Abstract
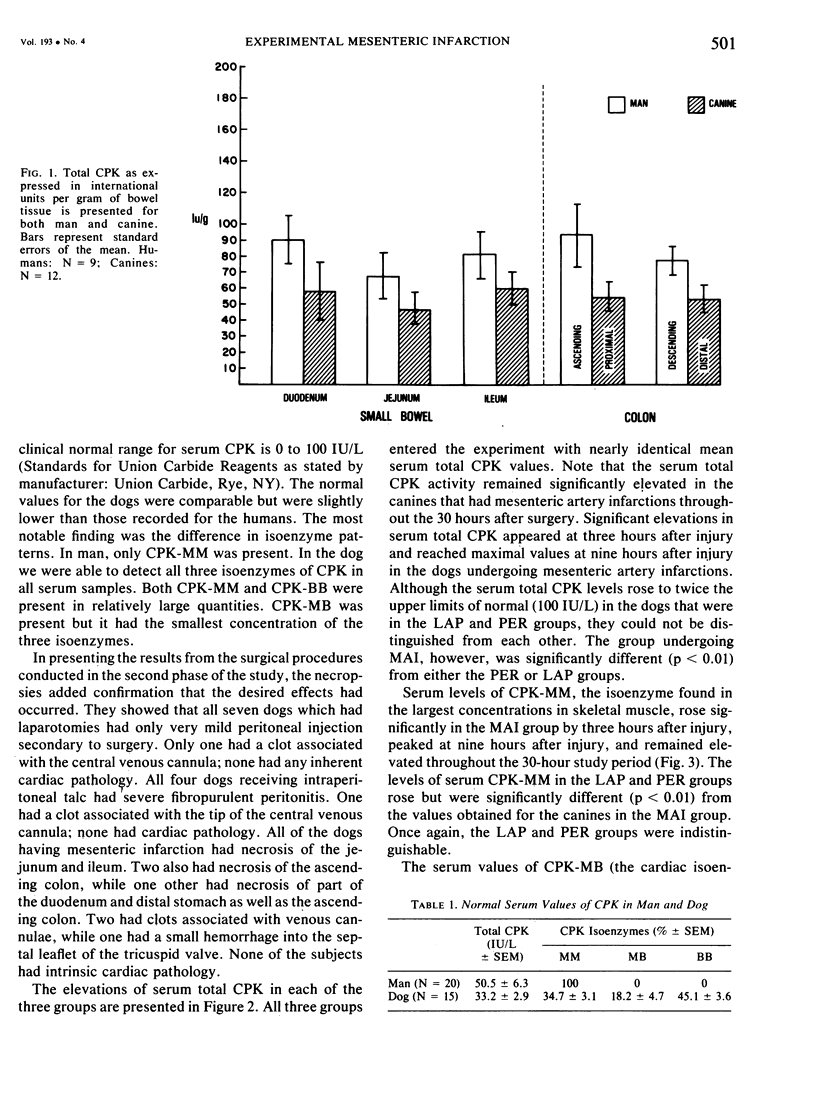
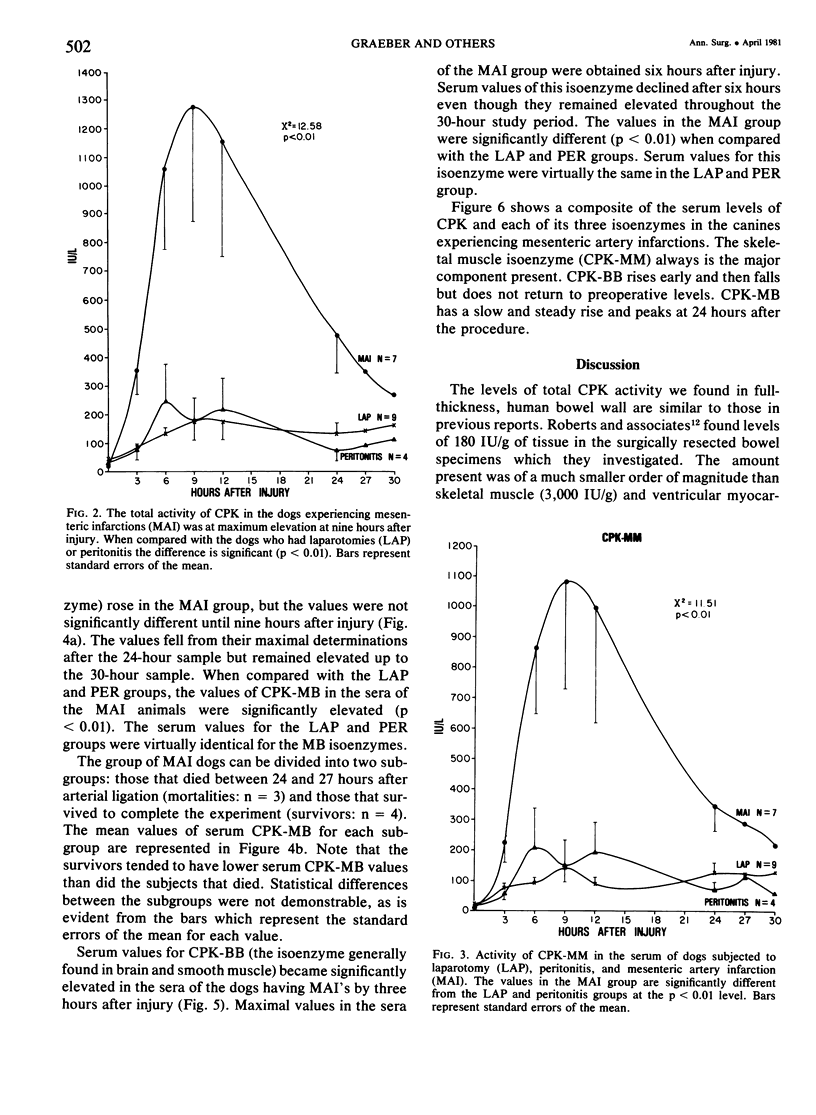
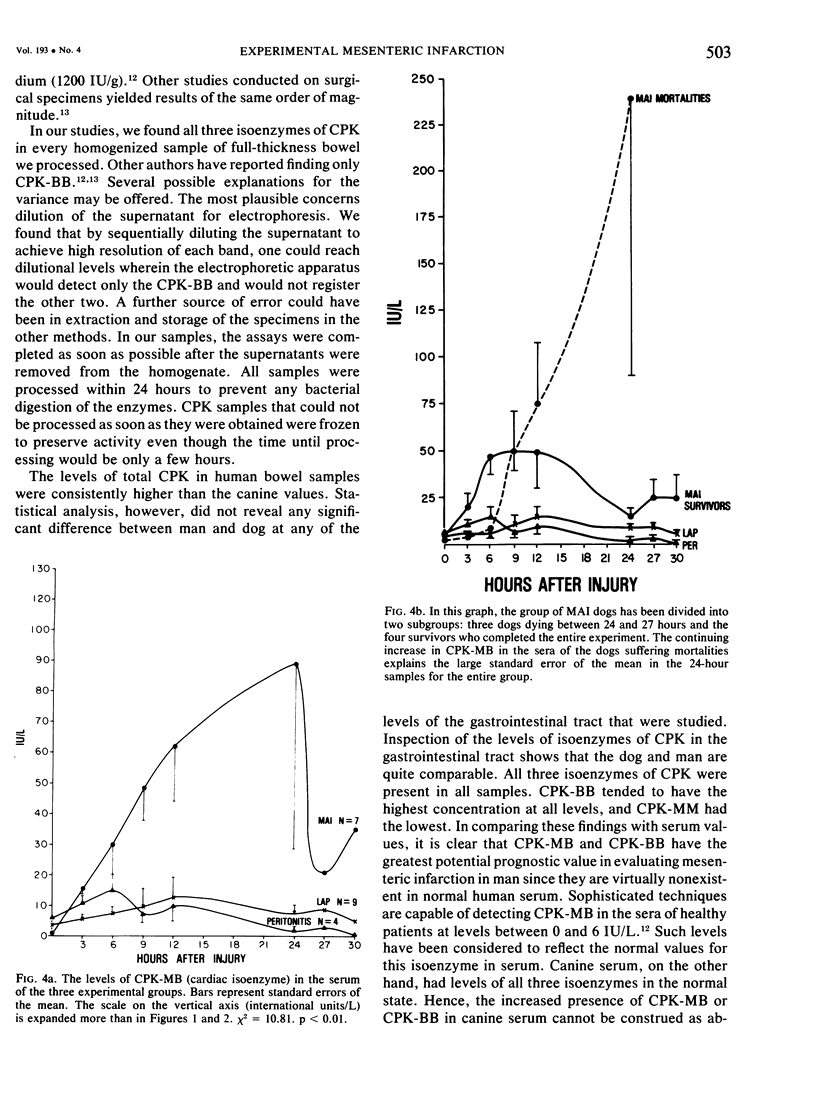
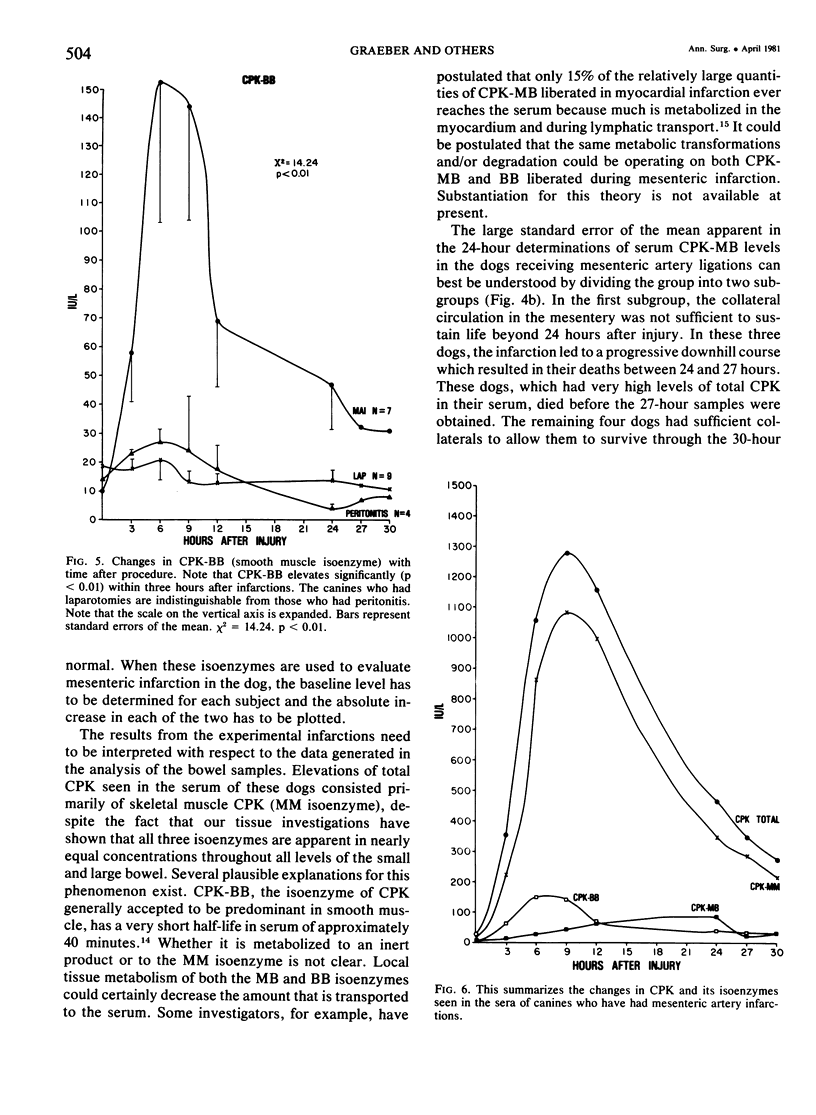
The changes in serum total CPK and its isoenzymes have not been delineated in acute mesenteric infarction. As measurement of serum CPK levels could conceivably be a useful diagnostic test for bowel infarction, this experiment was performed to assess changes in serum CPK levels in bowel infarction in dogs, using sham operation and talc peritonitis as controls. Laparotomies were performed in 20 dogs, and each was as signed randomly to one of three groups: those having laparotomy (LAP), talc peritonitis (PER), and superior mesenteric artery infarction (MAI). Mixed venous blood samples were obtained from all subjects for 30 hours after surgery. All animals were killed, and complete autopsies were performed. Confirmation of infarction and determination of its extent were obtained through both gross and microscopic examination of the gut in canines subjected to arterial infarction. Total serum CPK levels were determined by spectrophotometric analysis. Agarose gel electrophoresis was used to determine the levels of each of the isoenzymes. Significant elevations of CPK and CPK-MM occurred nine hours after injury. CPK-BB reached maximum elevation by six hours, while CPK-MB did not reach its maximum until 24 hours after injury. From data in the study we conclude that total CPK and its isoenzymes become elevated in the