Abstract
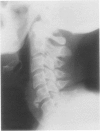
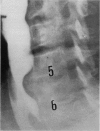
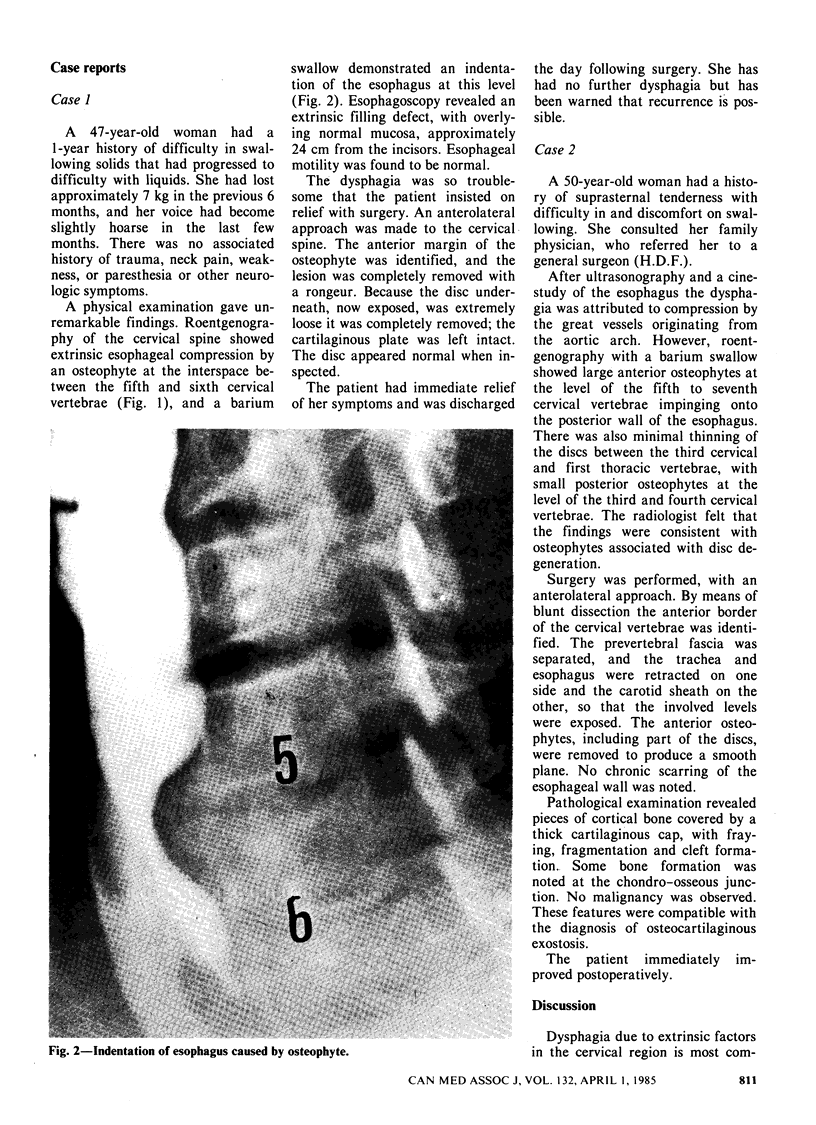
Two cases of dysphagia due to osteophytes at the level of the fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae are reported. The patients were two women aged 47 and 50 years. The diagnosis was confirmed by means of roentgenography, barium studies and, in one case, esophagoscopy. Both patients were successfully treated surgically. The importance of properly investigating cervical dysphagia is stressed. Doctors in many different fields of practice should be aware of this rare cause of dysphagia.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARNOLD H. Zur senilen ankylosierenden Hyperostose der Wirbelsäule (Forestier et Rotès). Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1957;88(3):337–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAHRS O. H., SCHMIDT H. W. Dysphagia caused by hypertrophic changes in the cervical spine: report of two cases. Ann Surg. 1959 Feb;149(2):297–299. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195902000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M. J., Stauffer R. N., Payne W. S. Ankylosing vertebral hyperostosis causing dysphagia. Arch Surg. 1974 Oct;109(4):567–570. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01360040081021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coventry M. B. Calcification in a cervical disc with anterior protrusion and dysphagia. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970 Oct;52(7):1463–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forestier J., Lagier R. Ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971 Jan;74:65–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girgis I. H., Guirguis N. N., Mourice M. Laryngeal and pharyngeal disorders in vertebral ankylosing hyperostosis. J Laryngol Otol. 1982 Jul;96(7):659–664. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100092951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECK C. V. Hoarseness and painful deglutition due to massive cervical exostoses. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956 Jun;102(6):657–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILDING D. A., TACHDJIAN M. O. Dysphagia and hypertrophic spurring of the cervical spine. N Engl J Med. 1960 Jul 7;263:11–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196007072630103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanamura H., Higuchi Y., Nakagawa M., Iwata H., Nogami H., Urist M. R. Solubilized bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) from mouse osteosarcoma and rat demineralized bone matrix. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980 May;(148):281–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano H., Suzuki H., Sakakibara T., Higuchi Y., Inoue K., Suzuki Y. Dysphagia due to hypertrophic cervical osteophytes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Jul;(167):168–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. R., Tepperman P. S., Jimenez J., Newman A. Cervical spine disease and dysphagia. Four new cases and a review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981 Jul;76(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann N. S., Brewer H., Sheth B. Upper esophageal dysphagia due to marked cervical lordosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1984 Feb;6(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks L. W., Renshaw T. S. Vertebral osteophytosis and dysphagia. Two case reports of the syndrome recently termed ankylosing hyperostosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973 Jan;55(1):197–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnesar P. Dysphagia due to cervical exostosis. Laryngoscope. 1970 Mar;80(3):469–471. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197003000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. C., TANNER N. C. The complications of gastroscopy and oesophagoscopy. Br J Surg. 1956 Jan;43(180):396–403. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004318010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders W. H. Cervical osteophytes and dysphagia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1970 Dec;79(6):1091–1097. doi: 10.1177/000348947007900611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seawright A. A., English P. B., Gartner R. J. Hypervitaminosis A and hyperostosis of the cat. Nature. 1965 Jun 12;206(989):1171–1172. doi: 10.1038/2061171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umerah B. C., Mukherjee B. K., Ibekwe O. Cervical spondylosis and dysphagia. J Laryngol Otol. 1981 Nov;95(11):1179–1183. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100092008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urist M. R., Mikulski A., Lietze A. Solubilized and insolubilized bone morphogenetic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1828–1832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HOVE R. Séquelle exceptionnelle de fracture de la colonne cervicale; dysphagie par compression oesophagienne. Acta Orthop Belg. 1953;19(8):397–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. A. Upper-esophageal perforation with a flexible endoscope secondary to cervical osteophytes. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Jan;25(1):66–68. doi: 10.1007/BF01312735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]