Abstract
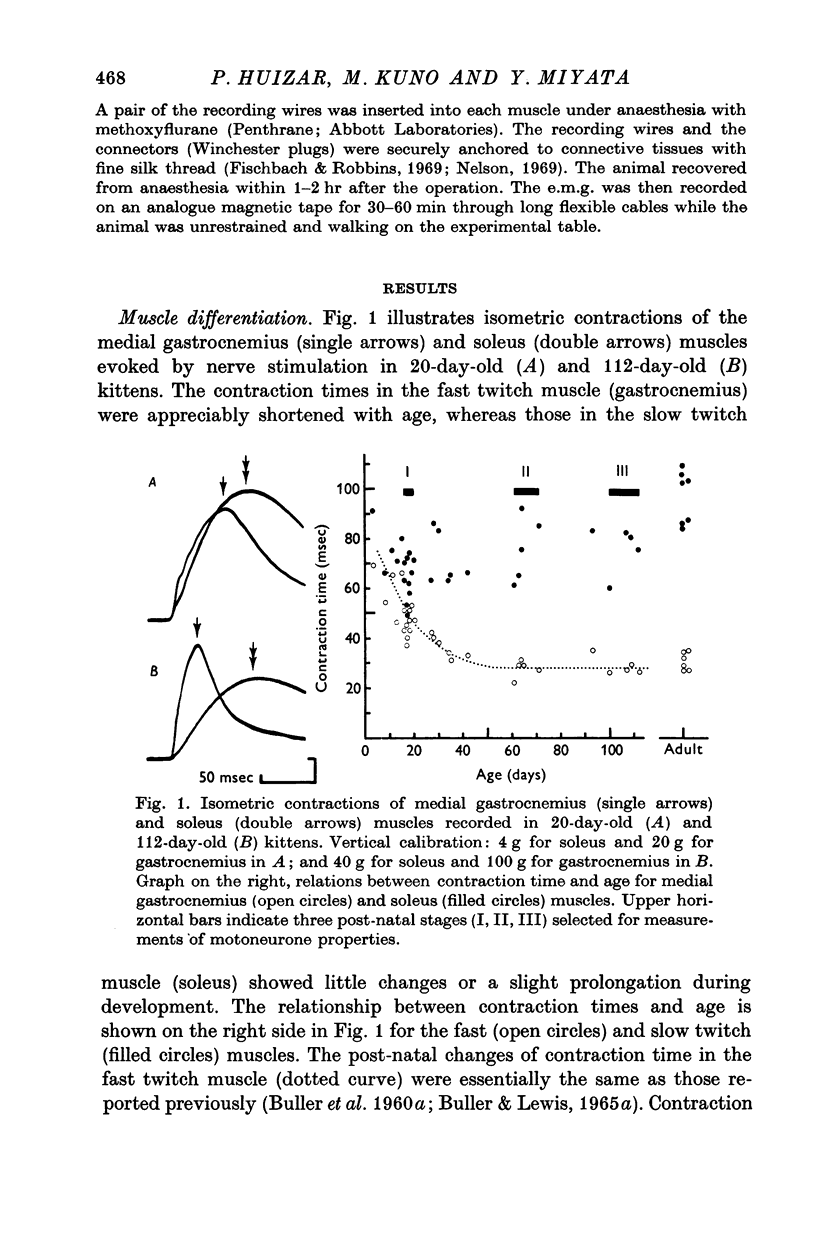
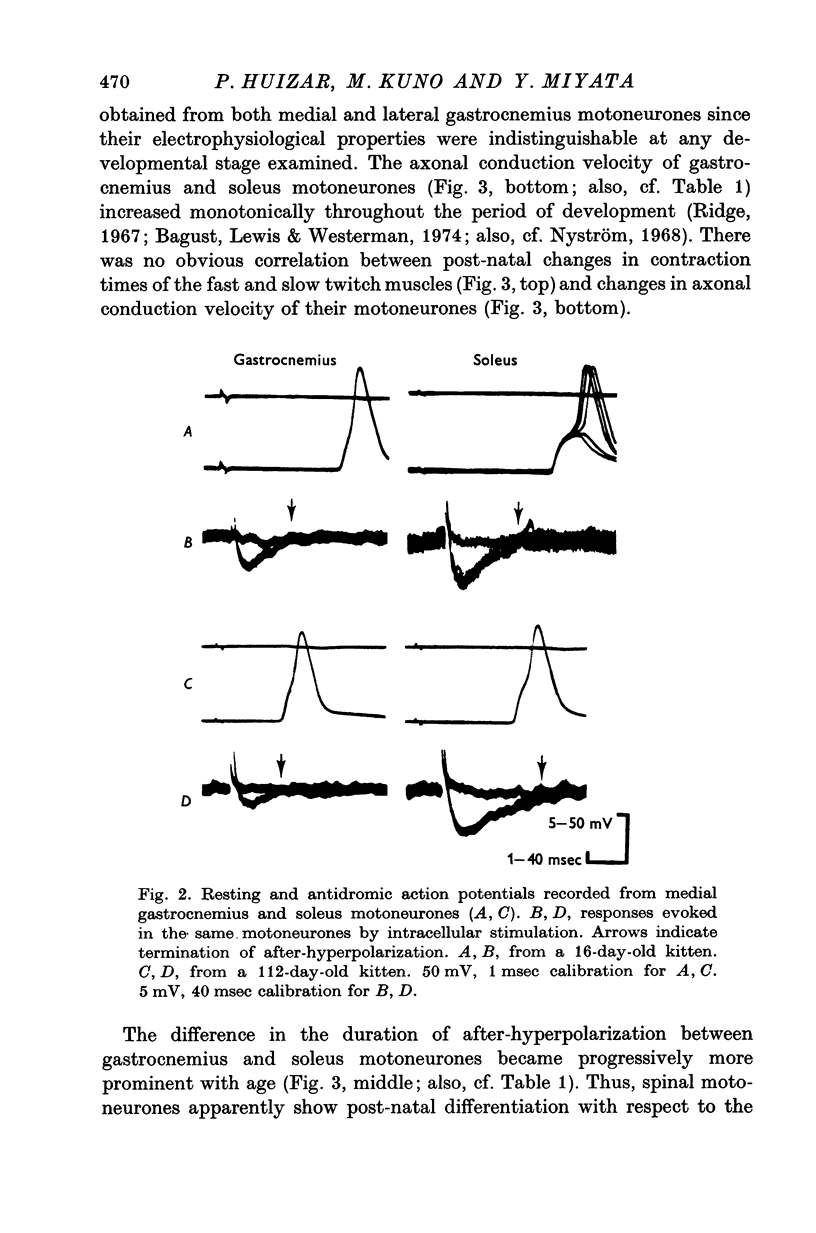
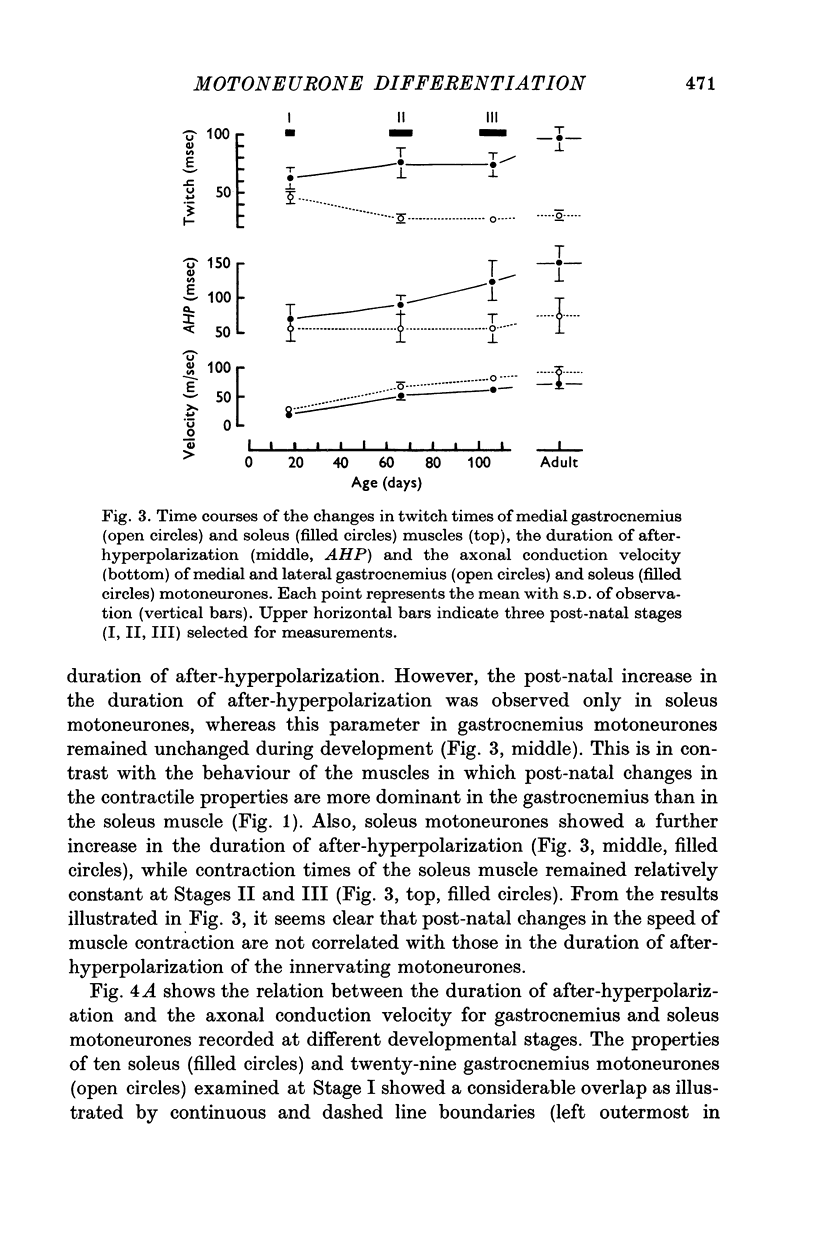
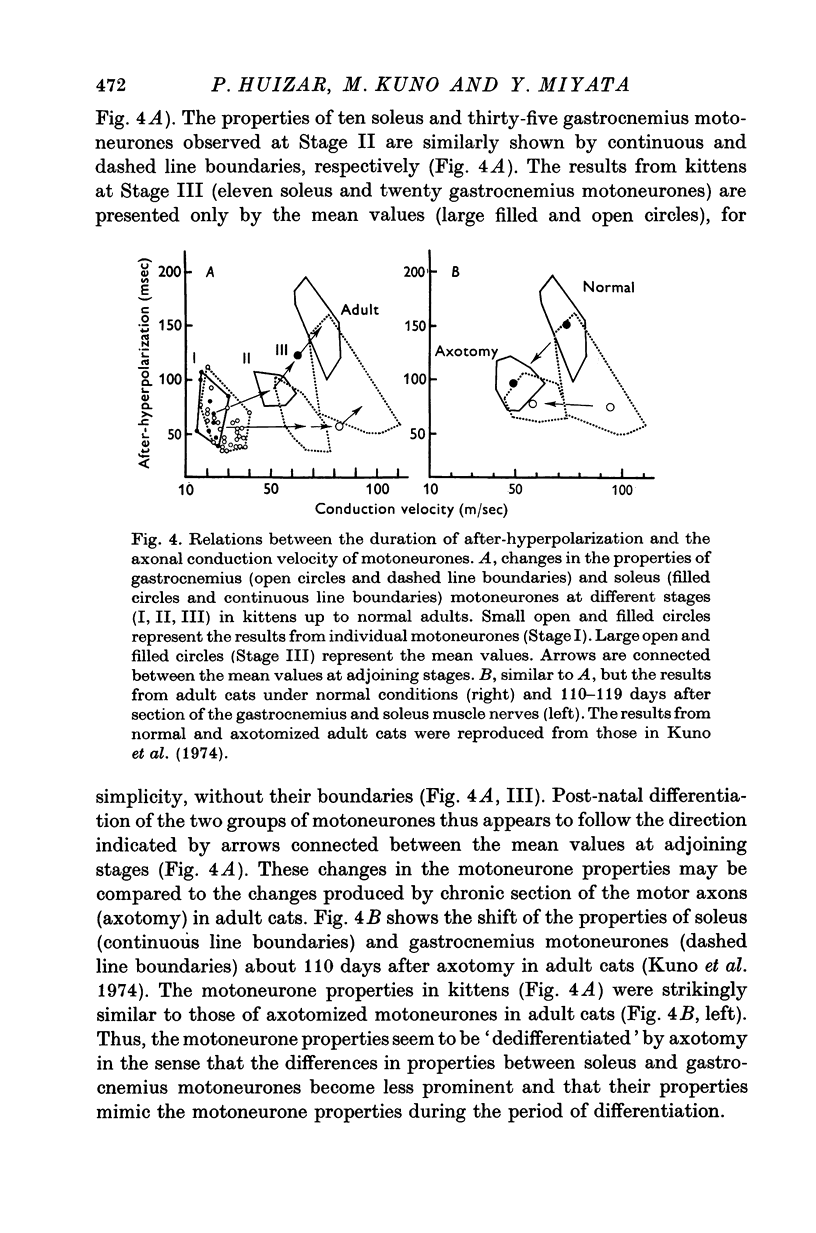
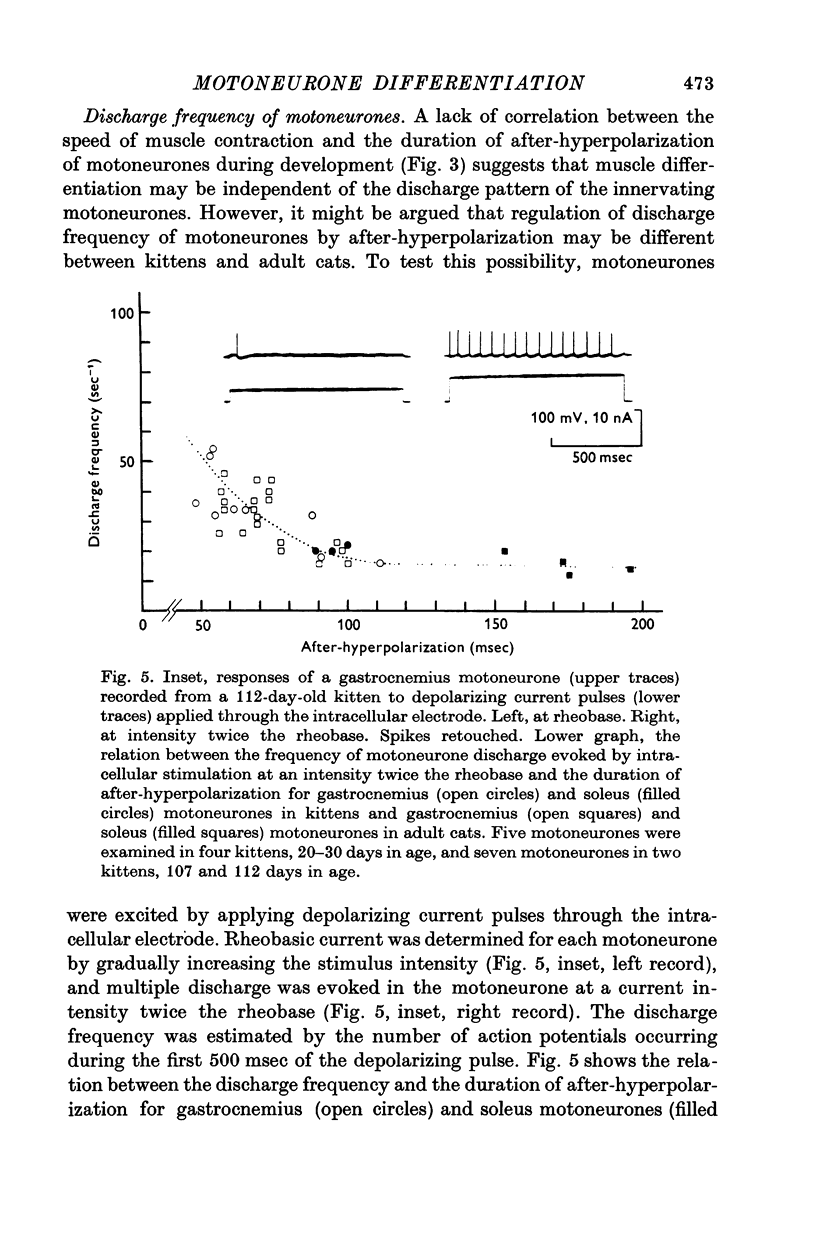
1. Isometric contractions of the medial gastrocnemius (fast switch) and soleus (slow twitch) muscles were recorded in kittens ranging in age from 3 to 112 days, as well as in adult cats. 2. It was confirmed that the speed of contraction of the gastrocnemius muscle becomes progressively faster during the first few weeks after birth, whereas contraction times of the soleus muscle show little changes or a slight prolongation during the period of post-natal development. 3. The properties of gastrocnemius (fast alpha) and soleus (slow alpha) motoneurons were examined with intracellular electrodes in kittens at three different stages; 16-20, 61-71 and 100-112 days in age. 4. The axonal conduction velocities of both gastrocnemius and soleus motoneurones increased monotonically throughout the period of development and showed no correlation with post-natal changes in contraction times of the innervated muscles. 5. The duration of after-hyperpolarization in soleus motoneurones became progressively longer with age, while that in gastrocnemius motoneurones remained virtually unchanged during development. 