Abstract
1. Small balloons were inserted through the left pulmonary veins so as to lie at the pulmonary vein—left atrial junctions.
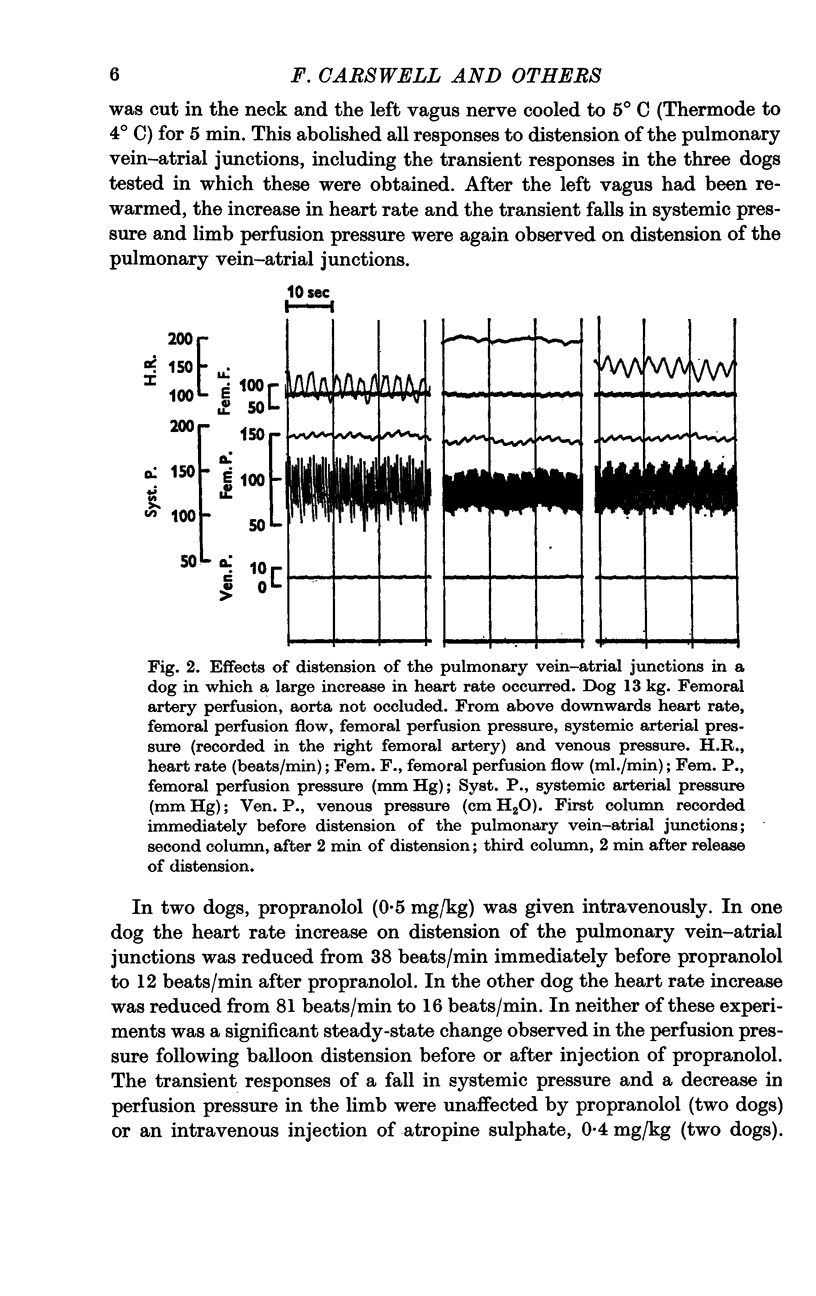
2. Distension of the balloons caused a reflex increase in heart rate. The afferent path was in the vagus nerves and the efferent path was in the cardiac sympathetic nerves.
3. Only small and variable changes in vascular resistance in a perfused hind limb accompanied the increase in heart rate when a steady state had been reached.
