Abstract
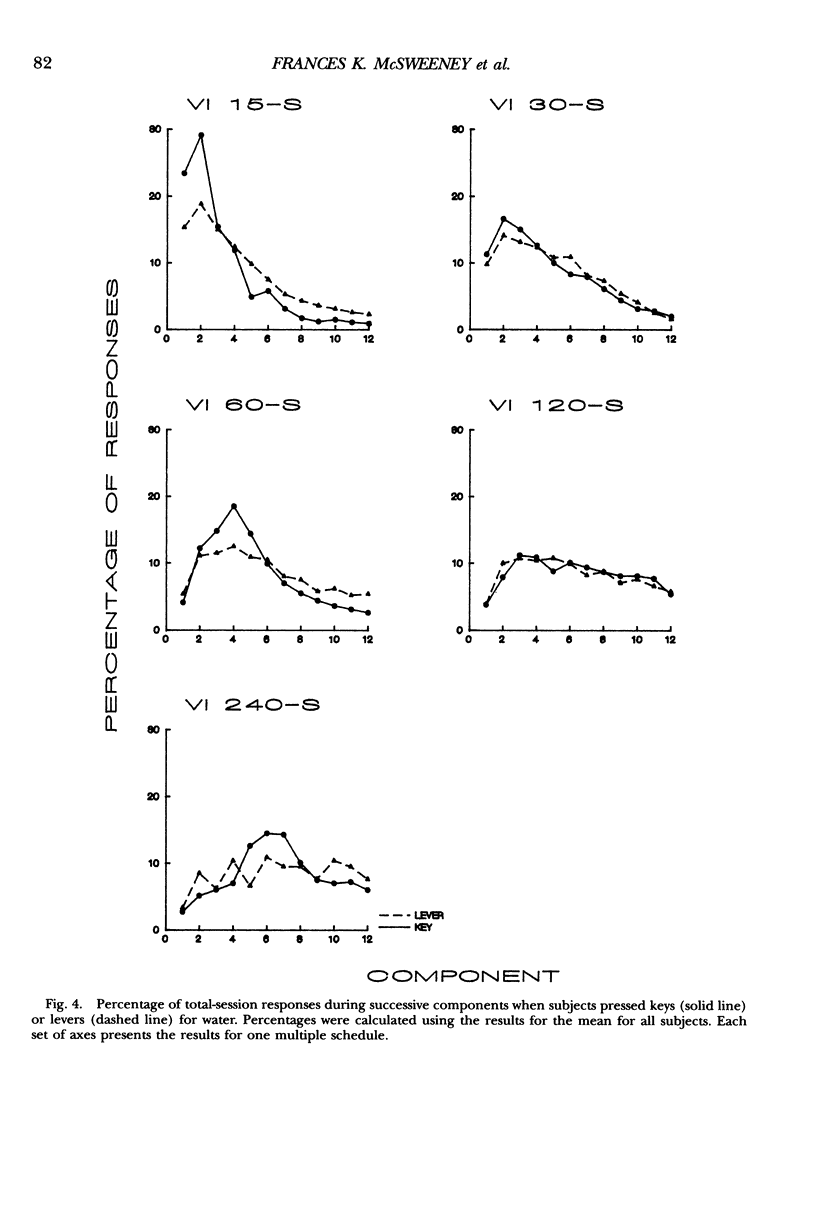
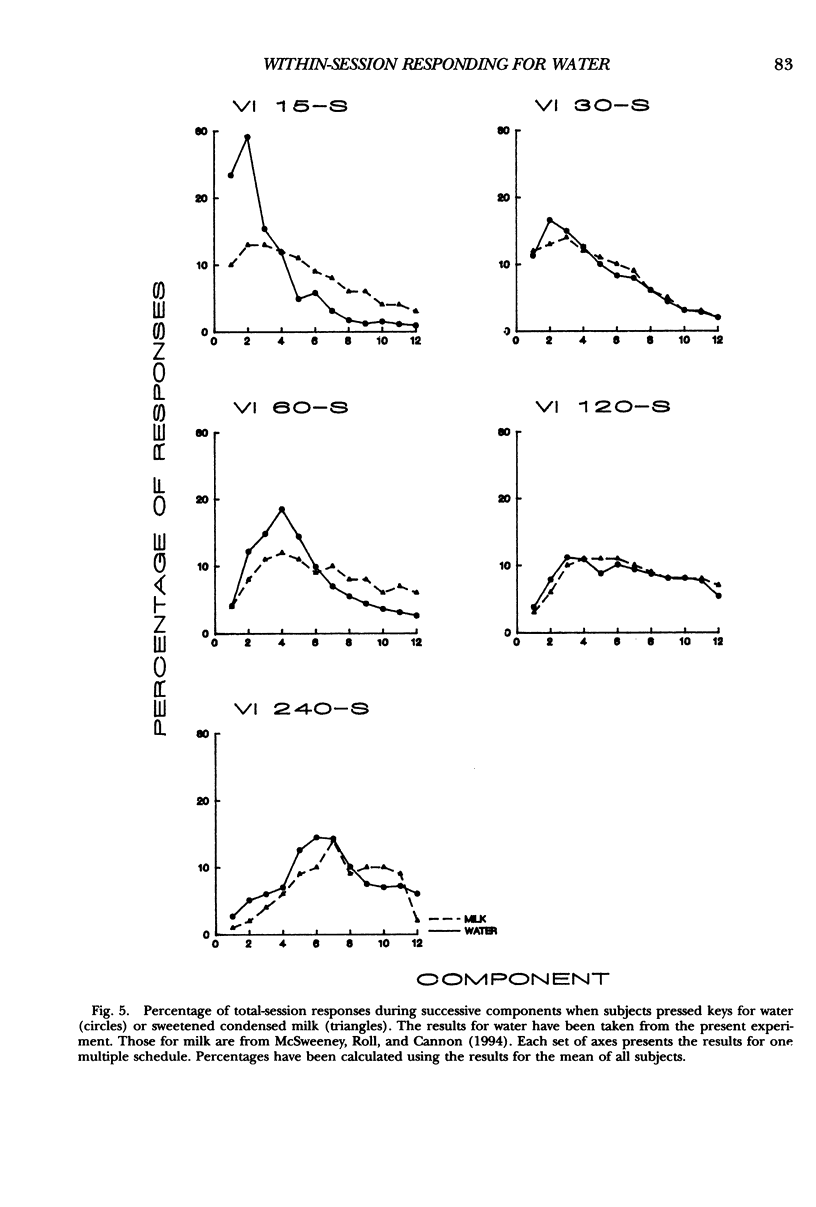
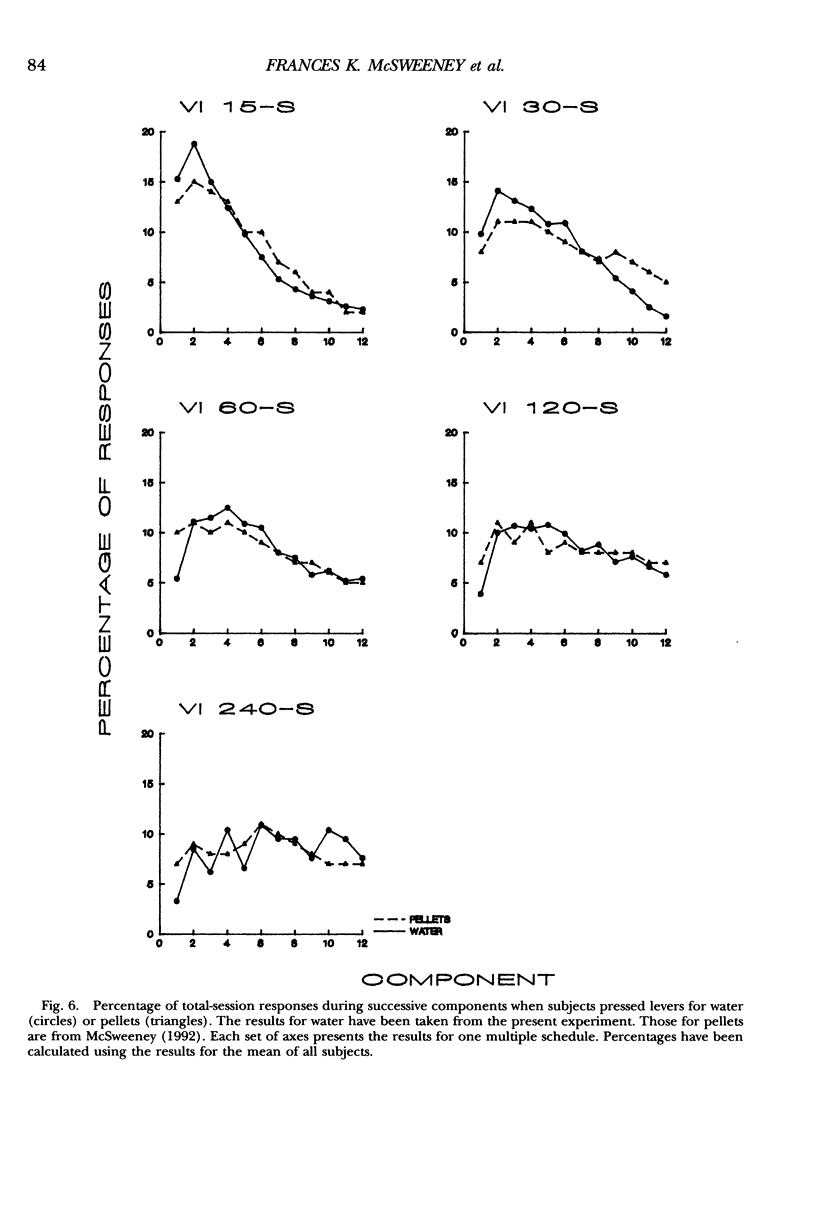
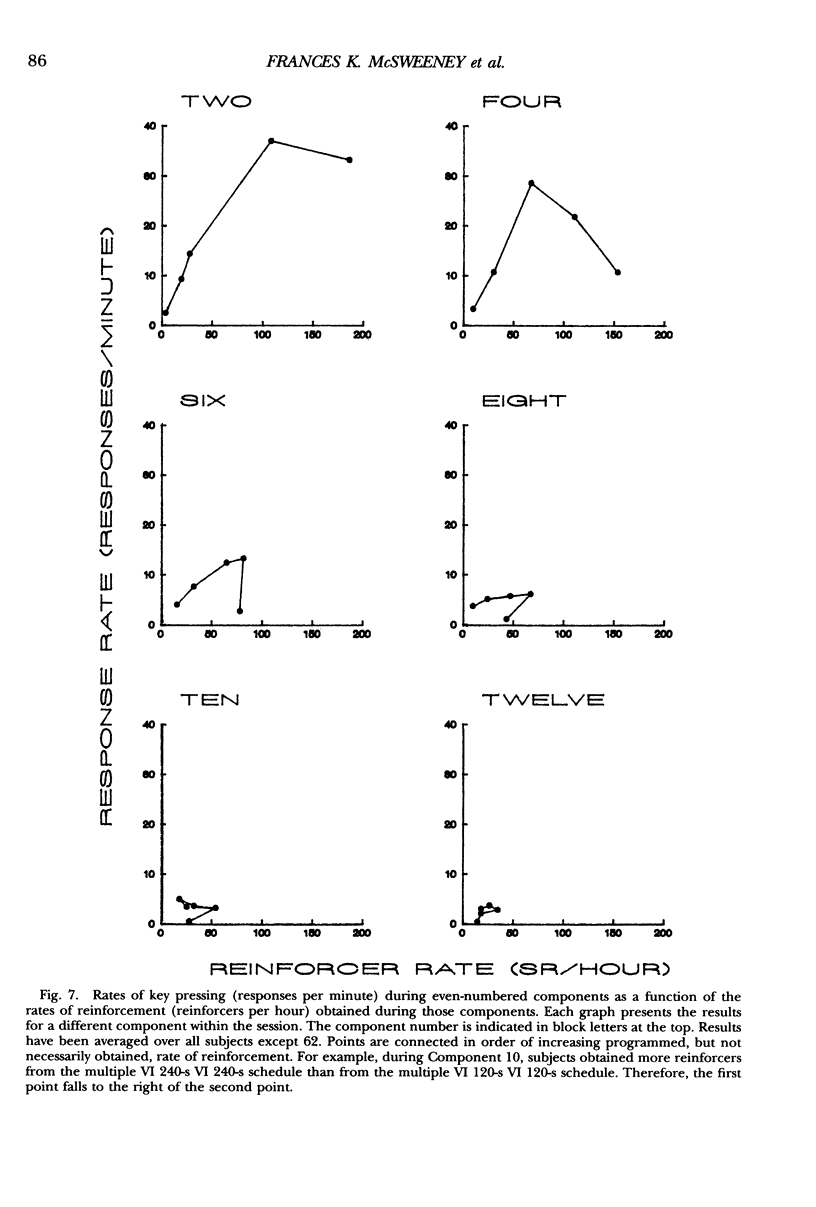
Rats pressed keys or levers for water reinforcers delivered by several multiple variable-interval schedules. The programmed rate of reinforcement varied from 15 to 240 reinforcers per hour in different conditions. Responding usually increased and then decreased within experimental sessions. As for food reinforcers, the within-session changes in both lever and key pressing were smaller, peaked later, and were more symmetrical around the middle of the session for lower than for higher rates of reinforcement. When schedules provided high rates of reinforcement, some quantitative differences appeared in the within-session changes for lever and key pressing and for food and water. These results imply that basically similar factors produce within-session changes in responding for lever and key pressing and for food and water. The nature of the reinforcer and the choice of response can also influence the quantitative properties of within-session changes at high rates of reinforcement. Finally, the results show that the application of Herrnstein's (1970) equation to rates of responding averaged over the session requires careful consideration.
Keywords: within-session patterns, multiple schedule, variable-interval schedule, food reinforcers, water reinforcers, key press, lever press, rats
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTERMAN M. E. PHYLETIC DIFFERENCES IN LEARNING. Am Psychol. 1965 Jun;20:396–410. doi: 10.1037/h0022328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Optimization and the matching law as accounts of instrumental behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Nov;36(3):387–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.36-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweeney F. K., Roll J. M. Responding changes systematically within sessions during conditioning procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1993 Nov;60(3):621–640. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1993.60-621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweeney F. K., Roll J. M., Weatherly J. N. Within-session changes in responding during several simple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1994 Jul;62(1):109–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1994.62-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


