Abstract
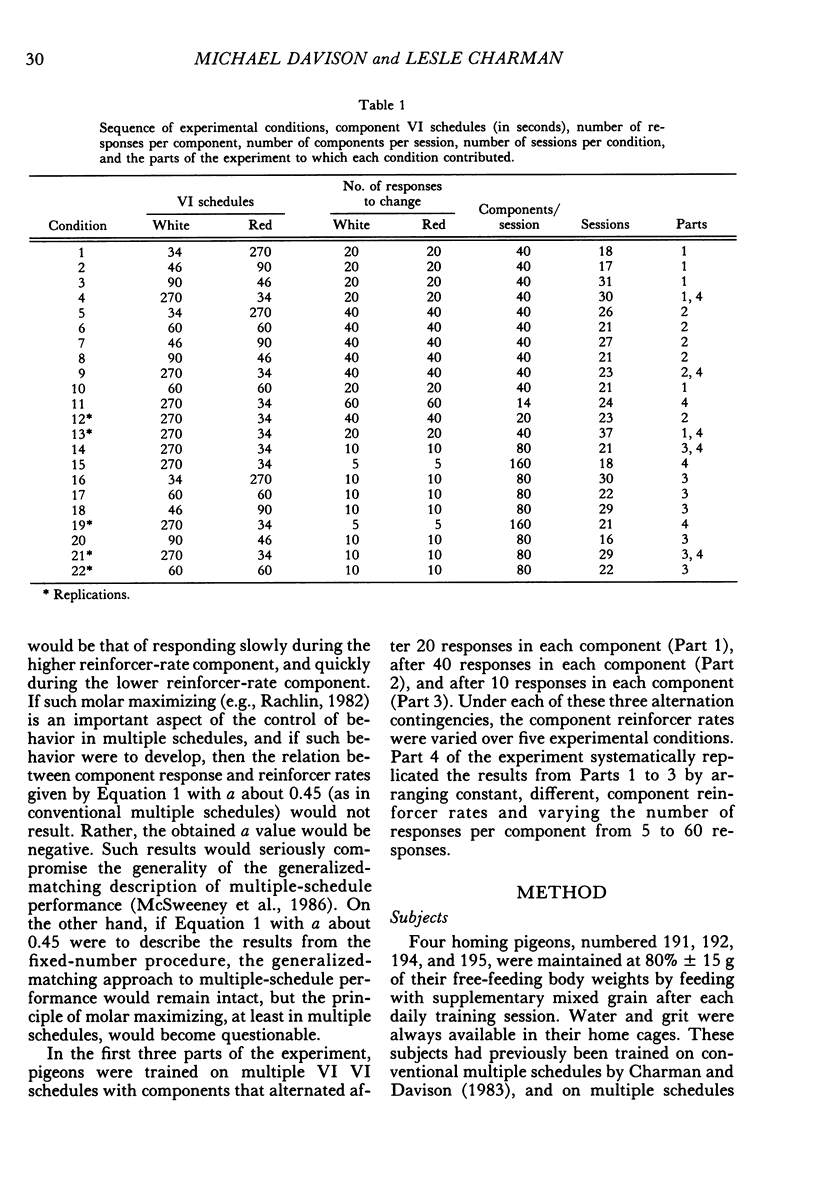
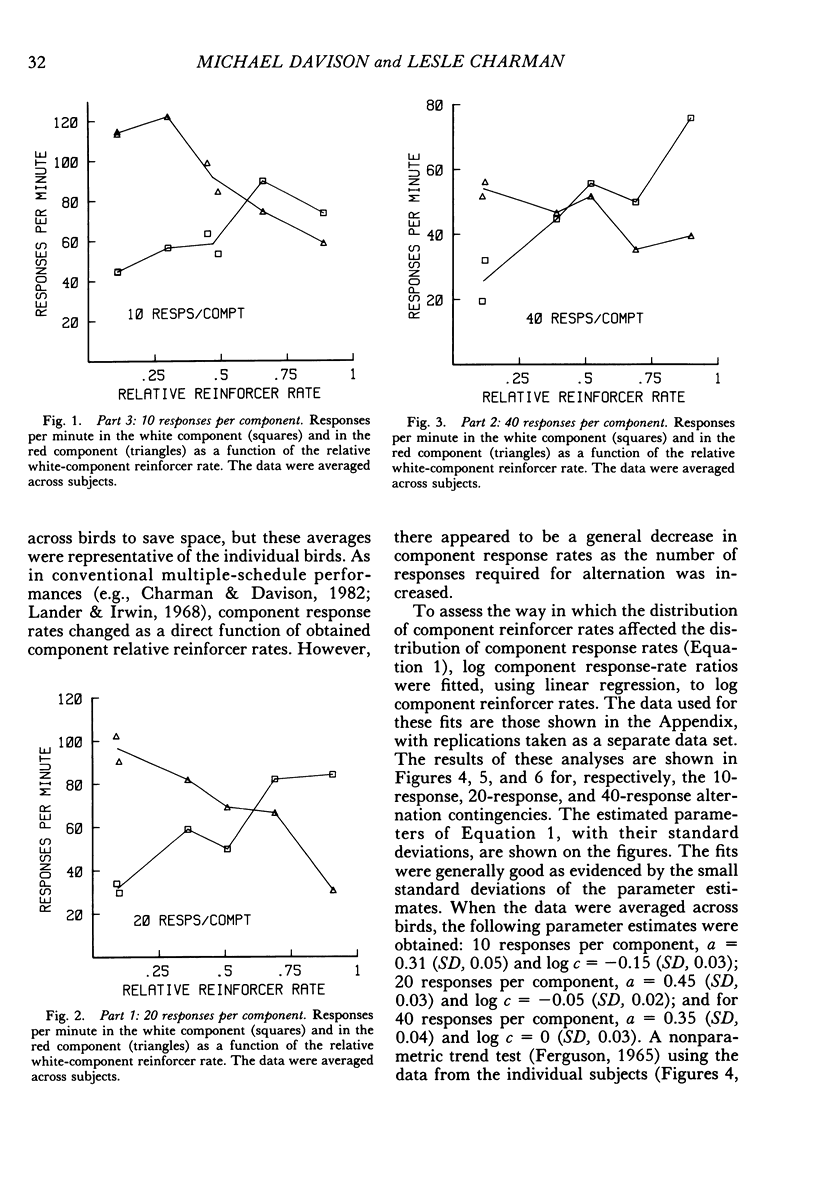
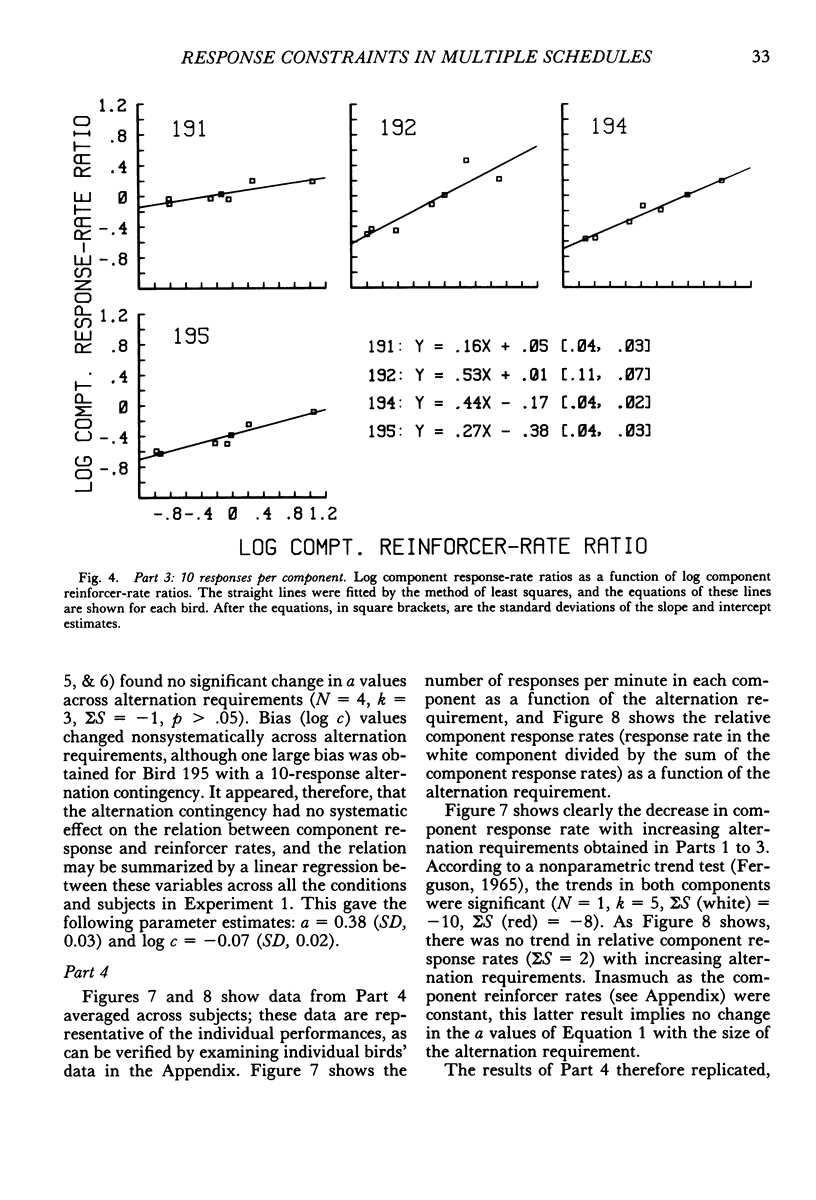
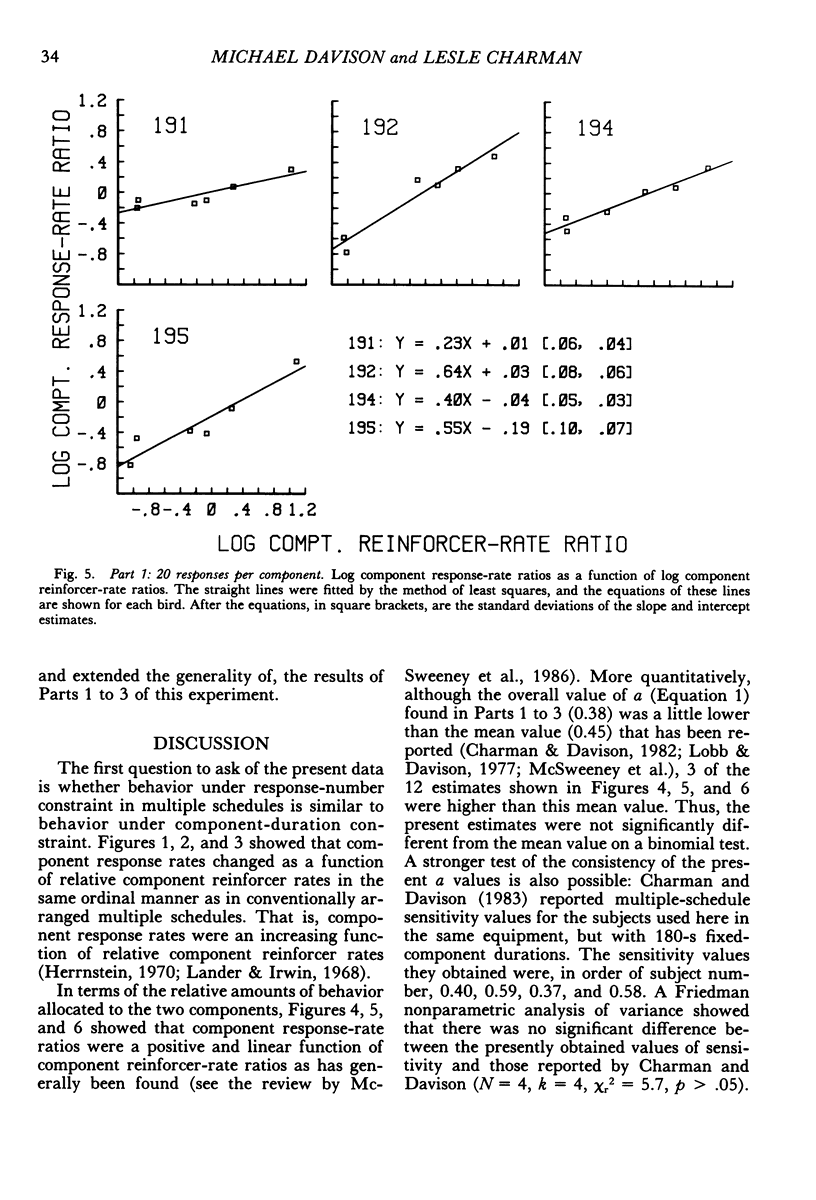
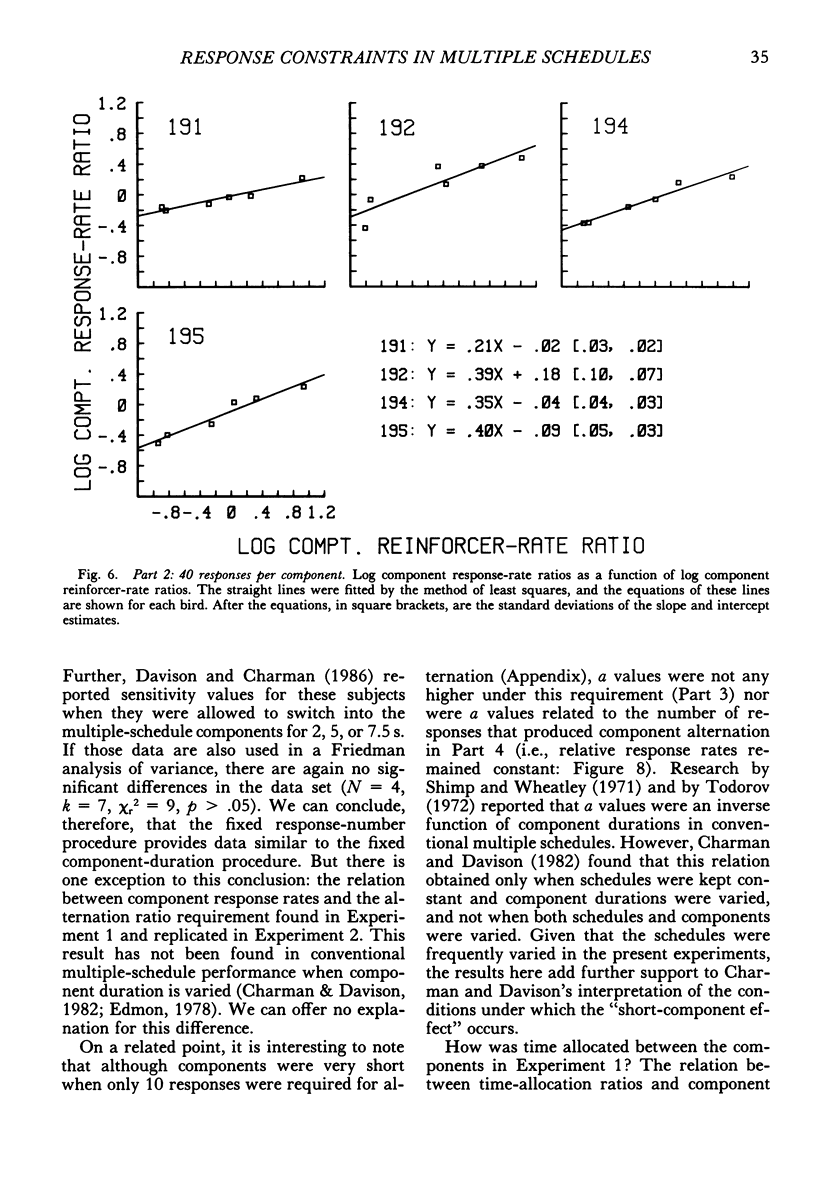
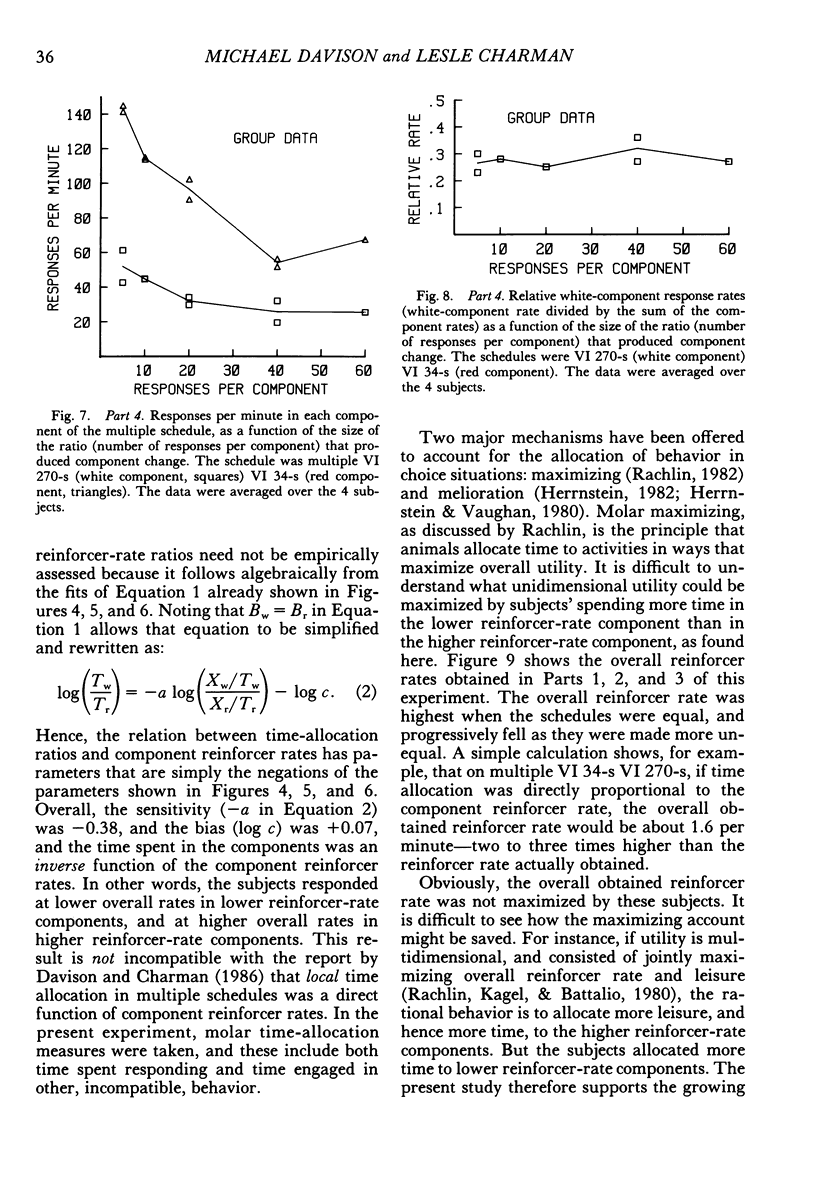
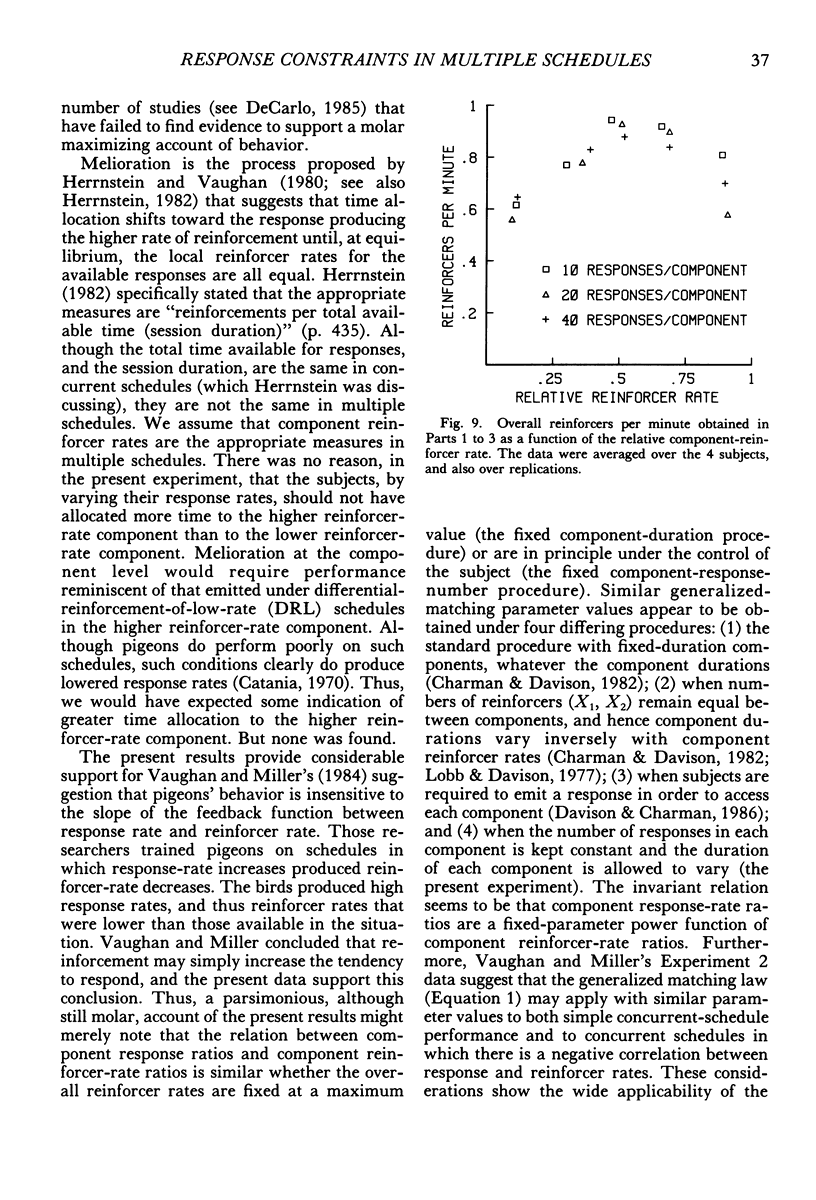
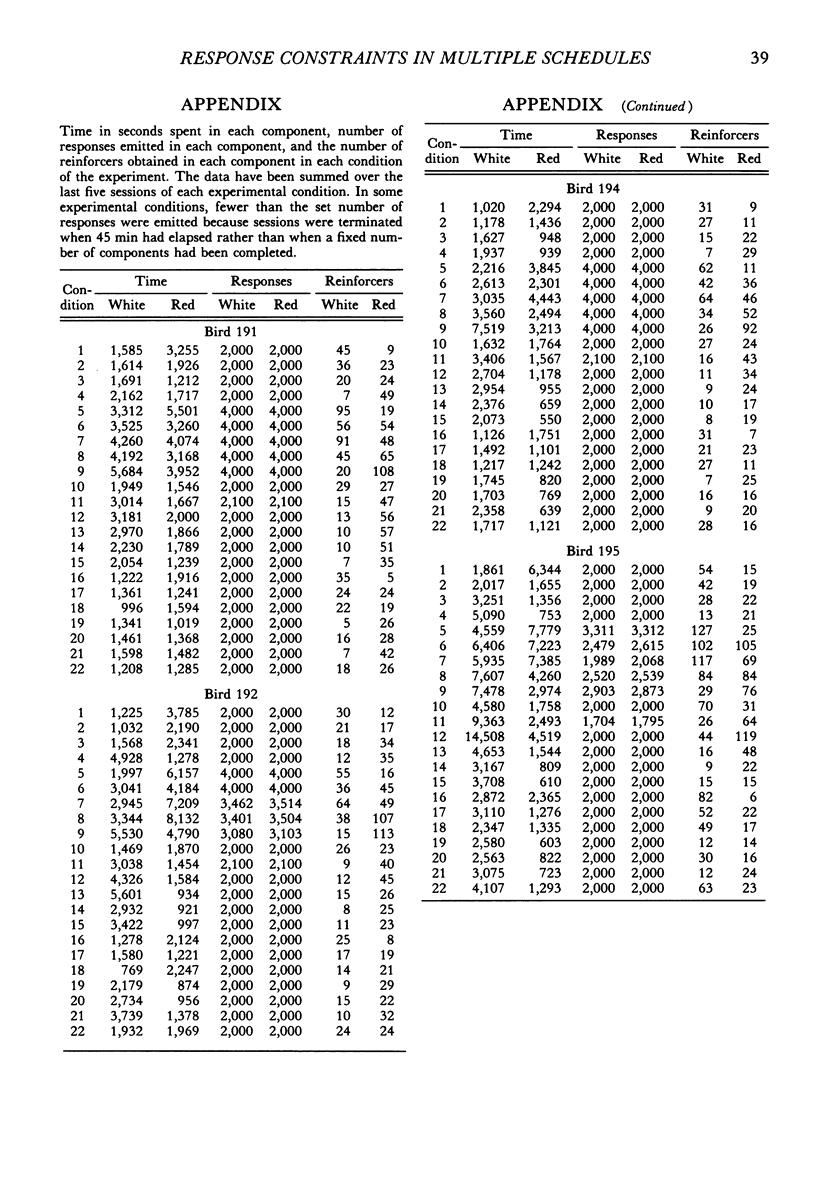
Four pigeons were trained on multiple variable-interval schedules in which components alternated after a fixed number of responses had been emitted. In Part 1, each component change occurred after 20 responses; in Part 2, the number was 40; and in Part 3, the number of responses before change was 10. Component reinforcer rates were varied over five experimental conditions in each of Parts 1 to 