Abstract
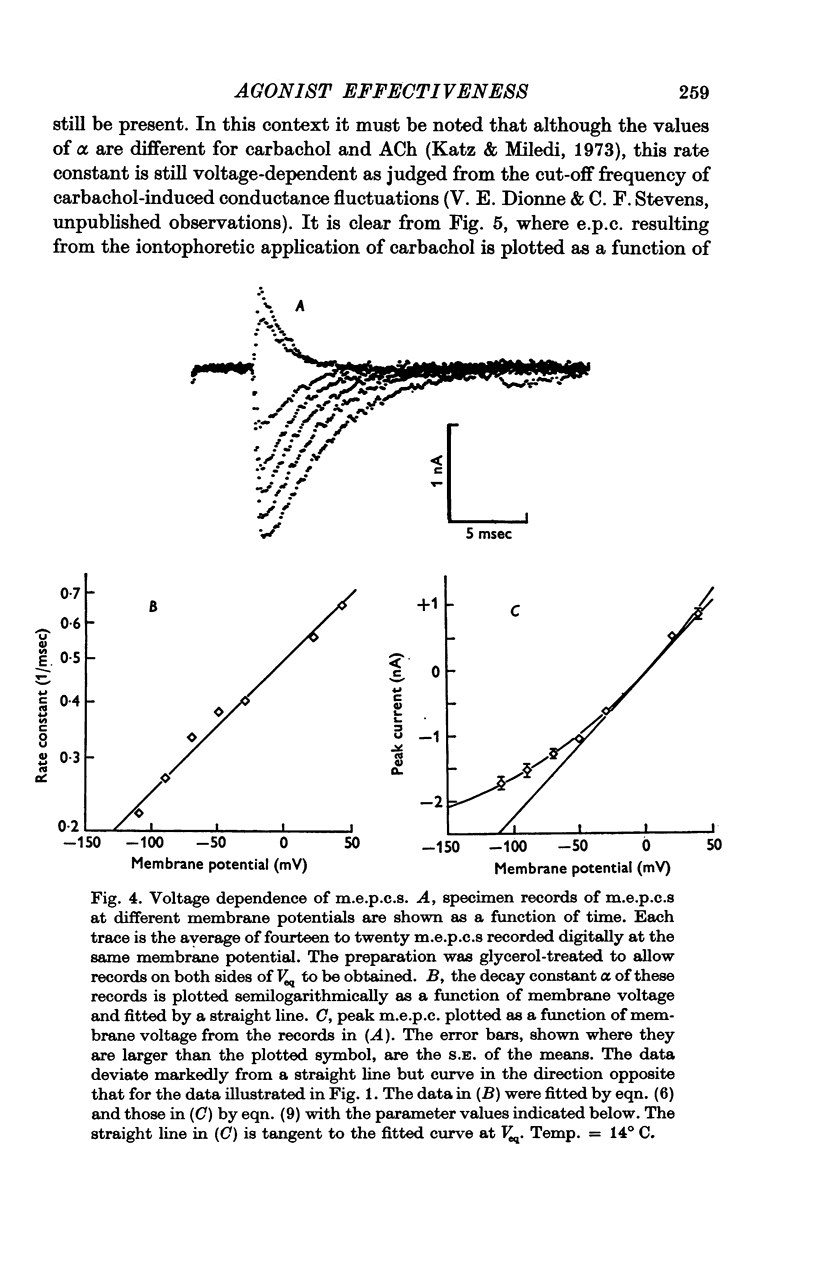
1. End-plate currents produced by nerve-released acetylcholine and iontophoretically applied acetylcholine and carbachol have been recorded from voltage-clamped frog cutaneous pectoris neuromuscular junctions made visible with Nomarski differential interference contrast optics. 2. The effectiveness of agonists - that is, the end-plate conductance change produced by a given dose-has been determined as a function of post-junctional membrane potential. 3. As the post-junctional membrane potential is made more negative, nerve-released acetylcholine becomes less effective whereas iontophoretically-applied agonists become more effective. 4. This voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness is mediated neither by end-plate current iontophoresis of agonist into the cleft nor through electric field effects on the esterase. 5. Influences of membrane potential on the opening and closing of end-plate channel gates can account quantitatively for the voltage-dependent effectiveness of both nerve-released and iontophoretically applied agonist.
Full text
PDF
























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum G. Determination of acetylcholinesterase by an organic substrate selective electrode. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90462-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K. A monolayer preparation of innervated skeletal muscle fibres of the m. cutaneus pectoris of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 22;348(3):257–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00587416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGEN M., HAMMES G. G. ELEMENTARY STEPS IN ENZYME REACTIONS (AS STUDIED BY RELAXATION SPECTROMETRY). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1963;25:1–38. doi: 10.1002/9780470122709.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Action potentials without contraction in frog skeletal muscle fibers with disrupted transverse tubules. Science. 1967 Dec 29;158(3809):1702–1703. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3809.1702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Miniature end-plate currents and potentials generated by quanta of acetylcholine in glycerol-treated toad sartorius fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H. Transients and relaxation kinetics of enzyme reactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:315–344. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson D. H., Terrar D. A. Influence of chloride ions on changes in membrane potential during prolonged application of carbachol to frog skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;47(2):363–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The characteristics of 'end-plate noise' produced by different depolarizing drugs. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):707–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Turkanis S. A., Weakly J. N. Correlation between nerve terminal size and transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):545–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocil F. Dependence of acetylcholine desensitization on the membrane potential of frog muscle fibre and on the ionic changes in the medium. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):507–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Lux H. D. Rapid changes of potassium concentration at the outer surface of exposed single neurons during membrane current flow. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):385–399. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Allosteric mechanisms at neuromuscular junctions. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1973 Jun;11(3):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Drug receptors and their function. Nature. 1971 May 14;231(5298):91–96. doi: 10.1038/231091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom J., Eisenman G., Walker J. L., Jr Electrical phenomena associated with the transport of ions and ion pairs in liquid ion-exchange membranes. I. Zero current properties. J Phys Chem. 1967 Nov;71(12):3862–3870. doi: 10.1021/j100871a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


