Abstract
This paper describes the Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Program developed and operated by the Committee on Drugs and Pharmaco-therapy of the Ontario Medical Association. Analyses were done to demonstrate some of the trends derived from the reports. Some of the clinical observations based on the reports, which are published quarterly and circulated to physicians and to pharmacy, nursing and hospital organizations, are also reviewed.
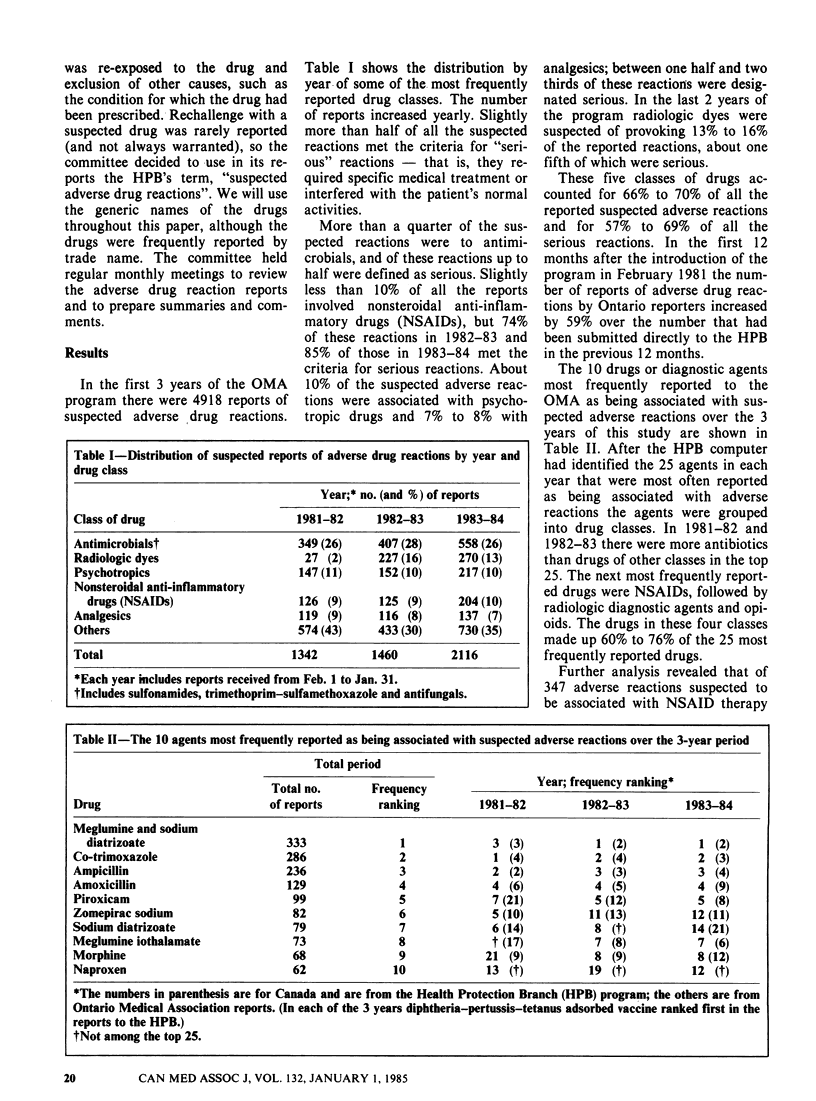
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong M. R. When is a clinical event an adverse drug reaction? Can Med Assoc J. 1978 Dec 9;119(11):1315-6, 1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowdey C. W. A guide to the pharmacology of placebos. Can Med Assoc J. 1983 Apr 15;128(8):921–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman W. H. Postmarketing surveillance of adverse drug reactions in general practice. I: search for new methods. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Apr 4;282(6270):1131–1132. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6270.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irey N. S. Adverse drug reactions and death. A review of 827 cases. JAMA. 1976 Aug 9;236(6):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F. E., Lasagna L. Adverse drug reactions. A critical review. JAMA. 1975 Dec 22;234(12):1236–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J. Editorial: Fatal reactions to drug therapy. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 8;291(6):302–303. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408082910610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasagna L. Discovering adverse drug reactions. JAMA. 1983 Apr 22;249(16):2224–2225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. L. Adverse effects of NSAIDs on renal function. Can Med Assoc J. 1984 Aug 1;131(3):189–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Med M. Prenatal development of lumbar intervertebral articulation. Folia Morphol (Praha) 1982;30(3):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo C. A., Busto U., Sellers E. M., Sandor P., Ruiz I., Roberts E. A., Janecek E., Domecq C., Greenblatt D. J. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Aug;30(2):239–245. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi A. C., Knapp D. E., Anello C., O'Neill R. T., Graham C. F., Mendelis P. S., Stanley G. R. Discovery of adverse drug reactions. A comparison of selected phase IV studies with spontaneous reporting methods. JAMA. 1983 Apr 22;249(16):2226–2228. doi: 10.1001/jama.249.16.2226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers E. M. Adverse drug reactions: uncommon or unrecognized? Can Med Assoc J. 1979 May 19;120(10):1200–1201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slone D., Shapiro S., Miettinen O. S., Finkle W. D., Stolley P. D. Drug evaluation after marketing. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Feb;90(2):257–261. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venning G. R. Validity of anecdotal reports of suspected adverse drug reactions: the problem of false alarms. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 23;284(6311):249–252. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6311.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


