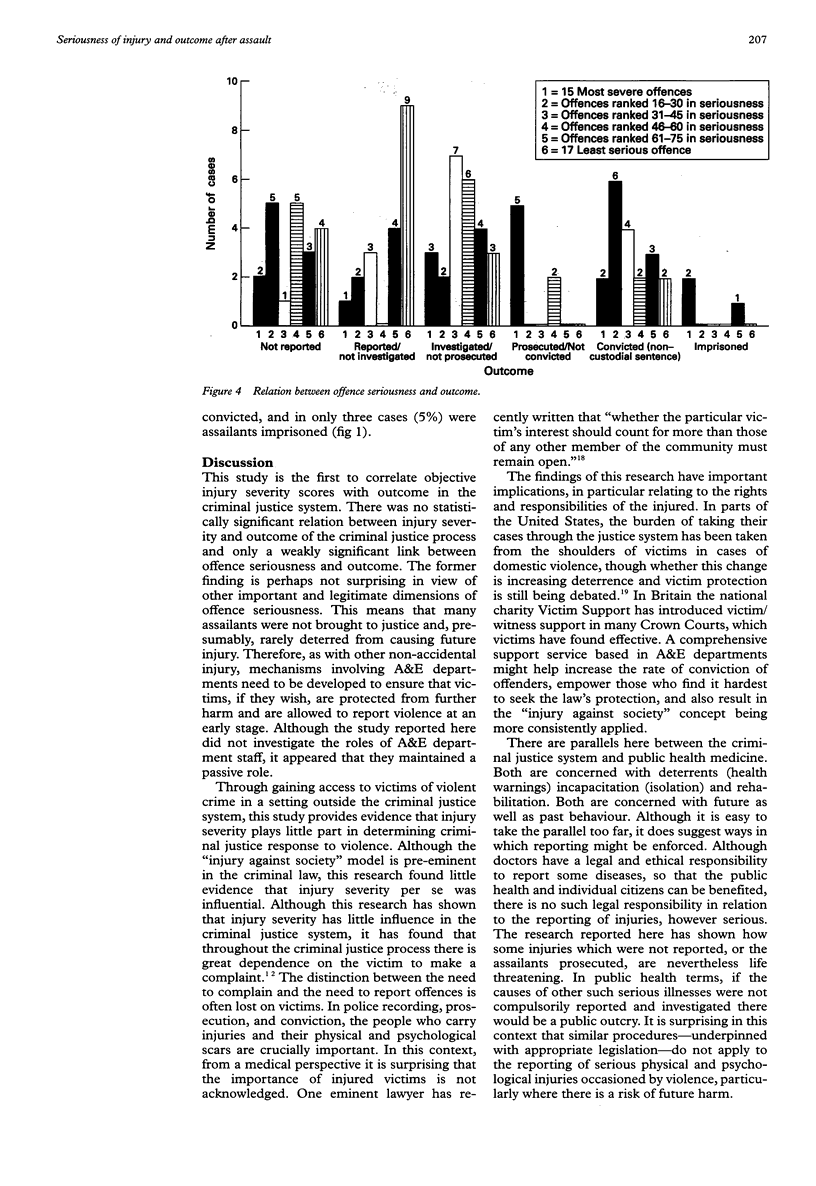
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the relation between injury severity in assault, offence seriousness, and outcome in the criminal justice system. METHODS: Prospective random sample of 93 assault victims who attended hospital were interviewed and examined and followed through the criminal justice system. Patient and police interviews were carried out at Bristol Royal Infirmary accident and emergency and outpatient departments, wards, and in Avon police stations and criminal courts. Severity of injury (injury severity score [ISS] assessed by the major trauma outcome study group), offence seriousness (Delphi panel of criminologists), and outcome in the criminal justice system were recorded. RESULTS: Median ISS was 4 (range 1-17). There was no significant correlation between ISS and outcome in the CJS (rs = 0.07). There was a weak correlation between offence seriousness and outcome (rs = -0.24, P = 0.019). CONCLUSIONS: Outcome in the criminal justice system was not predictable from injury severity scores and was only weakly linked to offence seriousness. Contacts with medical services are opportunities for protecting those at risk of violence.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali T., Shepherd J. P. The measurement of injury severity. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994 Feb;32(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(94)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. P., O'Neill B., Haddon W., Jr, Long W. B. The injury severity score: a method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. J Trauma. 1974 Mar;14(3):187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickley M. R., Shepherd J. P. The relationship between alcohol intoxication, injury severity and Glasgow Coma Score in assault patients. Injury. 1995 Jun;26(5):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0020-1383(95)00034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson D. H., Fryback D. G., Rose J. H., Prokop C. T., Detmer D. E., Rossmeissl J. C., Taylor C. M., Alemi F., Carnazzo A. J. An evaluation of multiple trauma severity indices created by different index development strategies. Med Care. 1983 Jul;21(7):674–691. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198307000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivara F. P., Shepherd J. P., Farrington D. P., Richmond P. W., Cannon P. Victim as offender in youth violence. Ann Emerg Med. 1995 Nov;26(5):609–614. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(95)70013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Morley R., Adshead G., Gillett G., Knight M. A. Should doctors be more proactive as advocates for victims of violence? BMJ. 1995 Dec 16;311(7020):1617–1621. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7020.1617a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Shapland M., Scully C. Recording by the police of violent offences; an Accident and Emergency Department perspective. Med Sci Law. 1989 Jul;29(3):251–257. doi: 10.1177/002580248902900311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]