6. The relation between the duration of after-hyperpolarization and the axonal conduction velocity in kitten motoneurones was similar to that observed in axotomized motoneurones of adult cats. 7. It is suggested that fast and slow alpha motoneurones show postnatal differentiation in terms of the duration of after-hyperpolarization and that axotomy leads to 'dedifferentiation' of the motoneurone properties. 8. Post-natal changes in the contractile properties of skeletal muscles were independent of the changes in the duration of after-hyperpolarization of the innervating motoneurones. However, it remains uncertain whether muscle differentiation is independent of the discharge pattern of the innervating motoneurones.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Differentiation of fast and slow muscles in the cat hind limb. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:399–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON MAMMALIAN CROSS-INNERVATED SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:343–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE DIFFERENTIATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLES IN THE KITTEN HIND LIMB. J Physiol. 1965 Feb;176:355–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. The properties of motor units in a fast and a slow twitch muscle during post-natal development in the kitten. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):75–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Perl E. R. Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibers to noxious stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;32(6):1025–1043. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Firing patterns of gastrocnemius motor units in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):631–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit types of cat triceps surae muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat after nerve cross-union. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):331–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVANANDAN M. S., ECCLES R. M., WESTERMAN R. A. SINGLE MOTOR UNITS OF MAMMALIAN MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:359–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The action potentials of the alpha motoneurones supplying fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):275–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., WILLIS W. D. THE EFFECT OF REPETITIVE STIMULATION UPON MONOSYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN KITTENS. J Physiol. 1965 Jan;176:311–321. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Eccles R. M., Kozak W. Further investigations on the influence of motoneurones on the speed of muscle contraction. J Physiol. 1962 Sep;163(2):324–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles R. M., Shealy C. N., Willis W. D. Patterns of innervation of kitten motoneurones. