Abstract
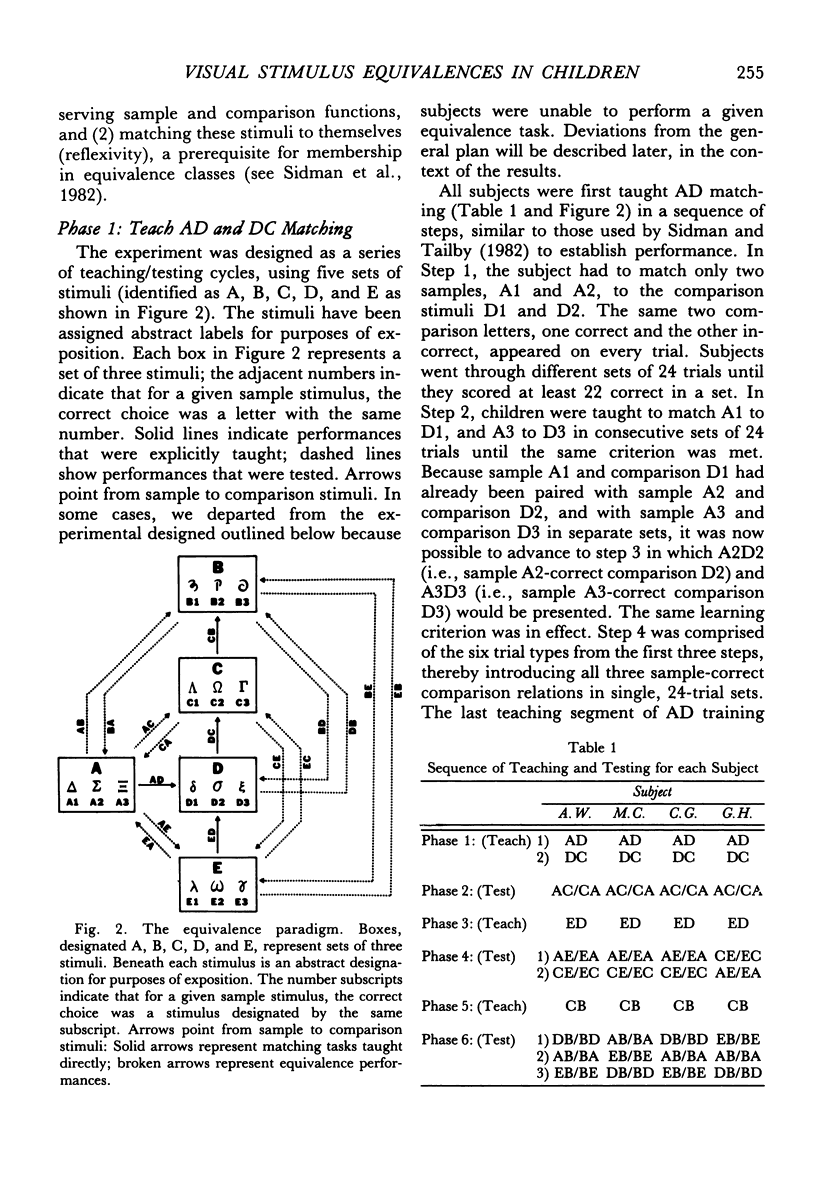
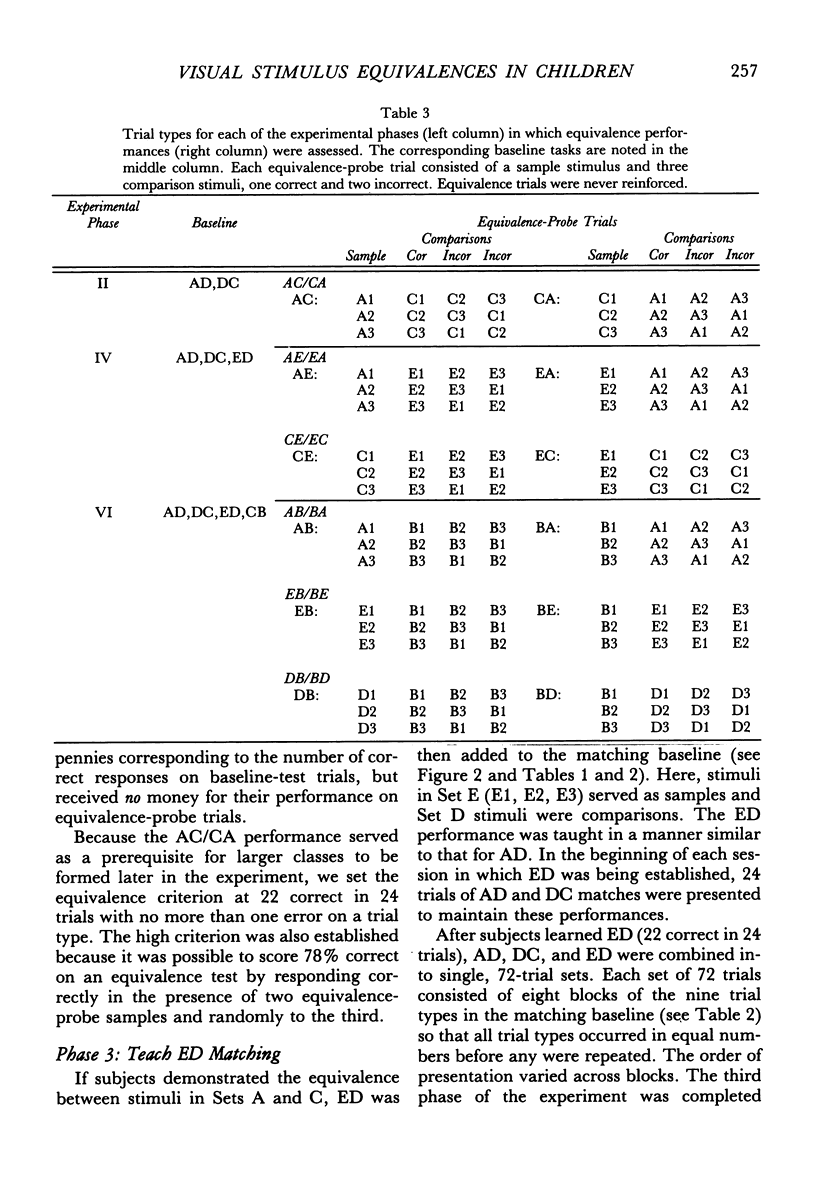
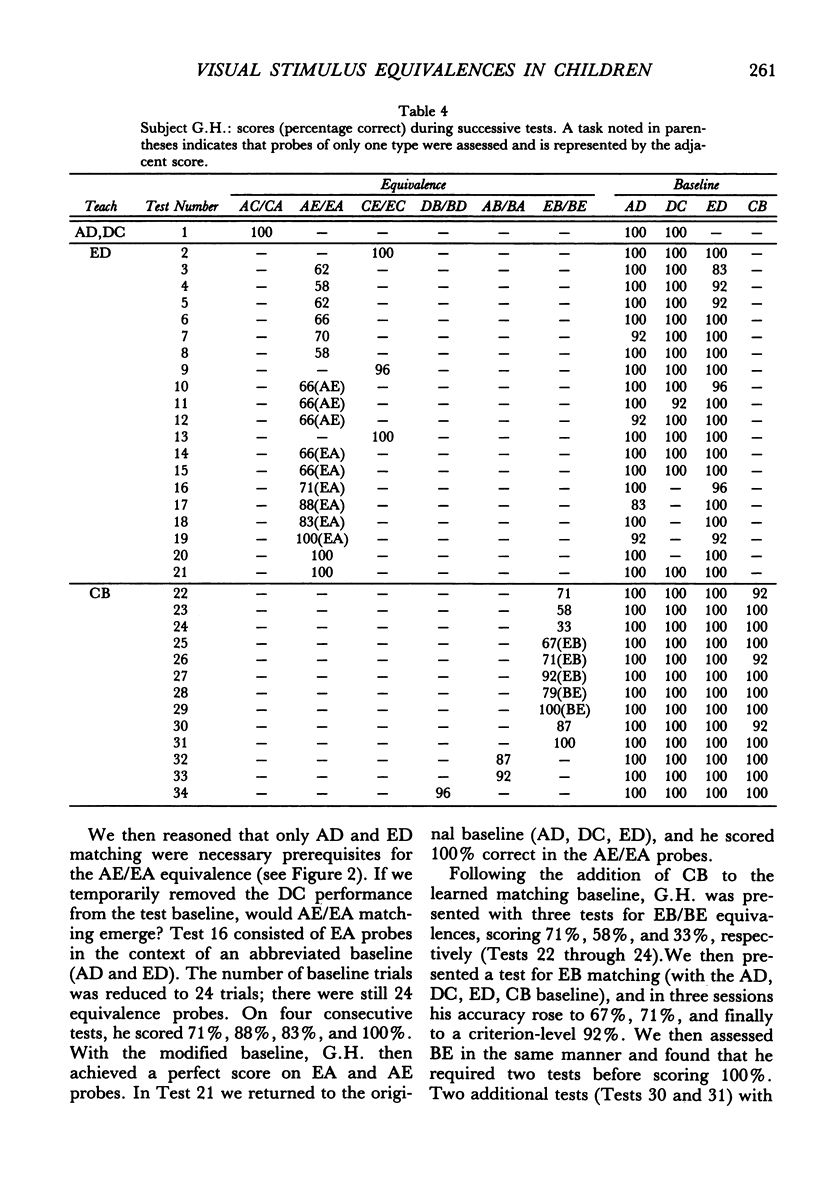
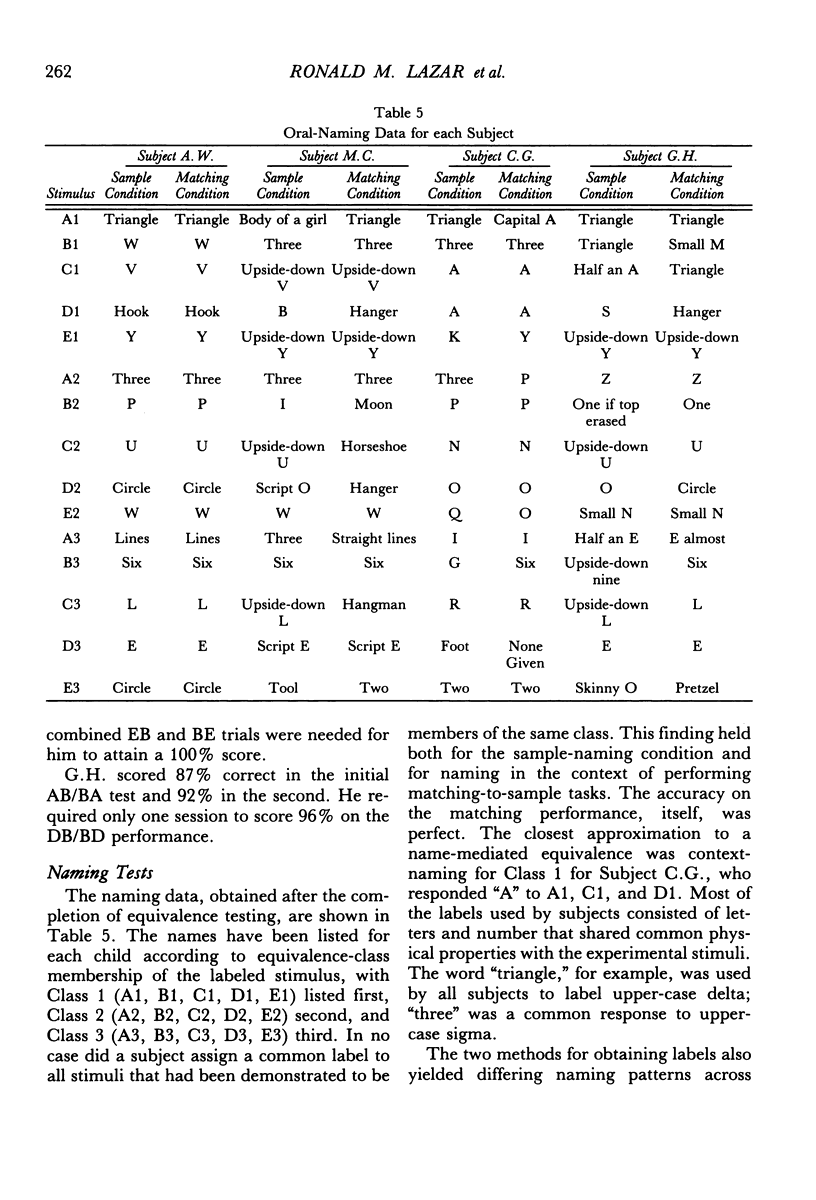
Four normal children were presented a series of matching-to-sample tasks, using five sets of visual stimuli designated A, B, C, D, and E. Stimulus equivalences were established by matching stimuli from one set to those from another set. Each set consisted of three stimuli, so matching set A to set D meant that each stimulus in set A served as a sample with all three stimuli in set D as comparisons. Subjects were first taught AD and DC matching and were then able to perform AC/CA matching without additional training. After ED was taught directly, CE/EC and AE/EA performances emerged. Following CB training, three new equivalences were demonstrated: AB/BA, EB/BE, and DB/BD. Oral naming of each stimulus showed that subjects had not assigned a common label to stimuli in the same class, indicating that naming is not necessary for the formation of stimulus equivalences. The absence of response mediation suggests that