Abstract
The consequences of near-lethal smoke inhalation in dogs were studied for a 72-hour period following injury. Progressive hypoxemia and decrease in compliance developed. Severe respiratory distress and frank pulmonary edema were not encountered. Respiratory insufficiecy was related more to alterations in ventilation perfusion ratios than to alveolar destruction. These data were related to clinical observations made by others. No deterioration of lung function was seen with crystalloid overload imposed upon smoke inhalation. The presence of bacterial infection in dogs surviving beyond 24 hours appears pathogenically significant.
Full text
PDF


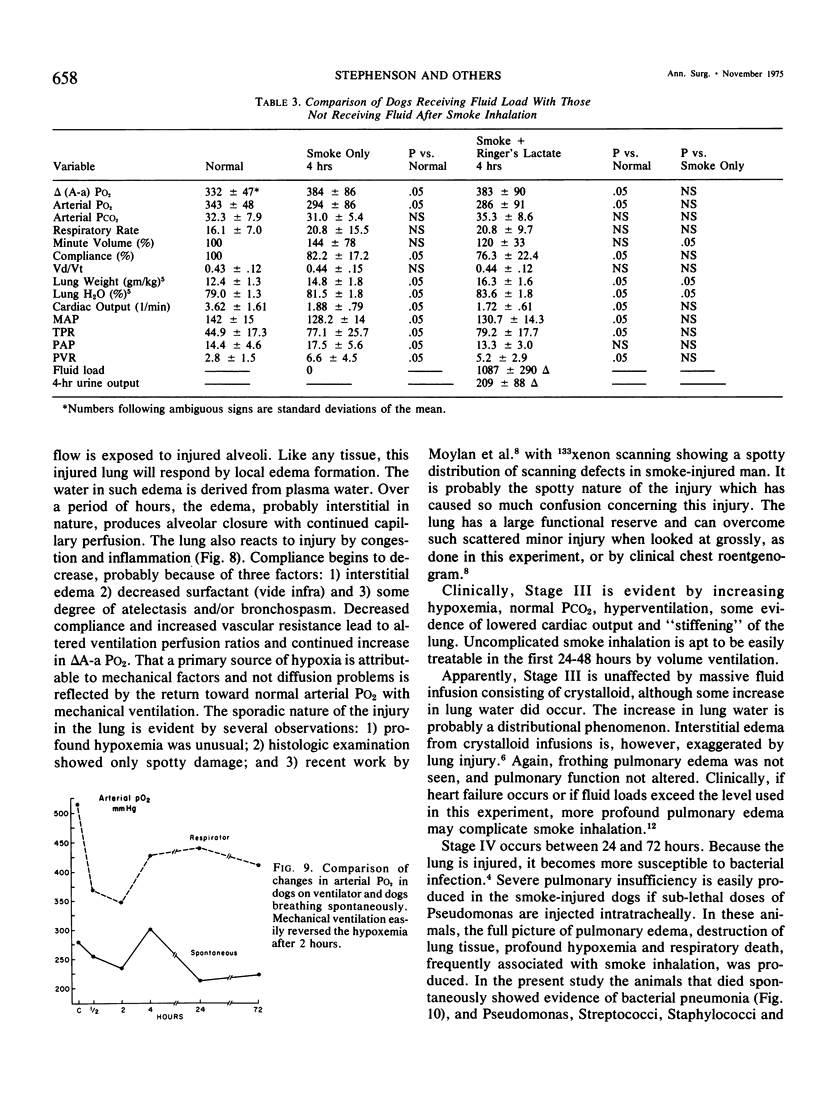


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achauer B. M., Allyn P. A., Furnas D. W., Bartlett R. H. Pulmonary complications of burns: the major threat to the burn patient. Ann Surg. 1973 Mar;177(3):311–319. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197303000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk J. L., Hagen J. F., Koo R., Beyer W., Dochat G. R., Rupright M., Nomoto S. Pulmonary insufficiency caused by epinephrine. Ann Surg. 1973 Oct;178(4):423–435. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197310000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. L., Fischer R. P. Pulmonary changes due to hemorrhagic shock resuscitation with isotonic and hypertonic saline. Surgery. 1974 Jun;75(6):881–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. L., Peter E. T. Compositional and histologic effects of fluid therapy following pulmonary contusion. J Trauma. 1974 Sep;14(9):783–790. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197409000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzon A. A., Seltzer B., Song I. C., Bromberg B. E., Karlson K. E. Respiratory mechanics in patients with inhalation burns. J Trauma. 1970 Jan;10(1):57–62. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197001000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz A. R., Henriques F. C., McLean R. The Effects of Inhaled Heat on the Air Passages and Lungs: An Experimental Investigation. Am J Pathol. 1945 Mar;21(2):311–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss G., Staunton C., Stein A. A. The centrineurogenic etiology of the acute respiratory distress syndromes. Universal, species--independent phenomenon. Am J Surg. 1973 Jul;126(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(73)80090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moylan J. A., Jr, Wilmore D. W., Mouton D. E., Pruitt B. A., Jr Early diagnosis of inhalation injury using 133 xenon lung scan. Ann Surg. 1972 Oct;176(4):477–484. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197210000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS A. W., TANNER J. W., COPE O. BURN THERAPY. IV. RESPIRATORY TRACT DAMAGE (AN ACCOUNT OF THE CLINICAL, X-RAY AND POSTMORTEM FINDINGS) AND THE MEANING OF RESTLESSNESS. Ann Surg. 1963 Nov;158:799–811. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196311000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt B. A., Jr, Flemma R. J., DiVincenti F. C., Foley F. D., Mason A. D., Jr, Young W. G., Jr Pulmonary complications in burn patients. A comparative study of 697 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1970 Jan;59(1):7–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skornik W. A., Dressler D. P. Lung bacterial clearance in the burned rat. Ann Surg. 1970 Nov;172(5):837–843. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197011000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. H., Martin J. D., Jr Pulmonary injury associated with thermal burns. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 Dec;129(6):1242–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. H., Rhame D. W., Corbitt J. D., Given K. S., Martin J. D., Jr Respiratory burns: a correlation of clinical and laboratory results. Ann Surg. 1967 Feb;165(2):157–168. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196702000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zikria B. A., Ferrer J. M., Floch H. F. The chemical factors contributing to pulmonary damage in "smoke poisoning". Surgery. 1972 May;71(5):704–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zikria B. A., Weston G. C., Chodoff M., Ferrer J. M. Smoke and carbon monoxide poisoning in fire victims. J Trauma. 1972 Aug;12(8):641–645. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197208000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]