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165(3):392–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Robbins N. Changes in contractile properties of disused soleus muscles. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):305–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL P. K., KUNO M. EXCITATORY AND INHIBITORY ACTIONS ON PHRENIC MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:274–289. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL P. K., KUNO M. PROPERTIES OF PHRENIC MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:258–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HENATSCH H. D., STEG G. Tonic and phasic ventral horn cells differentiated by post-tetanic potentiation in cat extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Sep 26;37(2-3):114–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G., SKOGLUND S., STEG G. Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Sep;20(5):470–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. Excitability following antidromic activation in spinal motoneurones supplying red muscles. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:374–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyata Y., Muñoz-Martinez E. J. Differential reaction of fast and slow alpha-motoneurones to axotomy. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):725–739. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H., Dahl H. A. Contractile properties of muscle: control by pattern of muscle activity in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Aug 27;187(1086):99–103. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G. Functional consequences of tenotomy in hind limb muscles of the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):321–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström B. Fibre diameter increase in nerves to "slow-red" and "fast-white" cat muscles during postnatal development. Acta Neurol Scand. 1968;44(3):265–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1968.tb05573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge R. M. The differentiation of conduction velocities of slow twitch and fast twitch muscle motor innervations in kittens and cats. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):293–304. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons S., Vrbová G. The influence of activity on some contractile characteristics of mammalian fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):535–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J. Reflex transmission in the kitten. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Mar;25:263–276. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


