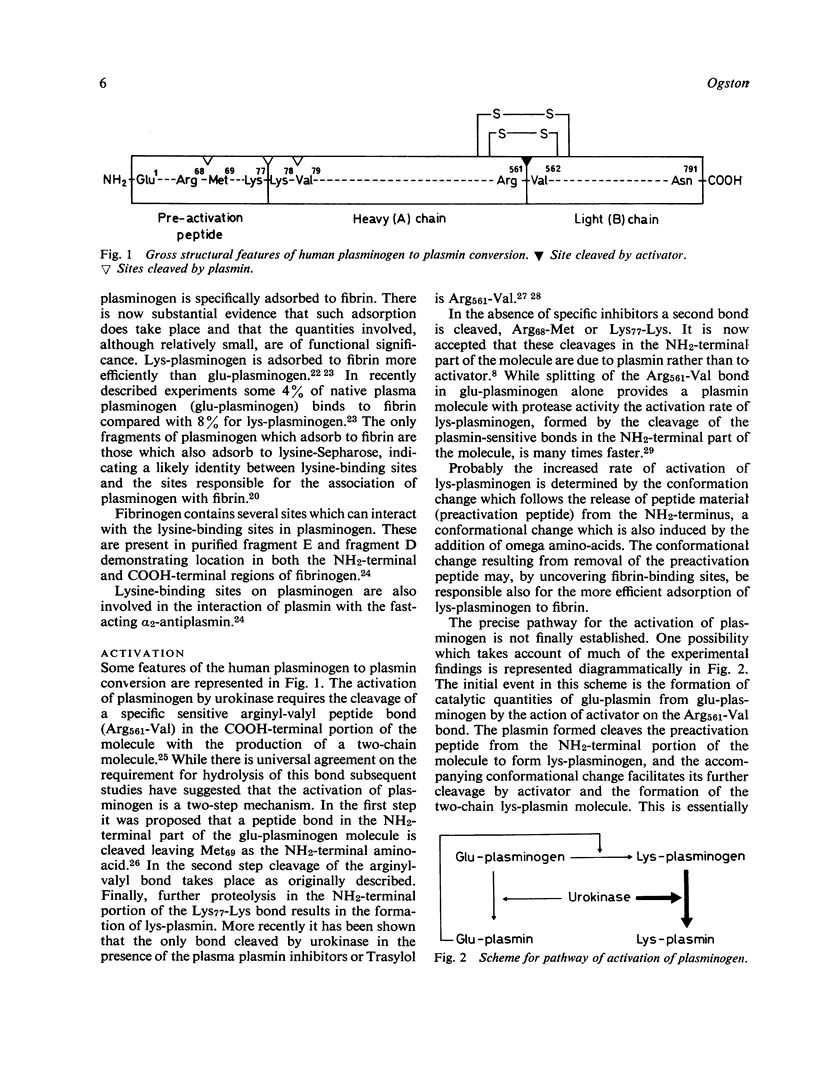
Full text
PDF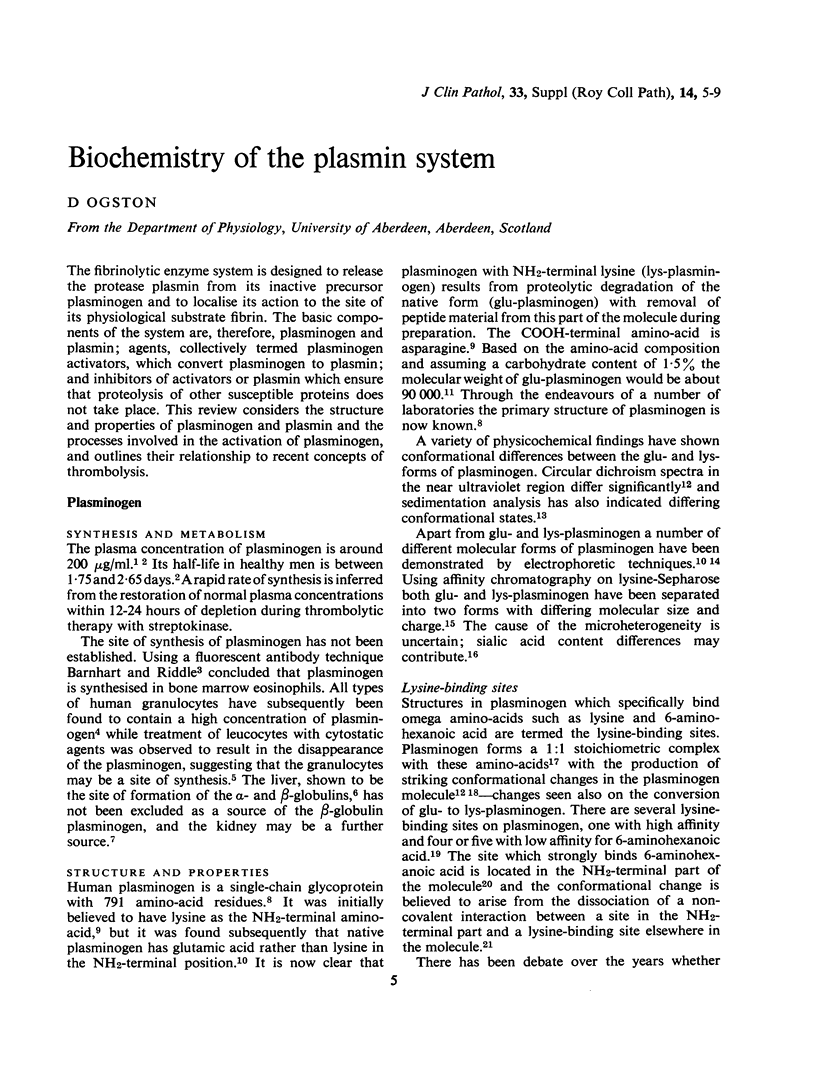



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abiko Y., Iwamoto M., Tomikawa M. Plasminogen-plasmin system. V. A stoichiometric equilibrium complex of plasminogen and a synthetic inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkjaersig N. The purification and properties of human plasminogen. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):171–182. doi: 10.1042/bj0930171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNHART M. I., RIDDLE J. M. Cellular localization of profibrinolysin (plasminogen). Blood. 1963 Mar;21:306–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camiolo S. M., Thorsen S., Astrup T. Fibrinogenolysis and fibrinolysis with tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase, streptokinase-activated human globulin, and plasmin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):277–280. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claeys H., Vermylen J. Physico-chemical and proenzyme properties of NH2-terminal glutamic acid and NH2-terminal lysine human plasminogen. Influence of 6-aminohexanoic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 11;342(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Tytgat G., Claeys H., Verstraete M., Wallén P. Metabolism of plasminogen in healthy subjects: effect of tranexamic acid. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1310–1318. doi: 10.1172/JCI106927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., de Maeyer L. Molecular biology of human plasminogen. I. Physiochemical properties and microheterogeneity. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Nov 15;34(2):396–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H. Effect of plasmin in vitro on clotting factors in plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Oct;56:644–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith R. F., Kline D. L. Kidney: primary source of plasminogen after acute depletion in the cat. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):141–142. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER L. L., BALE W. F. Synthesis of all plasma protein fractions except gamma globulins by the liver; the use of zone electrophoresis and lysine-epsilon-C14 to define the plasma proteins synthesized by the isolated perfused liver. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):125–132. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A., PERISUTTI G., DAVIS N. C. The destruction of glucagon, adrenocorticotropin and somatotropin by human blood plasma. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):14–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI103783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., DePasquale J. L., Wissler F. C. Quantitative determination of the binding of epsilon-aminocaproic acid to native plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):727–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLEMER L., RATNOFF O. D., BLUM L., LEPOW I. H. The inactivation of complement and its components by plasmin. J Exp Med. 1953 Apr;97(4):573–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquini R., Hershgold E. J. Effects of plasmin on human factor VIII (AHF). Blood. 