Abstract
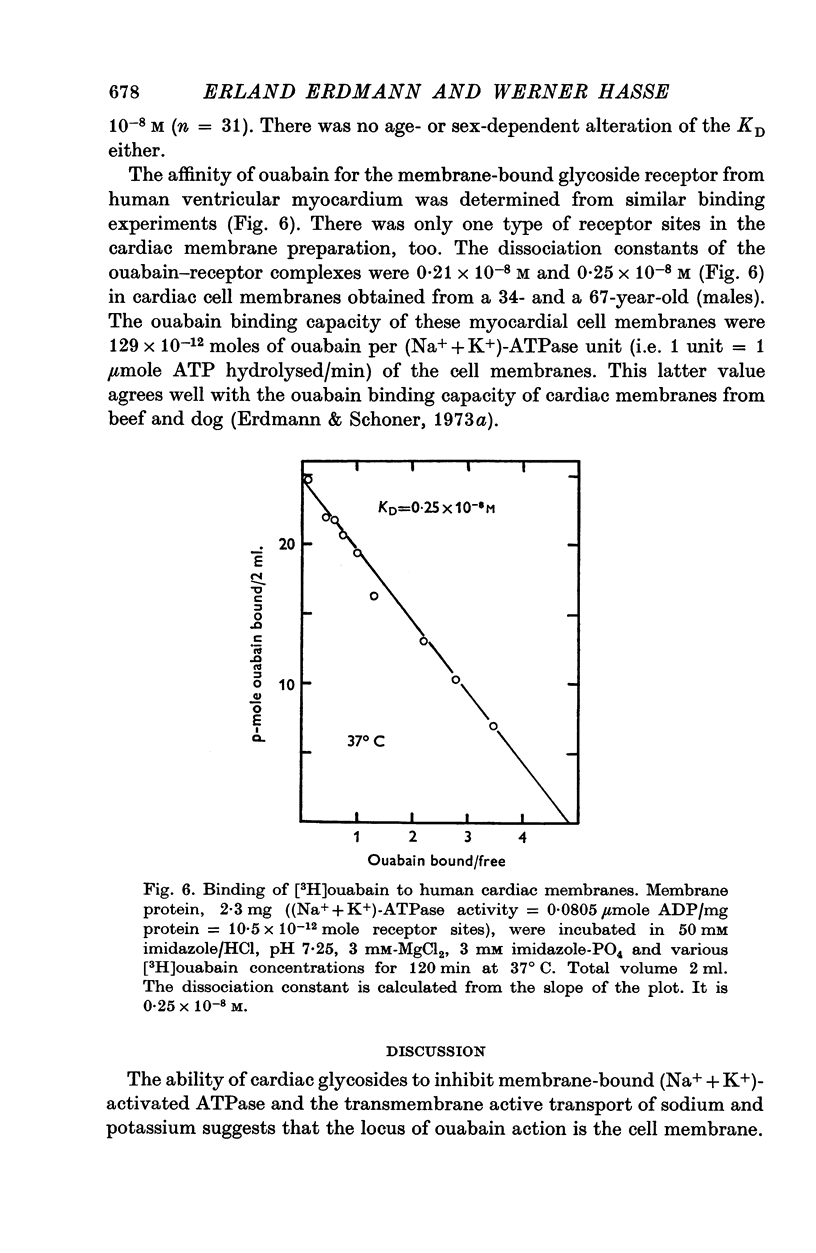
1. [3H]ouabain binding to human erythrocyte membranes is a time- and temperature-dependent process. The association of ouabain to the membrane-bound receptor follows second-order kinetics, while the dissociation is a monomolecular reaction. An association rate constant of 4-6 x 10(4) M-1 sec-1 and a dissociation rate constant of 1-4 x 10(-4) sec-1 were measured at 37 degrees C. The dissociation constant calculated from these data agrees with that determined from equilibrium binding experiments. There is only one type of ouabain binding sites with high affinity for the drug as reflected by the low dissociation constant of 0-28 x 10(-8) M. 2. The dissociation constants of the ouabain-receptor complexes from human erythrocyte and cardiac membranes are identical. 3. The maximal number of membrane-bound ouabain binding sites was measured from equilibrium binding experiments as 288 +/- 28 per single erythrocyte. Thus one receptor site corresponds to less than 1 mum2 of the membrane, provided the receptors are diffusely distributed on the surface of the membrane. 4. Neither the maximal number of ouabain receptors nor the affinity for the drug changes with the age or sex of the blood donor. 5. A maximal transport capacity for sodium of 5-6 m-equiv/hr.1. is calculated from the number of receptor sites per erythrocyte and from the turn-over number of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Willis J. S. Binding of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to intact cells. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R., Whittam R. Reconstitution of the sodium pump from protein and phosphatidylserine: features of ouabain binding. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):467–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor of liver and fat cell membranes. Fed Proc. 1973 Aug;32(8):1838–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Hoffman J. F. Partial purification of the ouabain-binding component and of Na,K-ATPase from human red cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):936–943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann E., Schoner W. Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na + +K + )-ATPase preparations from different tissues and species. Determination of kinetic constants and dissociation constants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann E., Schoner W. Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase preparations. 3. On the stability of the ouabain receptor against physical treatment, hydrolases and SH reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 22;330(3):316–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann E., Schoner W. Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase preparations. II. Effect of cations and nucleotides on rate constants and dissociation constants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 22;330(3):302–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Conlon T. P. The effects of sodium and potassium on ouabain binding by human erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):609–629. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Frantz C. Effects of cations on ouabain binding by intact human erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 1974;16(1):43–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01872406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Kiino D. R. Ouabain binding and cation transport in human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1845–1851. doi: 10.1172/JCI107367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Kilno D. R., Swartz T. J., Butler V. P., Jr Effects of digoxin-specific antibodies on accumulation and binding of digoxin by human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1820–1833. doi: 10.1172/JCI107364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. The relationship between G-strophanthin-binding capacity and ATPase activity in plasma-membrane fragments from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):122–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F. The red cell membrane and the transport of sodium and potassium. Am J Med. 1966 Nov;41(5):666–680. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L., Hansen O., Glynn I. M., Cavieres J. D. Antibodies to pig kidney (Na + +K + )-ATPase inhibit the Na + pump in human red cells provided they have access to the inner surface of the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 16;291(3):795–800. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaniike K., Erdmann E., Schoner W. Study on the differential modifications of (Na+ plus K+)-ATPase and its partial reactions by dimethylsulfoxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Properties of the two polypeptides of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7642–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Santi D. V., Spudich J. A. Biochemical studies on the mode of action of cytochalasin B. Preparation of (3H)cytochalasin B and studies on its binding of cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2268–2274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Schwartz A. Mechanism of cardiac glycoside inhibition of the (Na+-K+)-dependent ATPase from cardiac tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):655–663. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A., Kyte J. Photoaffinity labeling of the ouabain-binding site on (Na+ plus K+) adenosinetriphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2352–2356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J. Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium- und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(4):346–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEN A. K., POST R. L. STOICHIOMETRY AND LOCALIZATION OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN THE ERYTHROCYTE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A. K. The permeability of red cells to water and ions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):175–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A. K. The permeability of the human erythrocyte to sodium and potassium. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):57–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R., Ellory J. C., Kropp D. L., Dunham P. B., Hoffman J. F. Antibody-induced alterations in the kinetic characteristics of the Na:K pump in goat red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Apr;63(4):389–414. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner W., von Ilberg C., Kramer R., Seubert W. On the mechanism of Na+- and K+-stimulated hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate. 1. Purification and properties of a Na+-and K+-activated ATPase from ox brain. Eur J Biochem. 1967 May;1(3):334–343. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skou J. C. The relationship of the (Na + + K + )-activated enzyme system to transport of sodium and potassium across the cell membrane.. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):1–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01516049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


