Abstract
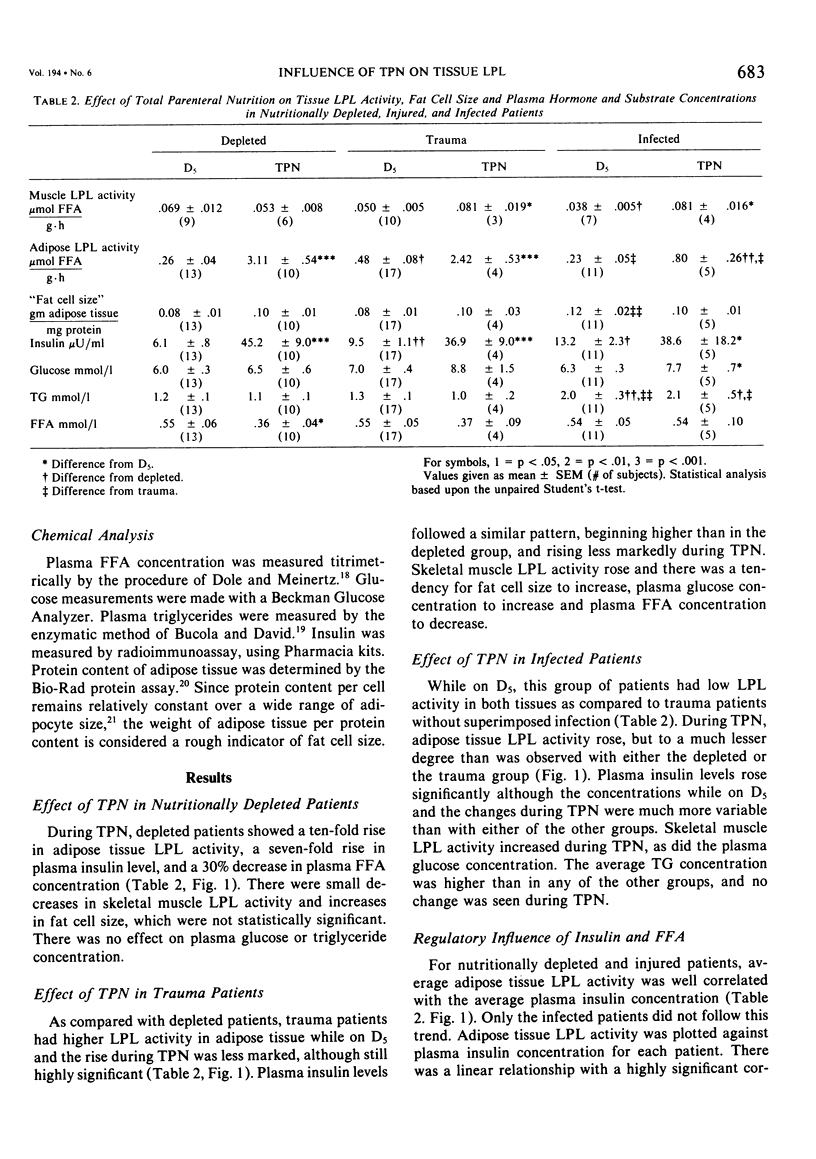
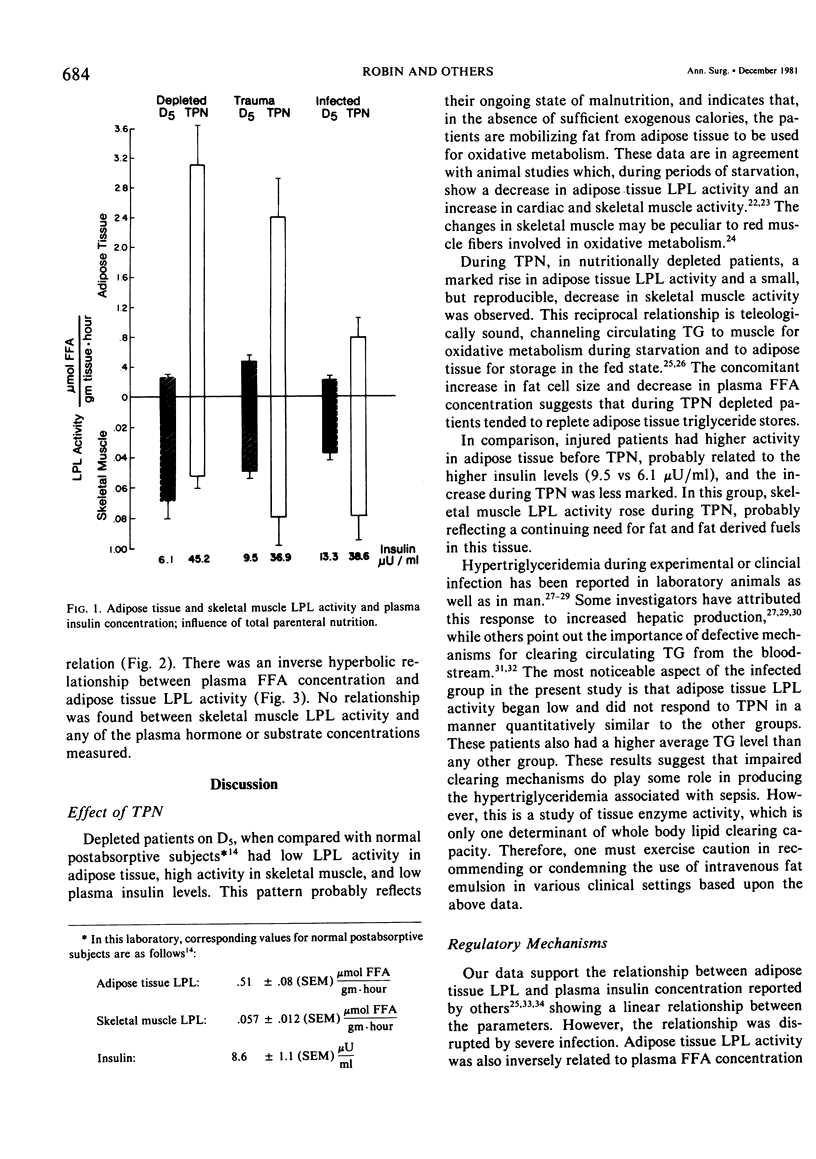
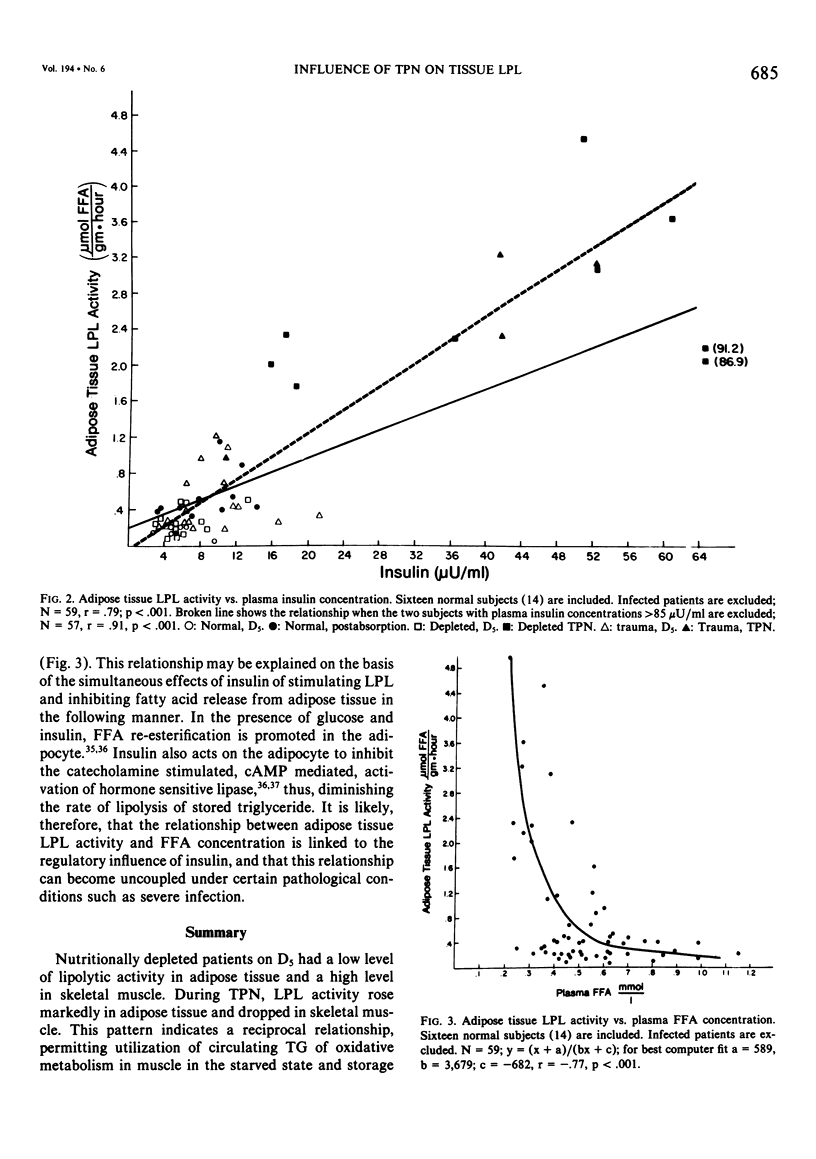
This study examines the influence of total parenteral nutrition (TPN) compared with 5% dextrose (D5) infusion on skeletal muscle and adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity in nutritionally depleted, injured and infected patients. The plasma concentrations of glucose, free fatty acid (FFA), triglyceride and insulin were also measured. During TPN, nutritionally depleted subjects showed an increase in adipose tissue LPL activity, "fat cell size," and plasma insulin concentration. Skeletal muscle LPL activity and plasma FFA concentration decreased. In comparison, trauma patients showed a less marked rise in adipose tissue LPL activity and skeletal muscle LPL activity increased. Infected patients had a much smaller rise in adipose tissue LPL activity than either of the other groups, and muscle activity rose. The depleted and injured patients showed a linear relationship between adipose tissue LPL activity and plasma insulin concentration and an inverse hyperbolic relationship between adipose tissue LPL activity and plasma FFA concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bark S., Holm I., Håkansson I., Wretlind A. Nitrogen-sparing effect of fat emulsion compared with glucose in the postoperative period. Acta Chir Scand. 1976;142(6):423–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfrage P., Vaughan M. Simple liquid-liquid partition system for isolation of labeled oleic acid from mixtures with glycerides. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom J. Percutaneous needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in physiological and clinical research. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;35(7):609–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Otway S., Robinson D. S. Effect of fasting on the clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) activity of fresh and defatted preparations of rat heart muscle. J Lipid Res. 1970 Mar;11(2):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Samols D. R., Rubenstein A. H. Effects of insulin on lipoprotein lipase activity in the rat heart and adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1271–1275. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. F., Fitzpatrick G. F., Cohen K. H., Moore F. D. Glycerol: major contributor to the short term protein sparing effect of fat emulsions in normal man. Ann Surg. 1975 Oct;182(4):386–394. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197510000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. F., Moore F. D. An intravenous fat emulsion as a nitrogen sparer: comparison with lucose. J Surg Res. 1973 Jun;14(6):501–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(73)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo G., David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns T. W., Terry B. E., Langley P. E., Robison G. A. Insulin inhibition of lipolysis of human adipocytes: the role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Diabetes. 1979 Nov;28(11):957–961. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.11.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Ayala E., Rill W. L., Little J. S. Effects of pneumococcal infection on rat liver microsomal enzymes and lipogenesis by isolated hepatocytes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Aug;30(8):1359–1363. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.8.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Riley S. E., Williams E. R., Robinson D. S. Effect of nutritional status on rat adipose tissue, muscle and post-heparin plasma clearing factor lipase activities: their relationship to triglyceride fatty acid uptake by fat-cells and to plasma insulin concentrations. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Mar;50(3):213–221. doi: 10.1042/cs0500213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiser R. H., Denniston J. C., Beisel W. R. Infection with Diplococcus pneumoniae and Salmonella typhimurium in monkeys: changes in plasma lipids and lipoproteins. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):54–60. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H., Yoshimura N., Fischer J. E. Does intravenous fat spare nitrogen in the injured rat? Am J Surg. 1980 Sep;140(3):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Kaye D., O'Leary W. M. Serum lipids in infection. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 13;281(20):1081–1086. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911132812001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Hamosh P. Lipoprotein lipase in rat lung. The effect of fasting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejee hoy K. N., Anderson G. H., Nakhooda A. F., Greenberg G. R., Sanderson I., Marliss E. B. Metabolic studies in total parenteral nutrition with lipid in man. Comparison with glucose. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):125–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI108252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann R. L., Matson C. F., Beisel W. R. Hypertriglyceridemia produced by endotoxin: role of impaired triglyceride disposal mechanisms. J Infect Dis. 1976 May;133(5):548–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.5.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann R. L., Matson C. F., Rowberg A. H., Beisel W. R. Defective lipid disposal mechanisms during bacterial infection in rhesus monkeys. Metabolism. 1976 Jun;25(6):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlar T. J., Borensztajn J. Oscillatory changes in muscle lipoprotein lipase activity of fed and starved rats. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):E316–E319. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.4.E316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees R. S., Fiser R. H., Jr, Beisel W. R., Bartelloni P. J. Effects of an experimental viral infection on plasma lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Metabolism. 1972 Sep;21(9):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder C., Chernick S. S., Fleck T. R., Scow R. O. Lipoprotein lipase and uptake of chylomicron triglyceride by skeletal muscle of rats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):860–864. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lithell H., Boberg J. Determination of lipoprotein-lipase activity in human skeletal muscle tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 27;528(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. M., 3rd, Wilmore D. W., Mason A. D., Jr, Pruitt B. A., Jr Effect of carbohydrate and fat intake on nitrogen excretion during total intravenous feeding. Ann Surg. 1977 Apr;185(4):417–422. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197704000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P. Human lipoprotein lipase activity: comparison of assay methods. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Aug 20;54(3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis C., Spanier A. H., Calder M., Shizgal H. M. Total parenteral nutrition with lipid. Am J Surg. 1978 Feb;135(2):164–171. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykälistö O. J., Smith P. H., Brunzell J. D. Determinants of human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. Effect of diabetes and obesity on basal- and diet-induced activity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1108–1117. doi: 10.1172/JCI108185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin A. P., Askanazi J., Greenwood M. R., Carpentier Y. A., Gump F. E., Kinney J. M. Lipoprotein lipase activity in surgical patients: influence of trauma and infection. Surgery. 1981 Aug;90(2):401–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salans L. B., Dougherty J. W. The effect of insulin upon glucose metabolism by adipose cells of different size. Influence of cell lipid and protein content, age, and nutritional state. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1399–1410. doi: 10.1172/JCI106623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz M. C., Garfinkel A. S., Huebotter R. J., Stewart J. E. A rapid assay for lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jan;11(1):68–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Khoo J. C. Hormone-sensitive lipase of adipose tissue. Fed Proc. 1977 Jun;36(7):1986–1990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gasquet P., Pequignot E. Changes in adipose tissue and heart lipoprotein lipase activities and in serum glucose, insulin and corticosterone concentrations in rats adapted to a daily meal. Horm Metab Res. 1973 Nov;5(6):440–443. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