matching to sample can form direct stimulus-stimulus associations. The data also provide support for the notion that generative performances are outcomes of existing stimulus-control relationships.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter D. E., Eckerman D. A. Symbolic matching by pigeons: rate of learning complex discriminations predicted from simple discriminations. Science. 1975 Feb 21;187(4177):662–664. doi: 10.1126/science.1114318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCKETT C. F. The origin of speech. Sci Am. 1960 Sep;203:89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar R. Extending sequence-class membership with matching to sample. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Mar;27(2):381–392. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.31-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- Santi A. The role of physical identity of the sample and correct comparison stimulus in matching-to-sample paradigms. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 May;29(3):511–516. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M., Cresson O., Jr Reading and crossmodal transfer of stimulus equivalences in severe retardation. Am J Ment Defic. 1973 Mar;77(5):515–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M., Cresson O., Jr, Willson-Morris M. Acquisition of matching to sample via mediated transfer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Sep;22(2):261–273. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M., Rauzin R., Lazar R., Cunningham S., Tailby W., Carrigan P. A search for symmetry in the conditional discriminations of rhesus monkeys, baboons, and children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Jan;37(1):23–44. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M. Reading and auditory-visual equivalences. J Speech Hear Res. 1971 Mar;14(1):5–13. doi: 10.1044/jshr.1401.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman M., Tailby W. Conditional discrimination vs. matching to sample: an expansion of the testing paradigm. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Jan;37(1):5–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradlin J. E., Cotter V. W., Baxley N. Establishing a conditional discrimination without direct training: a study of transfer with retarded adolescents. Am J Ment Defic. 1973 Mar;77(5):556–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradlin J. E., Dixon M. H. Establishing conditional discriminations without direct training: stimulus classes and labels. Am J Ment Defic. 1976 Mar;80(5):555–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromer R., Osborne J. G. Control of adolescents' arbitrary matching-to-sample by positive and negative stimulus relations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 May;37(3):329–348. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. K., Taylor M. M. Another look at phonetic symbolism. Psychol Bull. 1965 Dec;64(6):413–427. doi: 10.1037/h0022737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetherby B., Karlan G. R., Spradlin J. E. The development of derived stimulus relations through training in arbitrary-matching sequences. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):69–78. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


