Abstract
To analyze the effectiveness of peritoneal lavage and to define its limitations in the evaluation of patients who have sustained blunt abdominal trauma, a prospective study of 500 such patients was undertaken by the Trauma Service at the Naval Hospital, San Diego. Utilizing a qualitative colorometric method to evaluate the degree of hemoperitoneum, patients could rapidly be divided into three clinical groups: strongly positive, weakly positive, and negative. Using this method, patients with a strongly positive peritoneal lavage had a 94% incidence of significant intra-abdominal injuries. In 333 patients with a negative lavage, there was no documented incidence of significant intra-abdominal injuries. Visceral angiography and abdominal echography were utilized in this group of patients to identify those with significant intra-abdominal injuries. By utilizing this approach, there were only eight unnecessary celiotomies in the total group of 500 patients. It is concluded, therefore, that peritoneal lavage is a safe, rapid, and effective means of evaluating patients who have sustained blunt abdominal trauma.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caffee H. H., Benfield J. R. Is peritoneal lavage for the diagnosis of hemoperitoneum safe? Arch Surg. 1971 Jul;103(1):4–7. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1971.01350070030005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiVincenti F. C., Rives J. D., Laborde E. J., Fleming I. D., Cohn I., Jr Blunt abdominal trauma. J Trauma. 1968 Nov;8(6):1004–1013. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196811000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
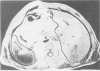
- Freimanis A. K., Asher W. M. Development of diagnostic criteria in echographic study of abdominal lesions. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1970 Apr;108(4):747–755. doi: 10.2214/ajr.108.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahadi M. R. Diagnostic peritoneal lavage. J Trauma. 1972 Nov;12(11):936–938. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197211000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
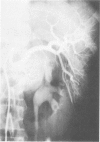
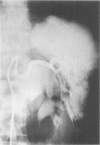
- Love L., Greenfield G. B., Braun T. W., Moncada R., Freeark R. J., Baker R. J. Arteriography of splenic trauma. Radiology. 1968 Jul;91(1):96–102. doi: 10.1148/91.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe R. J., Boyd D. R., Folk F. A., Baker R. J. The negative laparotomy for abdominal trauma. J Trauma. 1972 Oct;12(10):853–861. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197210000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard A. de L., Oropeza G. Mandatory operation for penetrating wounds of the abdomen. Am J Surg. 1968 Mar;115(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(68)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. R., Hildreth D. H. Abdominal paracentesis and peritoneal lavage in blunt abdominal trauma. J Trauma. 1971 Oct;11(10):824–829. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197110000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. R., Redman H. C., Hildreth D. H. Quantitative peritoneal lavage in blunt abdominal trauma. Arch Surg. 1972 Apr;104(4):536–543. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180040150026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. R. The serum amylase in blunt abdominal trauma. J Trauma. 1973 Mar;13(3):200–204. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197303000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry J. F., Jr, Strate R. G. Diagnostic peritoneal lavage in blunt abdominal trauma: indications and results. Surgery. 1972 Jun;71(6):898–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROOT H. D., HAUSER C. W., MCKINLEY C. R., LAFAVE J. W., MENDIOLA R. P., Jr DIAGNOSTIC PERITONEAL LAVAGE. Surgery. 1965 May;57:633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root H. D., Keizer P. J., Perry J. F., Jr The clinical and experimental aspects of peritoneal response to injury. Arch Surg. 1967 Oct;95(4):531–537. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330160001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thal E. R., Shires G. T. Peritoneal lavage in blunt abdominal trauma. Am J Surg. 1973 Jan;125(1):64–69. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. P., Shultz E. H., Benfield J. R. Celiac angiography in the management of splenic trauma. Arch Surg. 1969 Oct;99(4):494–497. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340160074017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]