Abstract
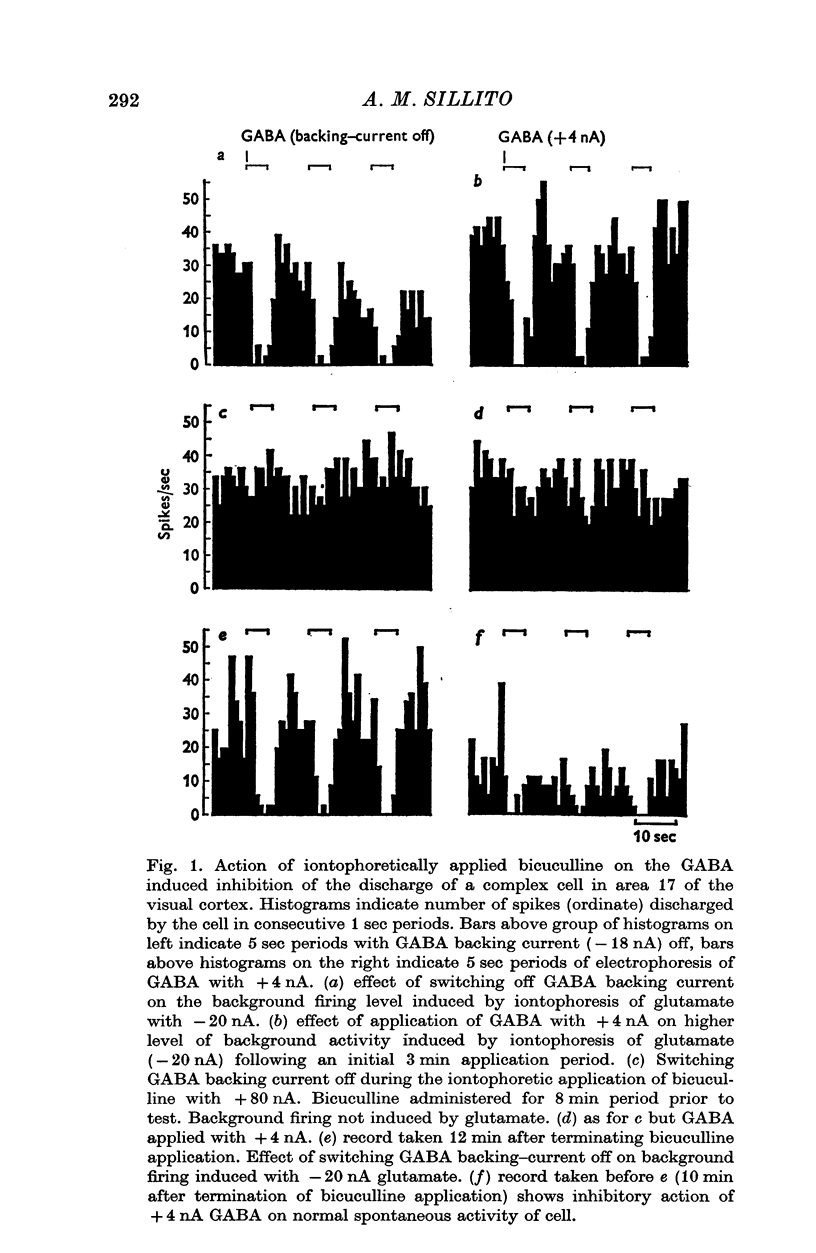
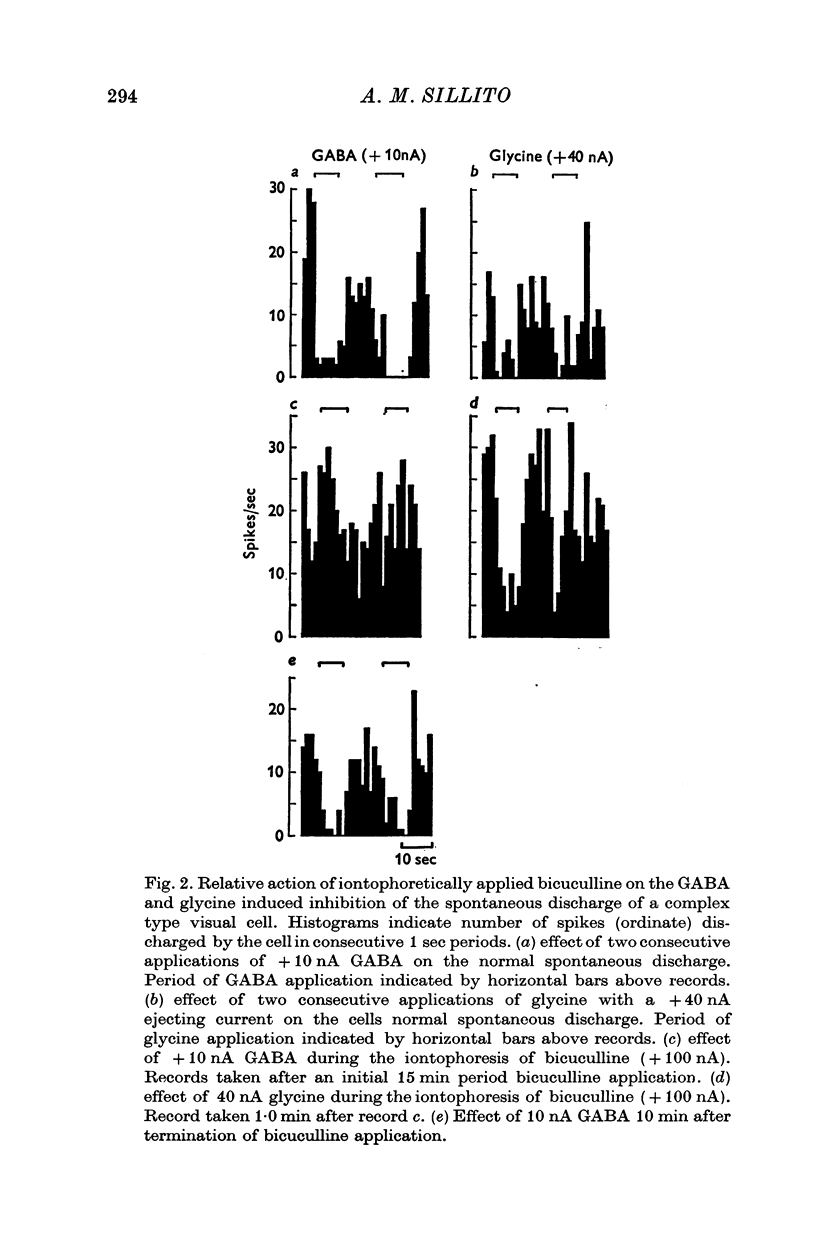
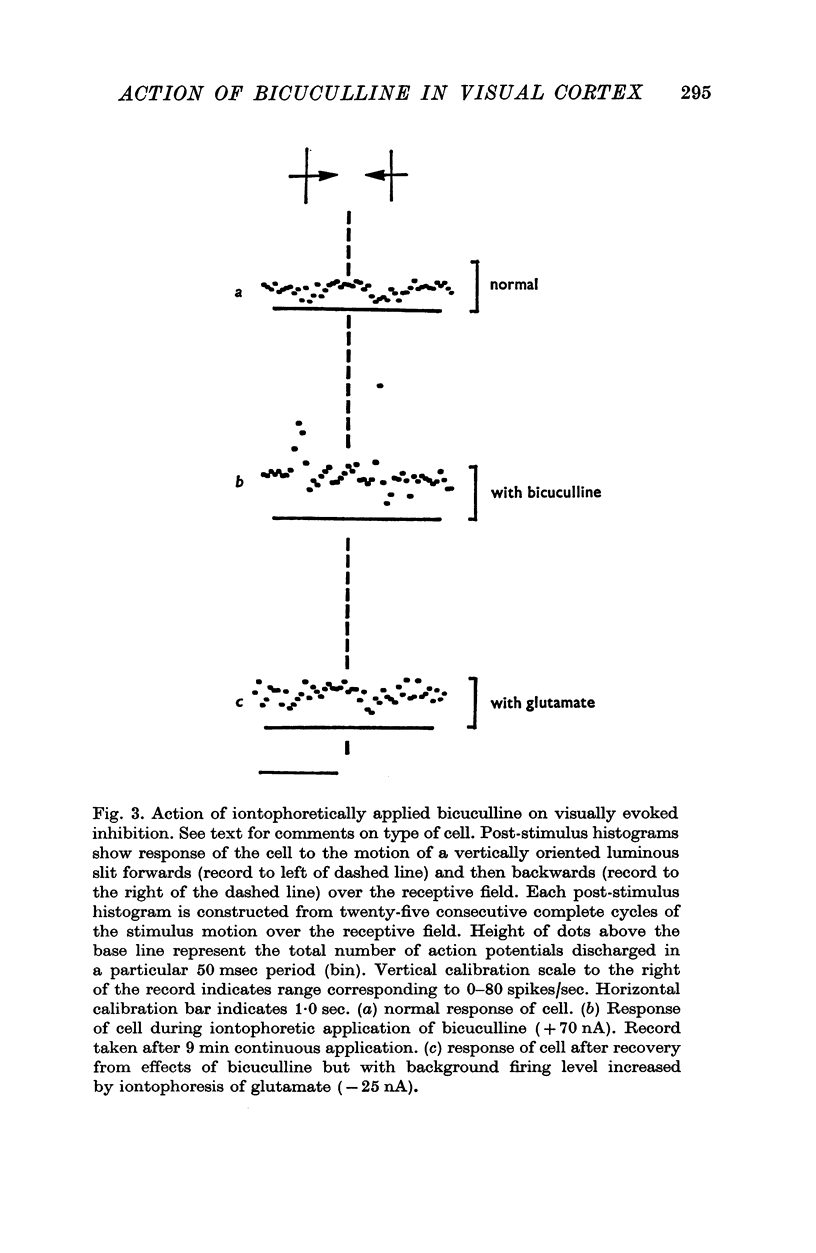
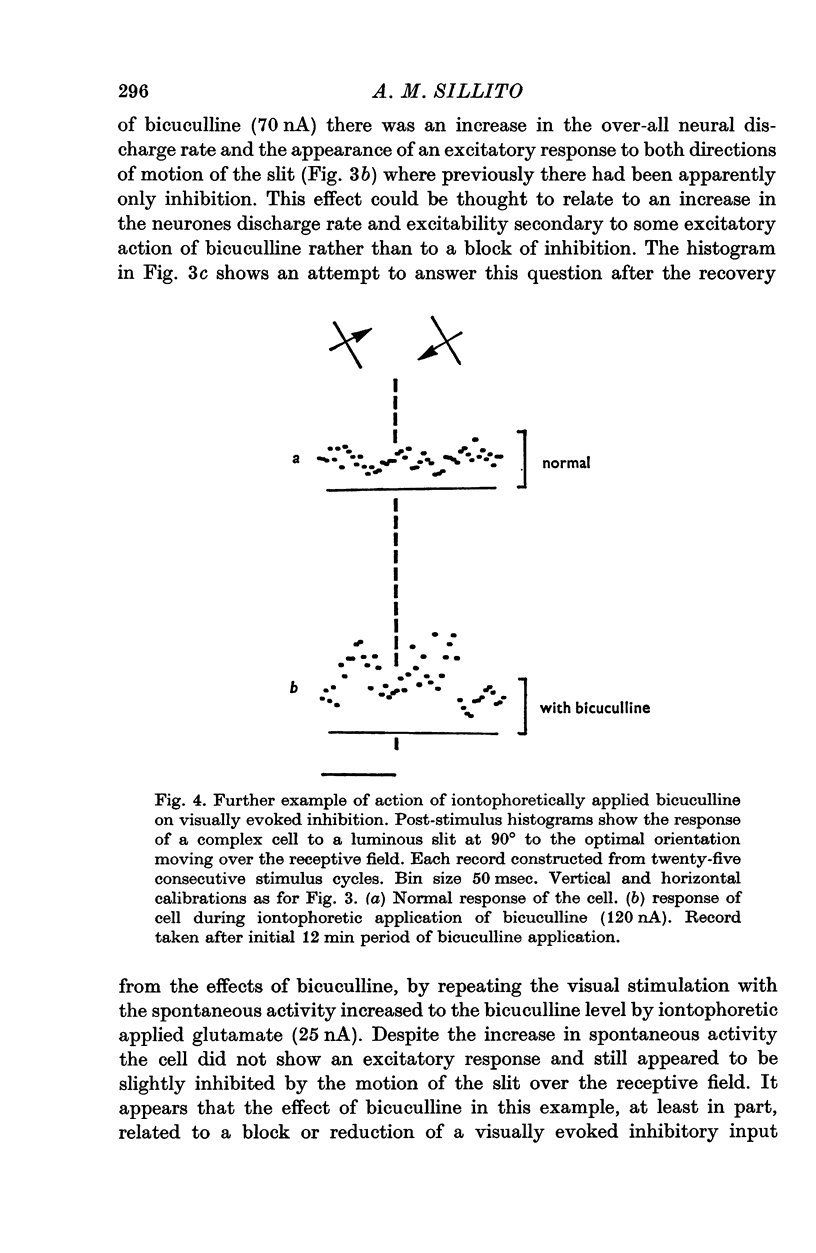
1. The iontophoretic application of the alkaloid bicuculline to neurones in area 17 of the cat's visual cortex effectively antagonized the inhibitory action of iontophoretically applied GABA in fifty-four out of sixty-two neurones examined. It had little or no effect on the inhibitory action of iontophoretically applied glycine. 2. At the stage that the iontophoretic application of bicuculline blocked the inhibitory action of GABA it also reduced or blocked visually evoked inhibitory influences acting on forty-three of the fifty-four cells. This effect on visually evoked inhibition was not reproduced by simply raising the neural spontaneous activity with iontophoretically applied glutamate. 3. For those seven neurones where the iontophoresis of bicuculline failed to block the inhibitory action of iontophoretically applied GABA it also failed to produce any change in visually evoked inhibition. 4. In all cases where a visually evoked inhibition of a cells resting discharge was reduced by the iontophoretic application of bicuculline, the inhibitory response was replaced by an excitatory response. The application of bicuculline also revealed excitatory responses to certain of the visual stimuli that previously appeared to exert neither inhibitory nor excitatory effects on a cell, and often where cells normally exhibited small excitatory responses it produced large increases in the magnitude of the evoked response. 5. These results indicate that the normal responses of the neurones examined in the present work, to the particular visual stimuli used, reflect an interaction between simultaneously evoked excitatory and inhibitory inputs. It is suggested that the iontophoretic application of bicuculline by blocking or reducing the inhibitory input moves the balance between the inputs in favour of the excitatory input. 