Abstract
1. A study has been made of the binding of radioactively labelled ouabain by desheathed rabbit vagus nerves, which consist mainly of non-myelinated fibres. The corresponding inhibition of the electrogenic sodium pump was also measured.
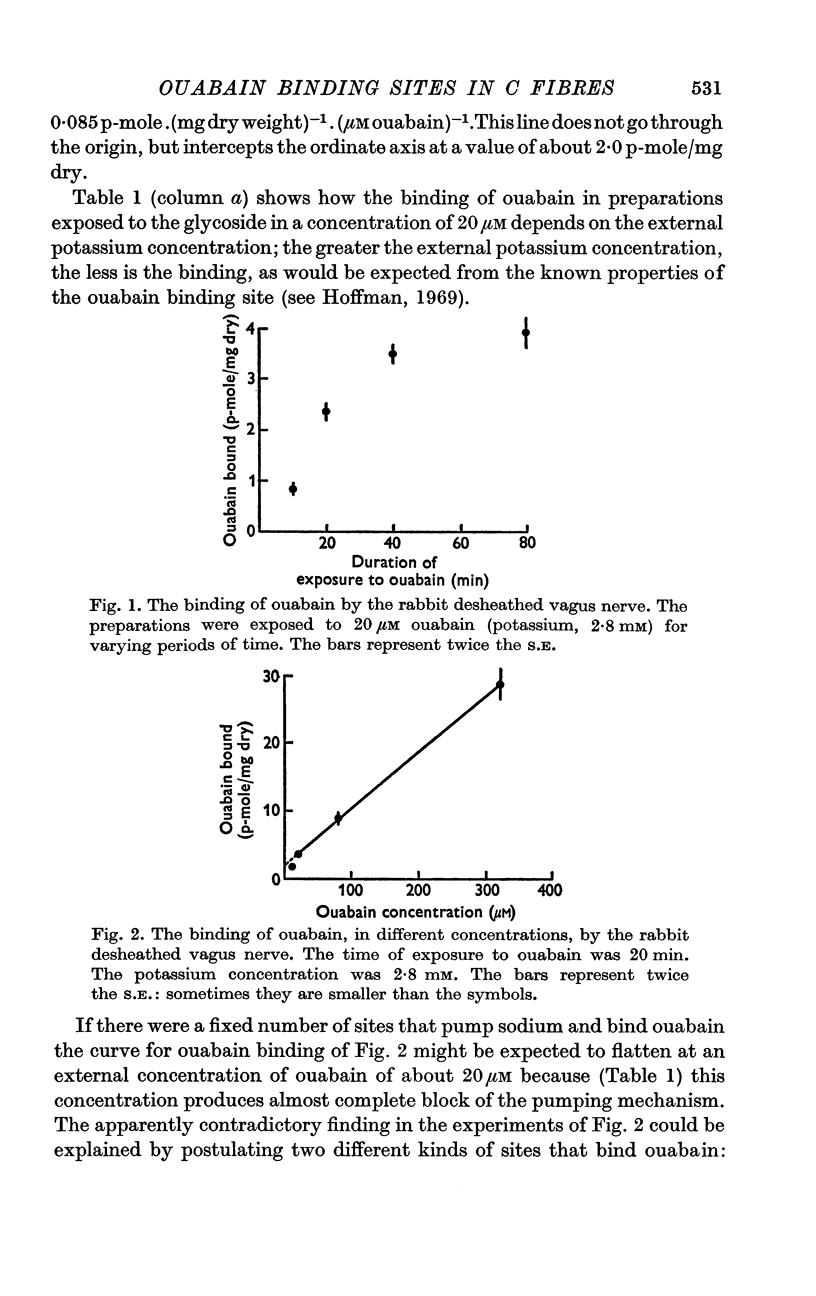
2. By varying the ouabain concentration and the external potassium concentration two kinds of binding sites could be distinguished: a first site specifically associated with pumping and whose ability to bind ouabain is dependent on the external presence of potassium; and a second site not associated with pumping and unaffected by external potassium.
3. Just complete inhibition of the sodium pumping mechanism is associated with a specific binding of ouabain of about 4·3 p-mole/mg dry nerve.
4. This gives an upper limit for the density of sodium pumping sites of about 750 per square micron.
5. The turnover rate (i.e. (cation pumped)/(number of sites)) at 20° C is about 22 sec-1.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Willis J. S. On the number of sodium pumping sites in cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):646–649. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Keynes R. D. Binding of tritiated digoxin to human red cell ghosts. Nature. 1969 Feb 22;221(5182):776–776. doi: 10.1038/221776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Ritchie J. M. The movements of labelled ions in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(2):333–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Narahashi T., Shaw T. I. An upper limit to the number of sodium channels in nerve membrane? J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):99–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. The ionic content of mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its alteration as a result of electrical activity. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):223–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog A., Ritchie J. M. A comparison of the effect of temperature, metabolic inhibitors and of ouabain on the electrogenic componen of the sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):523–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