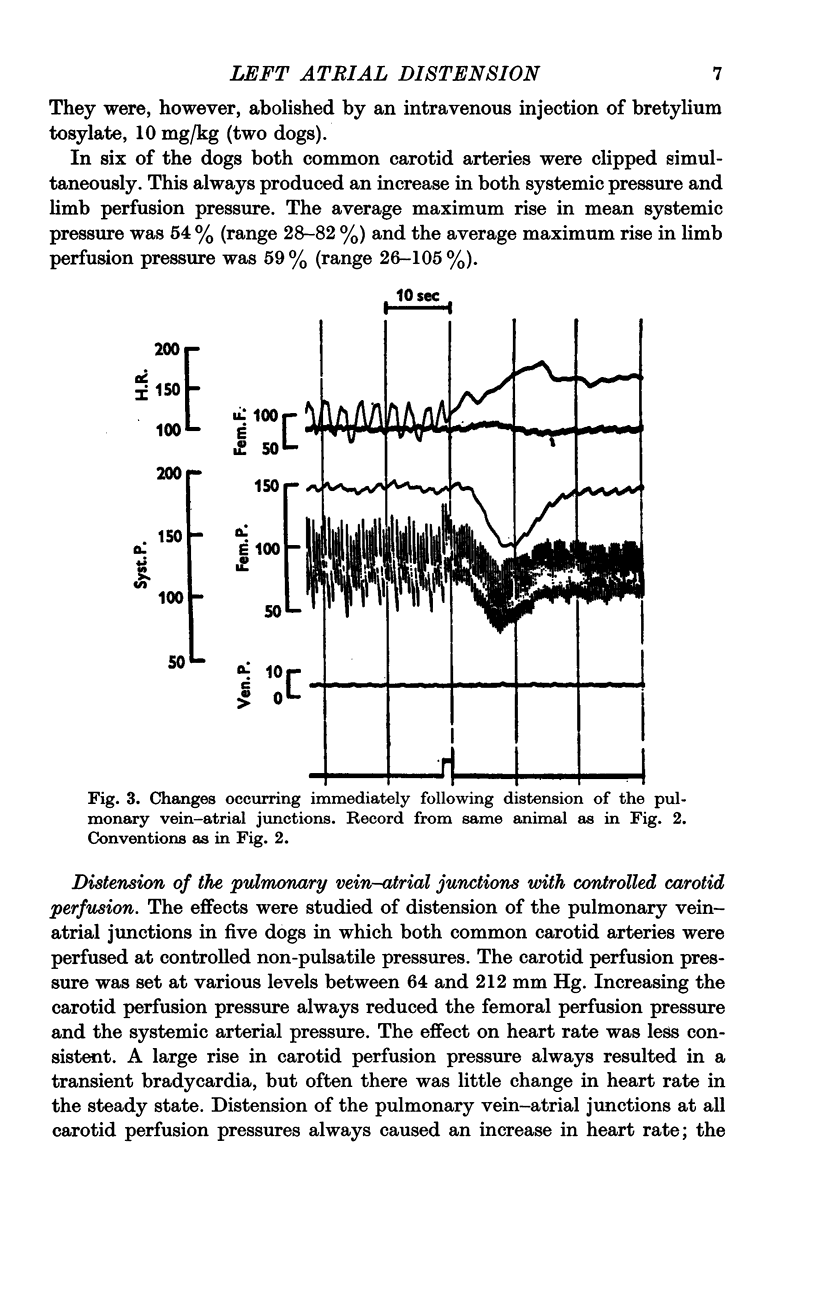
4. In about half of the experiments a transient vasodilatation was observed in the perfused hind limb, occurring immediately after distension of the pulmonary vein—atrial junctions and lasting about 22 sec.
5. The transient dilatation was due to a decrease in sympathetic vasoconstrictor nervous activity.
6. Stimulation of left atrial receptors causes an increase of sympathetic nervous activity to the heart but does not cause a corresponding increase in sympathetic nervous activity to the hind limbs.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIADO D. M., Jr, LI T. H., KALOW W., SCHMIDT C. F., TURNBULL G. L., PESKIN G. W., HESS M. E., WEISS A. J. Respiratory and circulatory reflexes from the perfused heart and pulmonary circulation of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1951 May;165(2):261–277. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.165.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AVIADO D. M., Jr, SCHMIDT C. F. Reflexes from stretch receptors in blood vessels, heart and lungs. Physiol Rev. 1955 Apr;35(2):247–300. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1955.35.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURA A. L., GREEN A. F. The actions of bretylium: adrenergic neurone blocking and other effects. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Dec;14:536–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLERIDGE J. C., HEMINGWAY A., HOLMES R. L., LINDEN R. J. The location of atrial receptors in the dog: a physiological and histological study. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):174–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAD H. W., GREEN J. H., NEIL E. A comparison of the effects of pulsatile and non-pulsatile blood flow through the carotid sinus on the reflexogenic activity of the sinus baroceptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1952 Dec;118(4):509–519. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDSOME J. R., LINDEN R. J. A REFLEX INCREASE IN HEART RATE FROM DISTENSION OF THE PULMONARY-VEIN-ATRIAL JUNCTIONS. J Physiol. 1964 Apr;170:456–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDSOME J. R., LINDEN R. J., NORMAN J. THE USE OF SYMPATHETIC BETA-RECEPTOR BLOCKING AGENTS IN THE INVESTIGATION OF REFLEX CHANGES IN HEART RATE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Jun;24:781–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledsome J. R., Linden R. J. The effect of distending a pouch of the left atrium on the heart rate. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):121–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J., Ledsome J. R., Linden R. J. A system for the measurement of respiratory and acid-base parameters in blood. Br J Anaesth. 1965 Jul;37(7):466–479. doi: 10.1093/bja/37.7.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves M. J. The respiratory response of the new-born lamb to inhaled CO-2 with and without accompanying hypoxia. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):78–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight P., Widdicombe J. G. Action potentials in afferent fibres from pericardial mechanoreceptors in the dog. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):259–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight P., Widdicombe J. G. Action potentials in fibres from receptors in the epicardium and myocardium of the dog's left ventricle. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):235–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


