Abstract
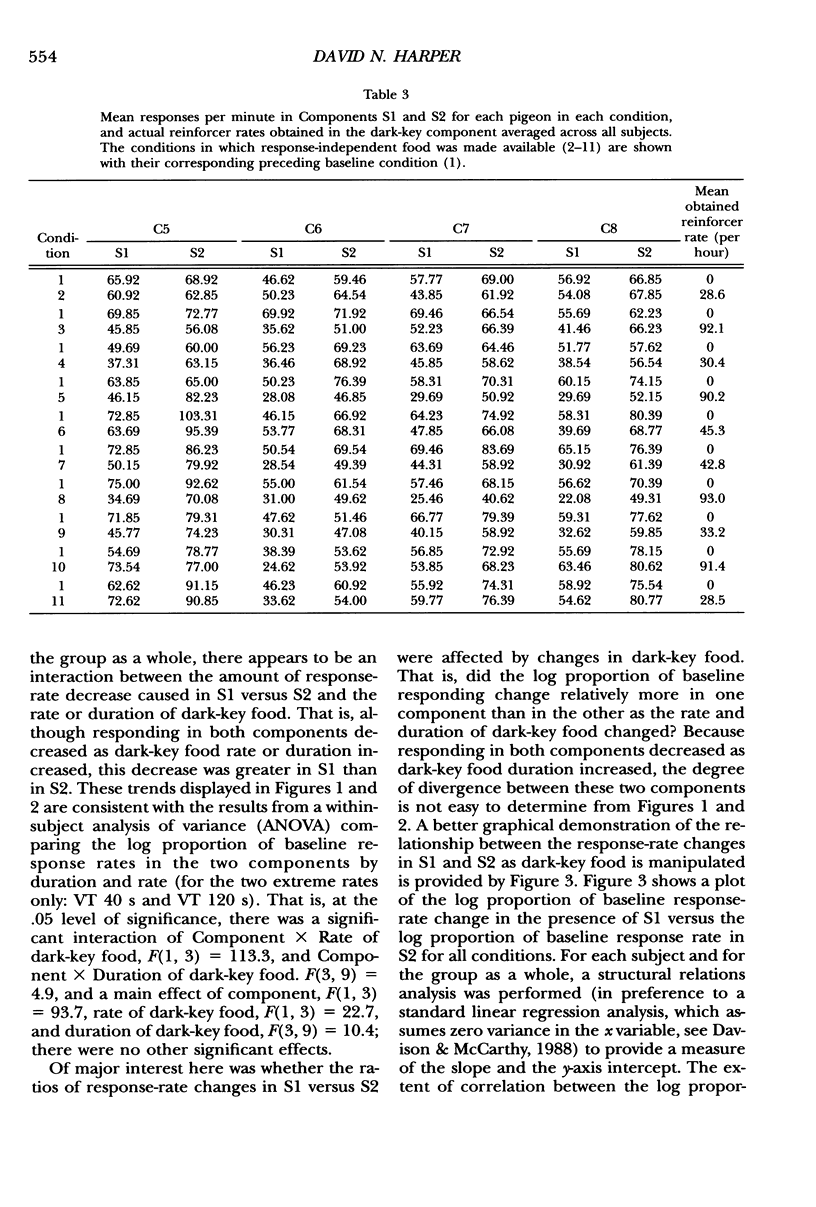