6. The present results support the view that GABA is an inhibitory transmitter in the visual cortex.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benevento L. A., Creutzfeldt O. D., Kuhnt U. Significance of intracortical inhibition in the visual cortex. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio238124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. O., Coombs J. S., Henry G. H. Receptive fields of simple cells in the cat striate cortex. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):31–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt O., Ito M. Functional synaptic organization of primary visual cortex neurones in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(4):324–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00233183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. Bicuculline, an antagonist of GABA and synaptic inhibition in the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):69–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. GABA, bicuculline and central inhibition. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1222–1224. doi: 10.1038/2261222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A., McLennan H. Antagonism between bicuculline and GABA in the cat brain. Brain Res. 1971 Oct 8;33(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Felix D. The effect of bicuculline upon synaptic inhibition in the cerebral and cerebellar corticles of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(2):301–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A., Game C. J., McCulloch R. M. Central action of bicuculline. J Neurochem. 1974 Sep;23(3):605–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Terbécis A. K. Bicuculline and thalamic inhibition. Exp Brain Res. 1972;16(2):210–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00233997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. Cortical inhibition and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00238327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Matthews E. K. Antagonism between strychnine and glycine, and bicuculline and GABA, in the ventromedial hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):599–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90490-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Krnjević K., Pumain R. Doubtful value of bicuculline as a specific antagonist of GABA. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):675–676. doi: 10.1038/228675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellon R. F. The marking of electrode tip positions in nervous tissue. J Physiol. 1971;214 (Suppl):12P–12P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti G. M., Fiore L. Post-synaptic inhibitory components of the responses to moving stimuli in area 17. Brain Res. 1974 Nov 8;80(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90728-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Mitchell J. F., Srinivasan V. The release of gamma-aminobutyric acid during inhibition in the cat visual cortex. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):519–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. The action of glycine on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00238328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Pumain R., Renaud L. The mechanism of excitation by acetylcholine in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):247–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Schwartz S. The action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):320–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00237558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Miller J. J. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and inhibition in the septal nuclei of the rat. