Abstract
A randomized, prospective comparison of radical peritoneal debridement and standard surgical management of peritonitis disclosed no differences in terms of hospital mortality for the frequency of reoperation for abscess. Adjunctive measures such as antibiotic therapy and peritoneal irrigation were identical between the groups. The groups were demographically and clinically similar but had a much lower incidence of intestinal obstruction than in the patients originally reported by Hudspeth.
Full text
PDF
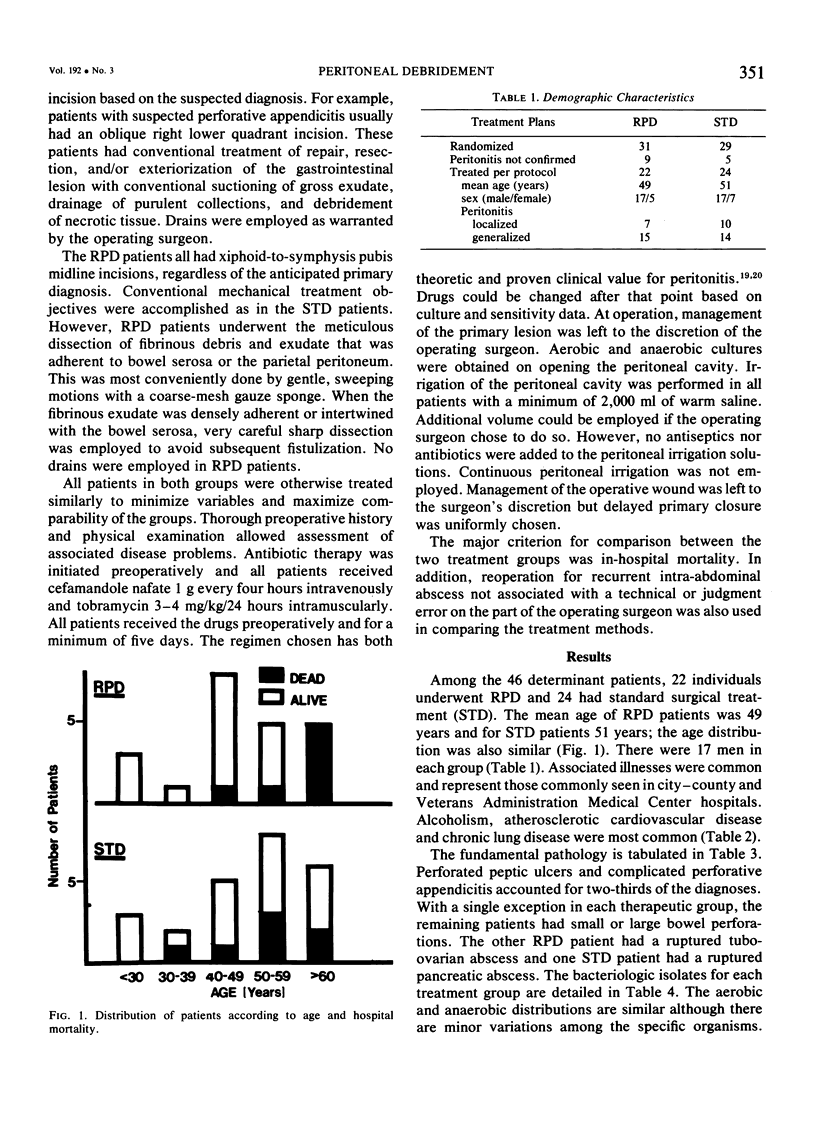

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARTZ C. P., BARNETT W. O., GROGAN J. B. Further studies concerning the pathogenesis and treatment of peritonitis. Ann Surg. 1962 May;155:756–767. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196205000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahrenholz D. H., Simmons R. L. Fibrin in peritonitis. I. Beneficial and adverse effects of fibrin in experimental E. coli peritonitis. Surgery. 1980 Jul;88(1):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A. Bodily response to infectious agents. JAMA. 1967 Dec 18;202(12):1085–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Hummel R. P., Hill E. O., Lewis S. Changing patterns in surgical infections. Ann Surg. 1973 Oct;178(4):436–445. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197310000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne M. K., Stoller J. L. Intraperitoneal noxythiolin in faecal peritonitis. Br J Surg. 1970 Jul;57(7):525–529. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800570711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton A. C., Courtney R. A., Miller H. H. Peritonitis treated with prolonged, intermittent peritoneal lavage. JAMA. 1969 Feb 17;207(7):1345–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiVincenti F. C., Cohn I., Jr Prolonged administration of intraperitoneal kanamycin in the treatment of peritonitis. Am Surg. 1971 Apr;37(4):177–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Garrison R. N., Polk H. C., Jr Clinical implications in bacteroides bacteremia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Aug;149(2):189–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hau T., Ahrenholz D. H., Simmons R. L. Secondary bacterial peritonitis: the biologic basis of treatment. Curr Probl Surg. 1979 Oct;16(10):1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0011-3840(79)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hau T., Hoffman R., Simmons R. L. Mechanisms of the adjuvant effect of hemoglobin in experimental peritonitis. I. In vivo inhibition of peritoneal leukocytosis. Surgery. 1978 Feb;83(2):223–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. S. Radical surgical debridement in the treatment of advanced generalized bacterial peritonitis. Arch Surg. 1975 Oct;110(10):1233–1236. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360160071012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna J. P., Currie D. J., MacDonald J. A., Mahoney L. J., Finlayson D. C., Lanskail J. C. The use of continuous postoperative peritoneal lavage in the management of diffuse peritonitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 Feb;130(2):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullan M. H., Barnett W. O. The clinical use of intraperitoneal cephalothin. Surgery. 1970 Mar;67(3):432–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr Generalized peritonitis: a continuing challenge. Surgery. 1979 Nov;86(5):777–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen M., Loewenthal J. Continuing peritoneal lavage in high-risk peritonitis. Surgery. 1979 Jun;85(6):603–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen M., Loewenthal J. Generalized infective peritonitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978 Aug;147(2):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. H., Guest B. S., Geheber C. E., Kolb L. D. Cefamandole in treatment of peritonitis. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S103–S109. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. H., Kolb L. D., Geheber C. E. Incidence and significance of intraperitoneal anaerobic bacteria. Ann Surg. 1975 May;181(5):705–715. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197505000-00027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


