Abstract
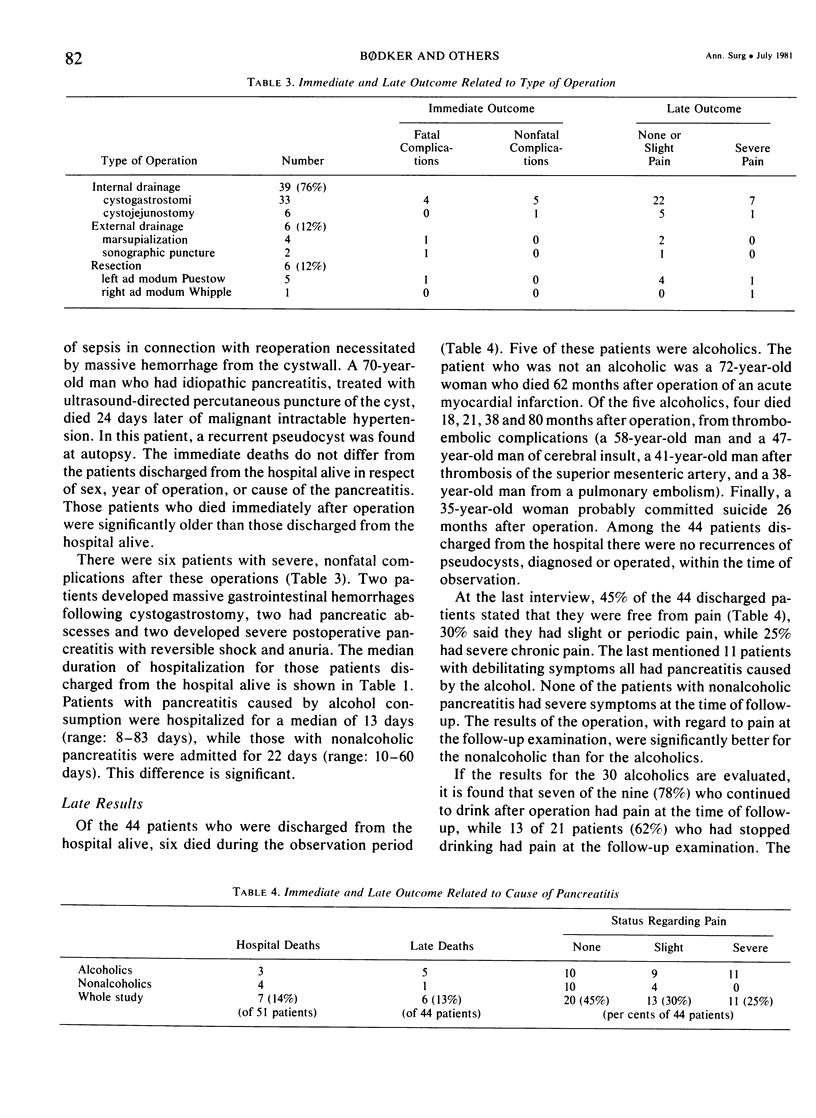
From 1968 to 1978, 37 men and 14 women, with a median age of 43 years, were operated on for a pancreatic pseudocyst. Alcohol abuse was the dominating cause in 65% of the patients. Internal drainage (medium risk patients) was carried out in 76%, external drainage (high risk patients) in 12%, and pancreatic resection (low risk patients) in 12% of the patients. The hospital mortality rate was 14%. The patients who died were significantly older than those discharged from the hospital alive. At the time of follow-up (1--11 years, median: 4 years) after operation, a further 13% had died. Thirty per cent of the alcoholic and none of the nonalcoholic patients had severe pain at follow-up examination. Evaluated by their ability to work and pain, the late results were poorer for the alcoholics who continued drinking, better for alcoholics who had stopped drinking and best for nonalcoholics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley E. L., Gonzalez A. C., Clements J. L., Jr Acute pancreatic pseudocysts: incidence and implications. Ann Surg. 1976 Dec;184(6):734–737. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197612000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elechi E. N., Callender C. O., Leffall L. D., Jr, Kurtz L. H. The treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts by external drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 May;148(5):707–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey C. F. Pancreatic pseudocyst--operative strategy. Ann Surg. 1978 Nov;188(5):652–662. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197811000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. G., Schmidt A. Acute pancreatitis. A study of 122 patients with acute pancreatitis observed for 5-15 years. World J Surg. 1979 Jul 30;3(3):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01556589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. W., Jr, Catalano P., Cooperman M., Hecht C., Carey L. C. Surgical decision-making in the treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Internal versus external drainage. Am J Surg. 1979 Dec;138(6):821–824. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak E. W., Michas C. A., Wolfman E. F., Jr Pancreatic pseudocyst: management in fifty-four patients. Am J Surg. 1978 Feb;135(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravelo H. R., Aldrete J. S. Analysis of forty-five patients with pseudocysts of the pancreas treated surgically. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 May;148(5):735–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatney C. H., Lillehei R. C. Surgical treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Analysis of 119 cases. Ann Surg. 1979 Apr;189(4):386–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. W., Badosa F. Individualization in treatment of pancreatic cysts. Am Surg. 1973 Oct;39(10):555–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