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):625–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. J., McLennan H. The action of bicuculline upon acetylcholine-induced excitations of central neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Aug;13(8):785–787. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew J. D., Daniels J. D. Gamma-aminobutyric acid antagonism in visual cortex: different effects on simple, complex, and hypercomplex neurons. Science. 1973 Oct 5;182(4107):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4107.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Blakemore C. Effects of bicuculline on functions of inhibition in visual cortex. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):375–377. doi: 10.1038/249375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M. The contribution of inhibitory mechanisms to the receptive field properties of neurones in the striate cortex of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):305–329. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spehlmann R., Daniels J. C., Smathers C. C., Jr Acetylcholine and the synaptic transmission of specific impulses to the visual cortex. Brain. 1971;94(1):125–138. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straughan D. W., Neal M. J., Simmonds M. A., Collins G. G., Hill R. G. Evaluation of bicuculline as a GABA antagonist. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):352–354. doi: 10.1038/233352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenneby G., Roberts E. Bicuculline and N-methylbicuculline--competitive inhibitors of brain acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):1025–1026. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallingford E., Ostdahl R., Zarzecki P., Kaufman P., Somjen G. Optical and pharmacological stimulation of visual cortical neurones. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 18;242(120):210–212. doi: 10.1038/newbio242210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