1973 Jan;41(1):105–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokopowicz J., Rejniak L., Niewiarowski S. Influence of cytostatic agents on fibrinolytic and proteolytic enzymes and on phagocytosis of guinea pig leucocytes. Experientia. 1967 Oct 15;23(10):813–814. doi: 10.1007/BF02146857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokopowicz J., Stormorken H. Fibrinolytic activity of leucocytes in smears of bone marrow and peripheral blood. Scand J Haematol. 1968;5(2):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1968.tb01727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner S. F., Goldfine I. D., Hart A., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Radioimmunoassay of human plasminogen and plasmin. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Aug;74(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Summaria L., Hsieh B., Shah R. J. The peptide chains of human plasmin. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen to plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2333–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Summaria L., Hsieh B., Shah R. J. The peptide chains of human plasmin. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen to plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2333–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rákóczi I., Wiman B., Collen D. On the biological significance of the specific interaction between fibrin, plasminogen and antiplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 3;540(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I. Studies on the conformational changes of plasminogen induced during activation to plasmin and by 6-aminohexanoic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summaria L., Arzadon L., Bernabe P., Robbins K. C. Studies on the isolation of the multiple molecular forms of human plasminogen and plasmin by isoelectric focusing methods. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4691–4702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summaria L., Boreisha I. G., Arzadon L., Robbins K. C. Activation of human Glu-plasminogen to Glu-plasmin by urokinase in presence of plasmin inhibitors. Streptomyces leupeptin and human plasma alpha1-antitrypsin and antithrombin III (plus heparin). J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3945–3951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summaria L., Hsieh B., Groskopf W. R., Robbins K. C. The isolation and characterization of the S-carboxymethyl beta (light) chain derivative of human plasmin. The localization of the active site on the beta (light) chain. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):5046–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summaria L., Spitz F., Arzadon L., Boreisha I. G., Robbins K. C. Isolation and characterization of the affinity chromatography forms of human Glu- and Lys-plasminogens and plasmins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3693–3699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., SHERRY S., WACHMAN J. The action of plasmin on synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S. Differences in the binding to fibrin of native plasminogen and plasminogen modified by proteolytic degradation. Influence of omega-aminocarboxylic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violand B. N., Castellino F. J. Mechanism of the urokinase-catalyzed activation of human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3906–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violand B. N., Sodetz J. M., Castellino F. J. The effect of epsilon-amino caproic acid on the gross conformation of plasminogen and plasmin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Iwanaga S. Differences between plasmic and tryptic digests of human S-sulfo-fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 19;154(2):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Wiman B. Characterization of human plasminogen. I. On the relationship between different molecular forms of plasminogen demonstrated in plasma and found in purified preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 20;221(1):20–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Doolittle R. F. Differential specificities of the thrombin, plasmin and trypsin with regard to synthetic and natural substrates and inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):577–590. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. Molecular mechanism of physiological fibrinolysis. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):549–550. doi: 10.1038/272549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. On the specific interaction between the lysine-binding sites in plasmin and complementary sites in alpha2-antiplasmin and in fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 25;579(1):142–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B. Primary structure of the B-chain of human plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Wallén P. Activation of human plasminogen by an insoluble derivative of urokinase. Structural changes of plasminogen in the course of activation to plasmin and demonstration of a possible intermediate compound. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Wallén P. Structural relationship between "glutamic acid" and "lysine" forms of human plasminogen and their interaction with the NH2-terminal activation peptide as studied by affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jan 15;50(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb09887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Wallén P. The specific interaction between plasminogen and fibrin. A physiological role of the lysine binding site in plasminogen. Thromb Res. 1977 Feb;10(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