3. Component response rates decreased as the specified number of responses per component was increased. However, the relation between component response-rate ratios and component reinforcer-rate ratios was independent of the specified number of responses per component, and was similar to that found when components alternate after fixed time periods. In the fourth part of the experiment, the results from Parts 1 to 3 were systematically replicated by keeping the component reinforcer rates constant, but different, while the number of responses that produced component alternation was varied from 5 to 60 responses. The results showed that multiple-schedule performance under component-response-number constraint is similar to that under conventional component-duration constraint. They further suggest that multiple-schedule response rates are controlled by component reinforcer rates and not by principles of maximizing overall reinforcer rates or meliorating component reinforcer rates.
Keywords: multiple schedules, time allocation, response allocation, response constraints, molar maximizing, melioration, generalized matching, pecking, pigeons
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Matching, undermatching, and overmatching in studies of choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Sep;32(2):269–281. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzas A., Baum W. M. Behavioral contrast of time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Mar;25(2):179–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charman L., Davison M. On the effects of component durations and component reinforcement rates in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 May;37(3):417–439. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M., Charman L. On the measurement of time allocation on multiple variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Nov;46(3):353–362. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.46-353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCarlo L. T. Matching and maximizing with variable-time schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 Jan;43(1):75–81. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmon E. L. Multiple schedule component duration: a reanalysis of Shimp and Wheatley (1971) and Todorov (1972). J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Sep;30(2):239–241. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G., Irwin R. J. Multiple schedules: effects of the distribution of reinforcements between component on the distribution of responses between conponents. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):517–524. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Multiple and concurrent schedule performance: independence from concurrent and successive schedule contexts. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jul;28(1):27–39. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Performance in concurrent interval schedules: a systematic replication. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):191–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. P., White K. G. Temporal constraint on choice: Sensitivity and bias in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 May;39(3):405–426. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweeney F. K., Farmer V. A., Dougan J. D., Whipple J. E. The generalized matching law as a description of multiple-schedule responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Jan;45(1):83–101. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P., Wheatley K. L. Matching to relative reinforcement frequency in multiple schedules with a short component duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):205–210. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov J. C. Component duration and relative response rates in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):45–49. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan W., Jr, Miller H. L., Jr Optimization versus response-strength accounts of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Sep;42(2):337–348. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.42-337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. G. Behavioral contrast as differential time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Mar;29(2):151–160. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


