Abstract
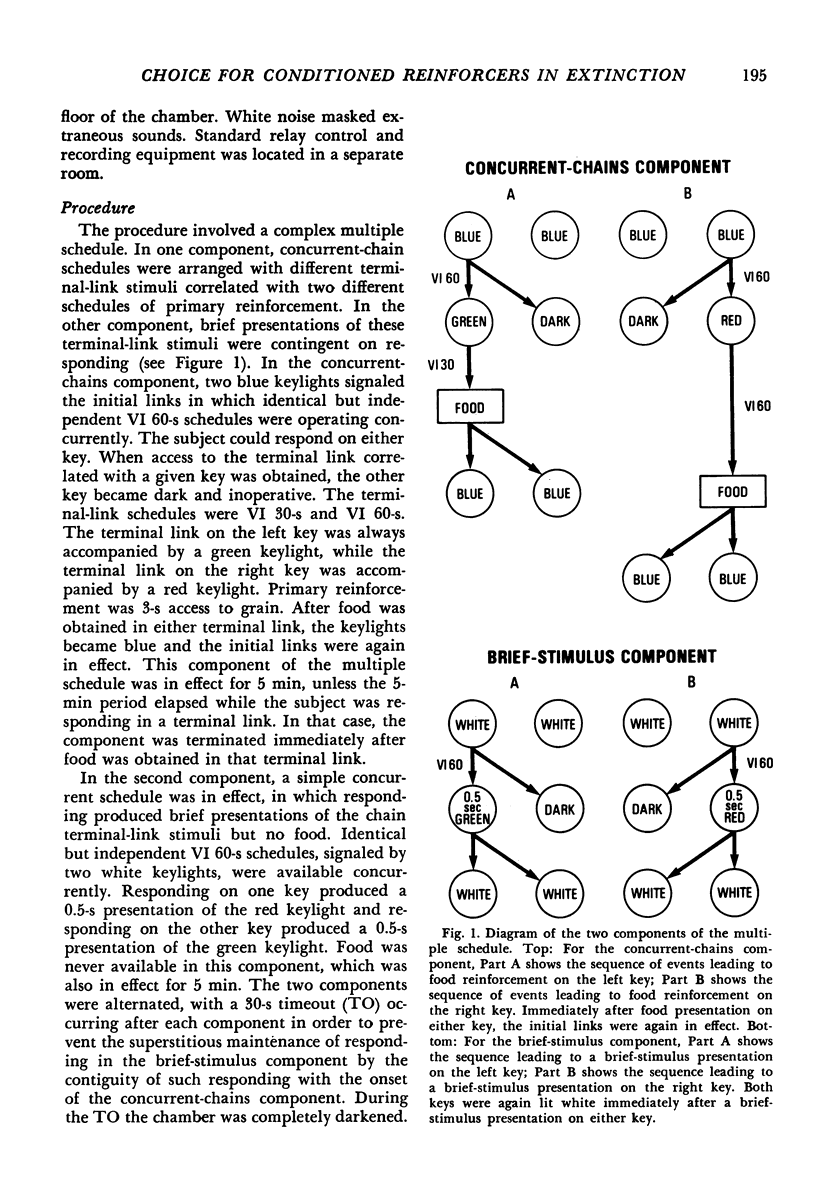
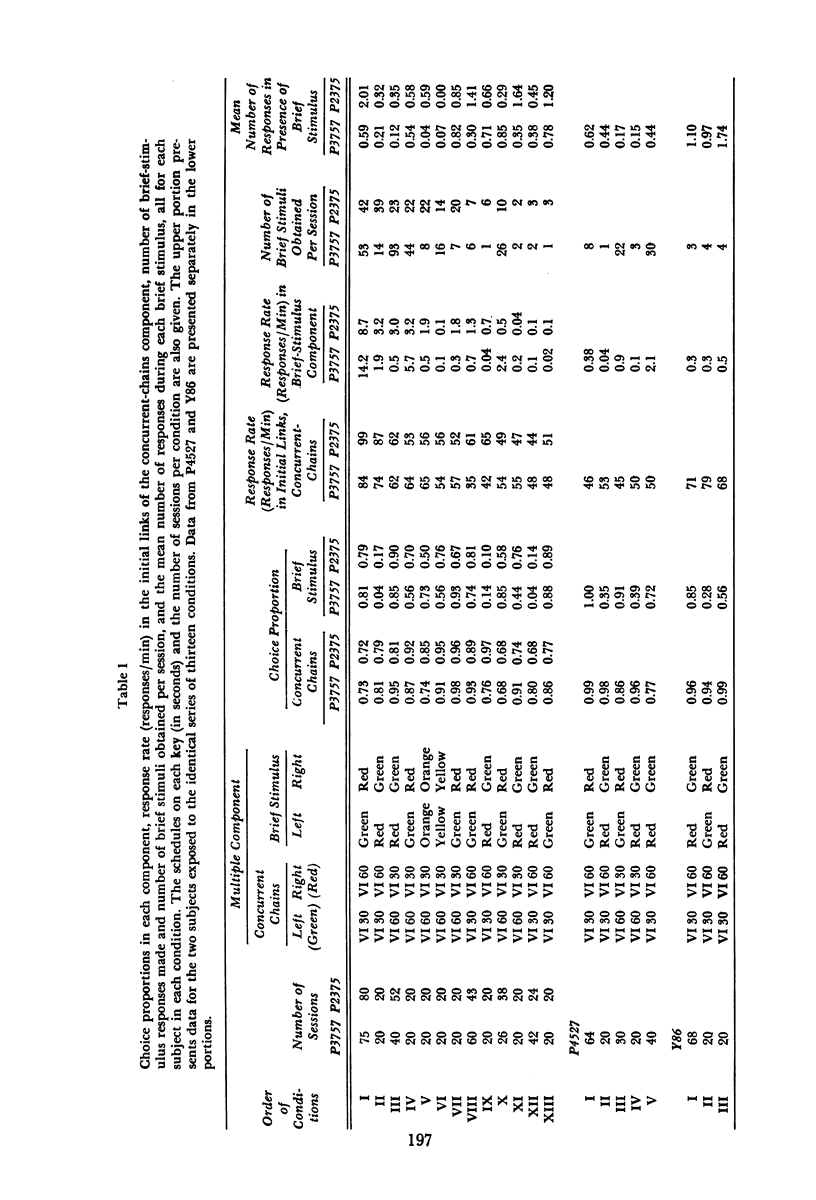
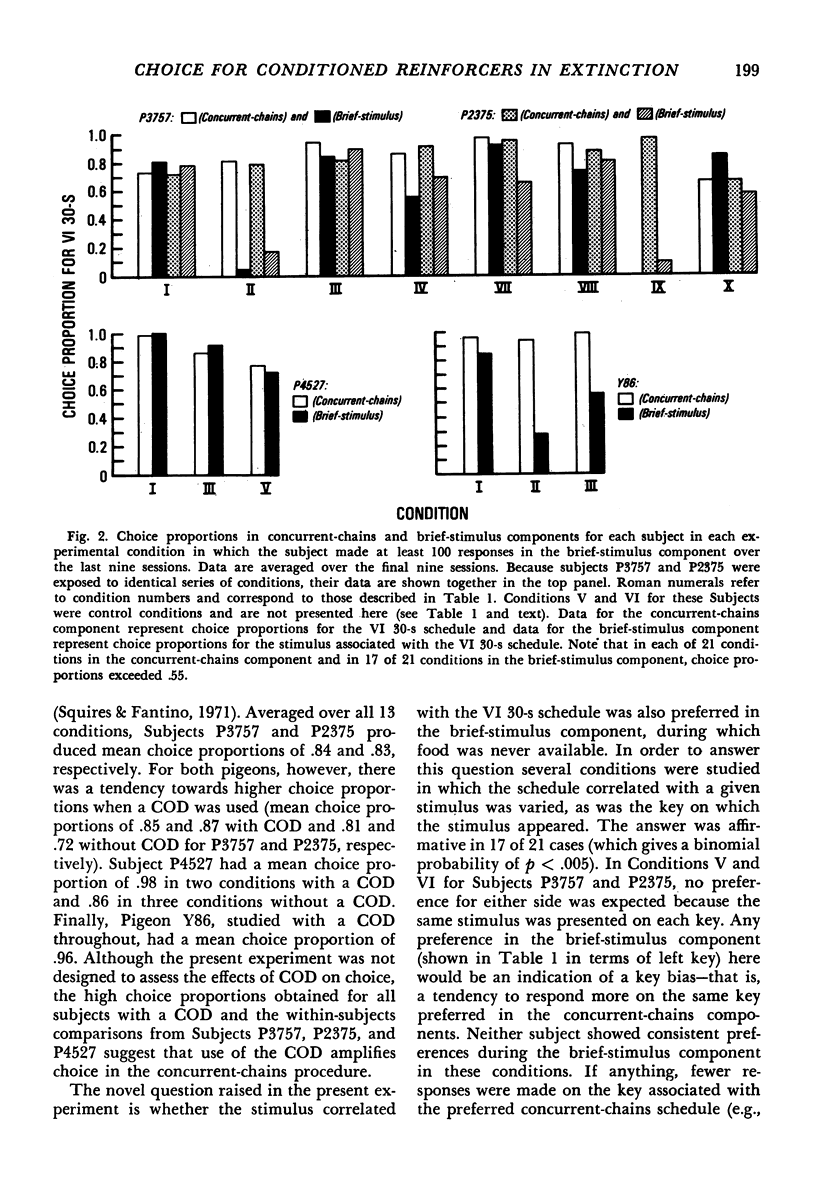
Pigeons responded in a multiple schedule in which concurrent schedules of brief-stimulus presentation alternated with a component in which food was available (concurrent-chains component). In the initial links of the concurrent-chains component subjects chose either of two stimuli each correlated with the terminal link of one chain. The terminal links involved either variable-interval 30-second or variable-interval 60-second schedules. In the brief-stimulus component subjects chose between 0.5-second presentations of the terminal-link stimuli from the concurrent-chains component. Responding was generally maintained in the brief-stimulus component in two subjects for more than 300 sessions, suggesting that brief stimuli were conditioned reinforcers. During the brief-stimulus component, in 17 of 21 cases for which a minimal number of responses occurred, choice proportions above 0.55 were obtained for the brief-stimulus presentations correlated with the higher rate of primary reinforcement in the concurrent-chains component. These results support the suggestion that choice in conventional concurrent-chains procedures is partially controlled by production of the terminal-link stimuli.
Keywords: conditioned reinforcement, choice, brief-stimulus presentations, multiple schedules, concurrent-chains schedules, delay-reduction hypothesis, variable-interval schedules, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan B., Fantino E. The psychological distance to reward. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):23–34. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Davison M. Choice: Some quantitative relations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):1–13. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Fantino E. Effects on choice of reinforcement delay and conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jan;29(1):77–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J. TECHNIQUE FOR SUSTAINING BEHAVIOR WITH CONDITIONED REINFORCEMENT. Science. 1963 Nov 8;142(3593):682–684. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3593.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