serum of canines subjected to experimental superior mesenteric artery infarction. That CPK-BB elevations peak in the first 12 hours after injury and CPK-MB in the second 12 hours after injury may be of particular diagnostic significance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doran G. R. Appearance of creatine kinase BB isoenzyme in the serum of a patient suffering from infarction of the colon. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Mar 15;92(3):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. W., MacDonald R. P., Natho G. J., Murdock K. J. Serum creatine phosphokinase: evaluation of a commercial spectrophotometric method. Clin Chem. 1967 Nov;13(11):994–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itano M. The detection of CPK1 (BB) in serum. A summary of sixteen cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Mar;65(3):351–355. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/65.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIELSEN L., LUDVIGSEN B. Improved method for determination of creatine kinase. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:159–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER I. T. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of creatine phosphokinase and myokinase. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):116–122. doi: 10.1042/bj0610116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottinger L. W. The surgical management of acute occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery. Ann Surg. 1978 Dec;188(6):721–731. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197812000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Gowda K. S., Ludbrook P. A., Sobel B. E. Specificity of elevated serum MB creatine phosphokinase activity in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1975 Oct 6;36(4):433–437. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(75)90890-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Henry P. D., Sobel B. E. An improved basis for enzymatic estimation of infarct size. Circulation. 1975 Nov;52(5):743–754. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.5.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Henry P. D., Witteeveen S. A., Sobel B. E. Quantification of serum creatine phosphokinase isoenzyme activity. Am J Cardiol. 1974 May 6;33(5):650–654. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(74)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosalki S. B. An improved procedure for serum creatine phosphokinase determination. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):696–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsung S. H. Creatine kinase isoenzyme patterns in human tissue obtained at surgery. Clin Chem. 1976 Feb;22(2):173–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. H., Steciw B. Evaluation of a new procedure for measuring serum creatine kinase activity. Clin Chem. 1970 May;16(5):370–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


