Abstract
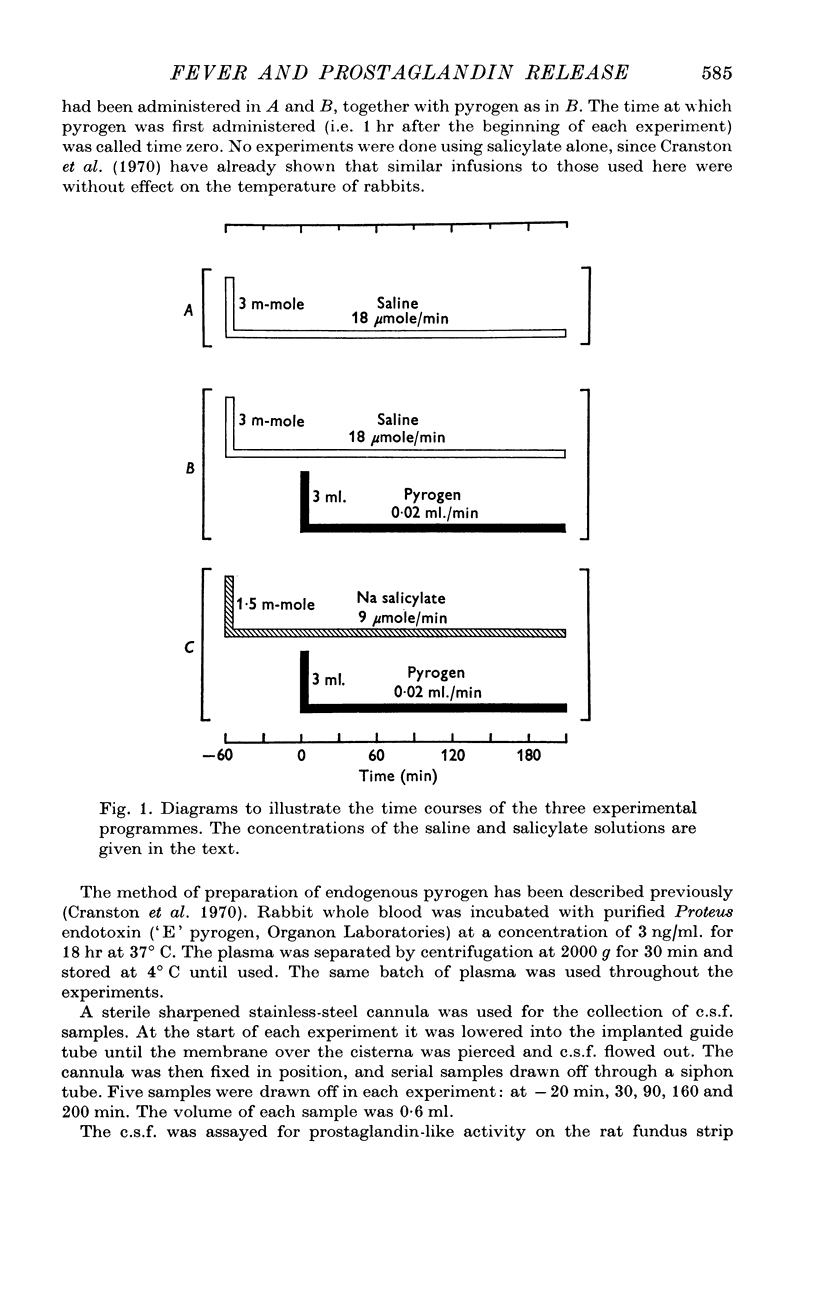
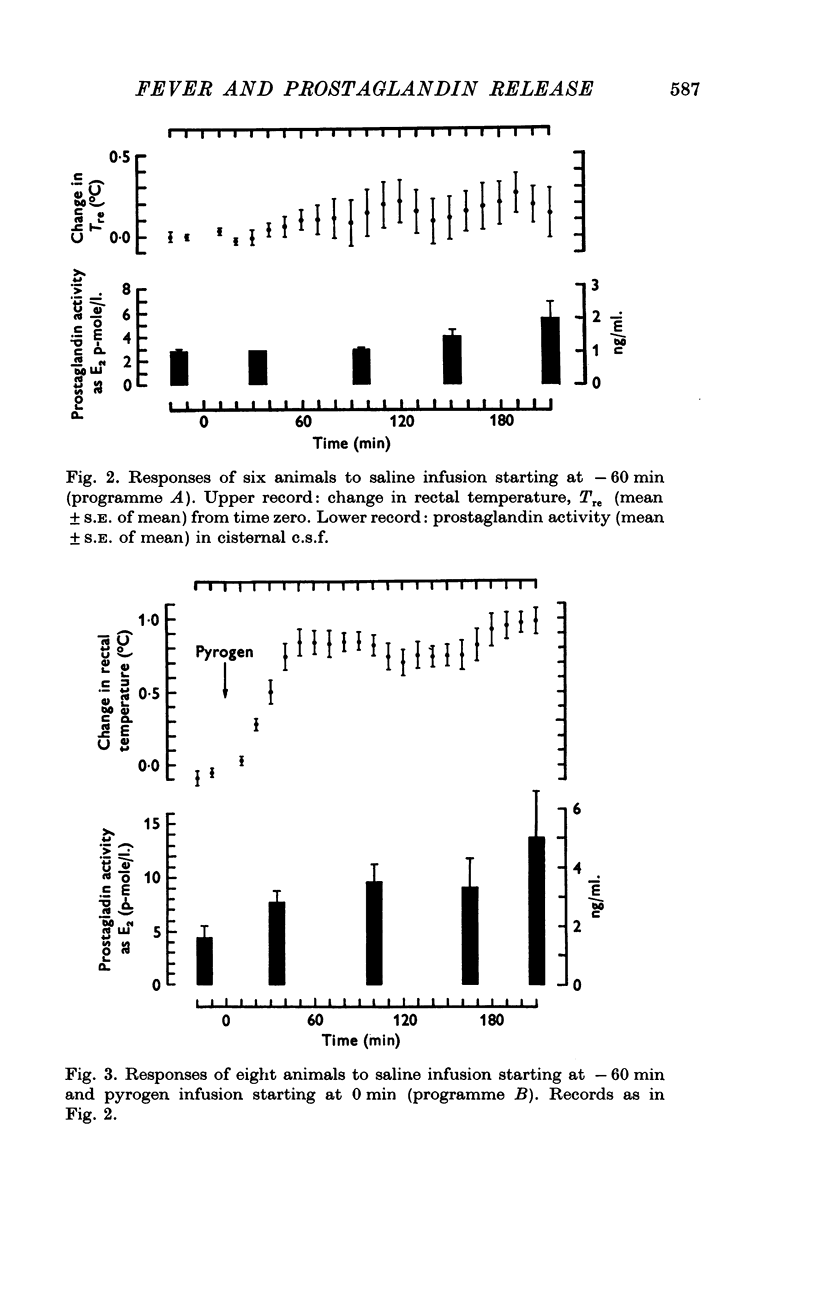
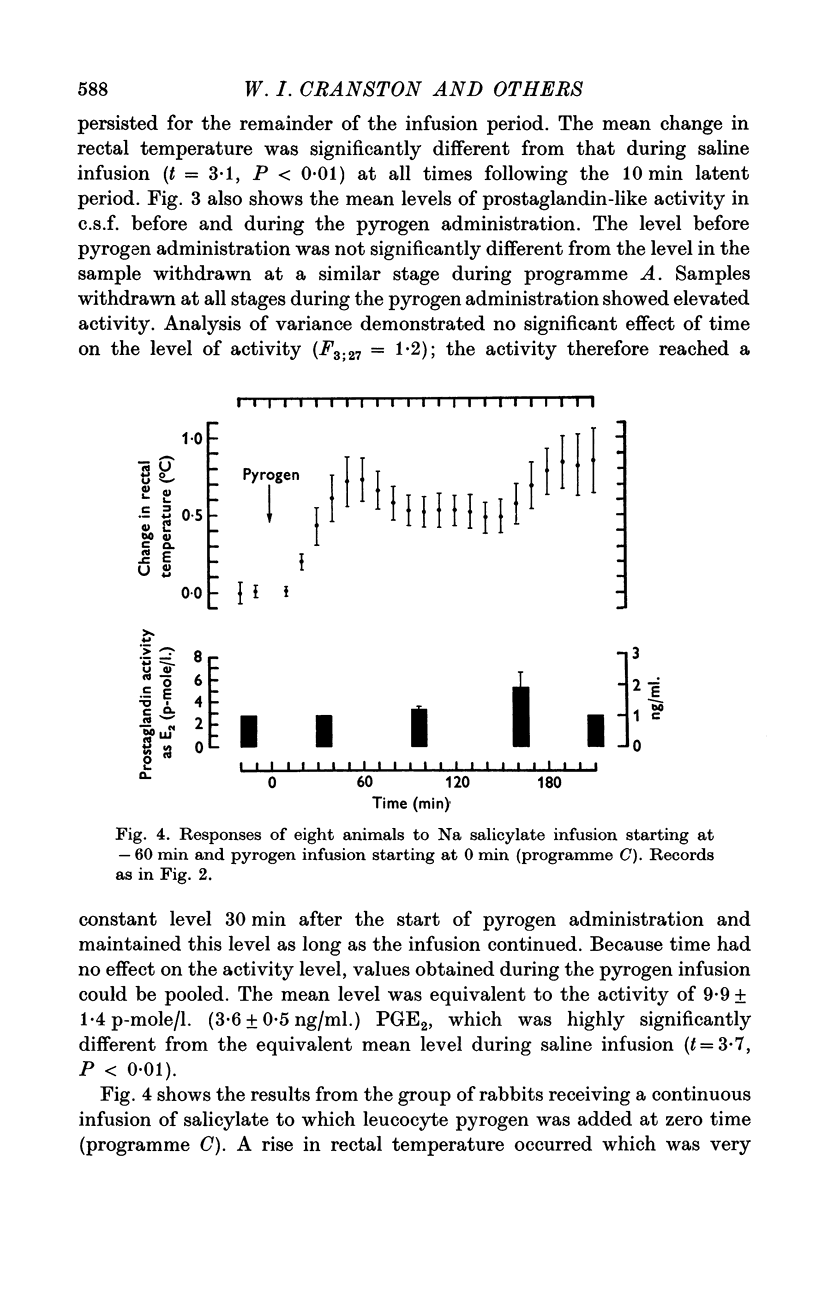
1. Sustained fever has been induced in conscious rabbits by I.V. injection and infusion of endogenous pyrogen. 2. Cerebrospinal fluid (e.s.f.) was sampled from the cisterna magna at hourly intervals. The concentration of prostaglandin increased in parallel with rectal temperature. The prostaglandin was identified as one of the E series. 3. When sodium salicylate (1-5 m-mole followed by a continuous infusion of 9 mumole/min) was started 1 hr before endogenous pyrogen, the febrile response to the pyrogen was not significantly diminished but no rise of prostaglandin concentration was detected in c.s.f. 4. This dissociation between fever and prostaglandin concentration means that changes in cisternal prostaglandin concentration cannot be accepted as evidence that prostaglandin mediates the febrile response.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cranston W. I., Hellon R. F., Mitchell D. Proceedings: Fever and brain prostaglandin release. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):27P–29P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Luff R. H., Rawlins M. D., Rosendorff C. The effects of salicylate on temperature regulation in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1970 May;208(1):251–259. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Luff R. H., Rawlins M. D., Wright V. A. Influence of the duration of experimental fever on salicylate antipyresis in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;41(2):344–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb08035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawshaw L. I., Stitt J. T. Behavioural and autonomic induction of prostaglandin E-1 fever in squirrel monkeys. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):197–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey P. K., Feldberg W., Gupta K. P., Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Further studies on the role of prostaglandin in fever. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(3):629–646. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozois R. R., Thompson C. J. Presence of prostaglandins E2 and A2 in canine gastric secretions. Life Sci. 1974 Sep 1;15(5):975–986. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P., Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effect of pyrogen and antipyretics on prostaglandin acitvity in cisternal c.s.f. of unanaesthetized cats. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):279–303. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P. Pyrogen fever and prostaglandin-like activity in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):41–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Fever produced by prostaglandin E1. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(3):547–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Further studies on prostaglandin E 1 fever in cats. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):739–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales J. R., Bennett J. W., Baird J. A., Fawcett A. A. Thermoregulatory effects of prostaglandins E 1 , E 2 , F 1 and F 2 in the sheep. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Mar 21;339(2):125–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00587179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellon R. F. Monoamines, pyrogens and cations: their actions on central control of bodytemperature. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Dec;26(4):289–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp-Dormston W. K., Siegert R. Identification of prostaglandin E by radioimmunoassay in cerebrospinal fluid during endotoxin fever. Naturwissenschaften. 1974 Mar;61(3):134–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00606298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp-Dormston W. K., Siegert R. Prostaglandins of the E and F series in rabbit cerebrospinal fluid during fever induced by Newcastle disease virus, E. coli-endotoxin, or endogenous pyrogen. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun 19;159(4):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02123737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. J., East P. F. Effects of prostaglandin E 2 on the body temperature of conscious rats and cats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 May;197(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanner J. H. Substances that inhibit the actions of prostaglandins. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Jan;133(1):133–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T. Prosaglandin E1 fever induced in rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):163–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Miert A. S., van Essen J. A., Tromp G. A. The antipyretic effect of pyrazolone derivatives and salicylates on fever induced with leukocytic or bacterial pyrogen. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Jun;197(2):388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