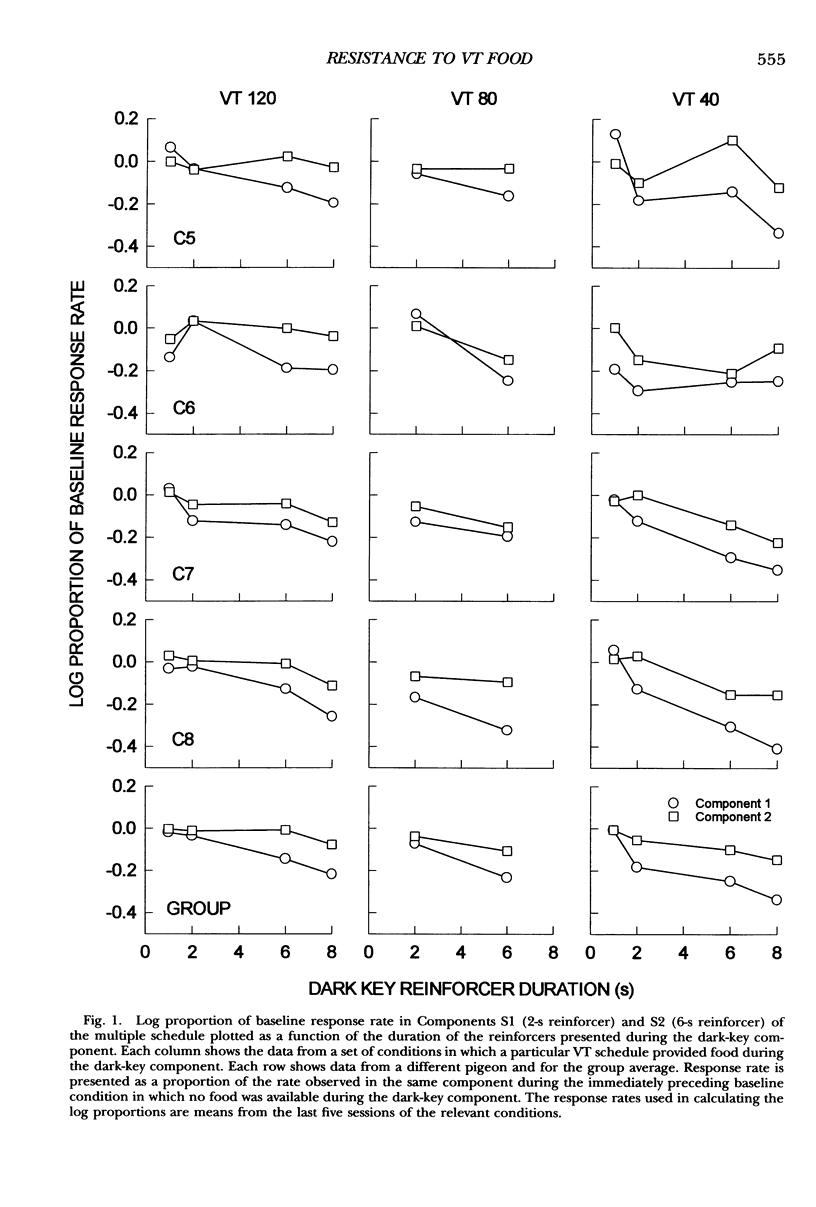
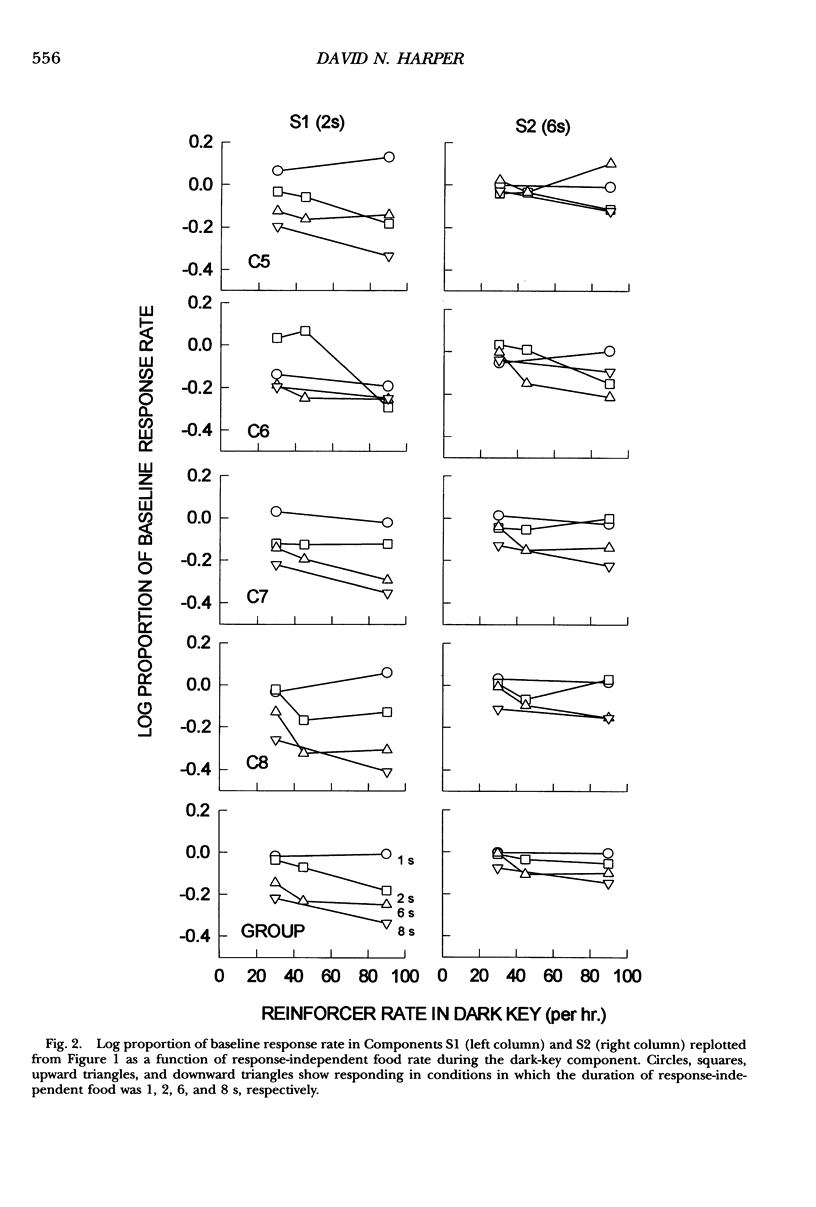
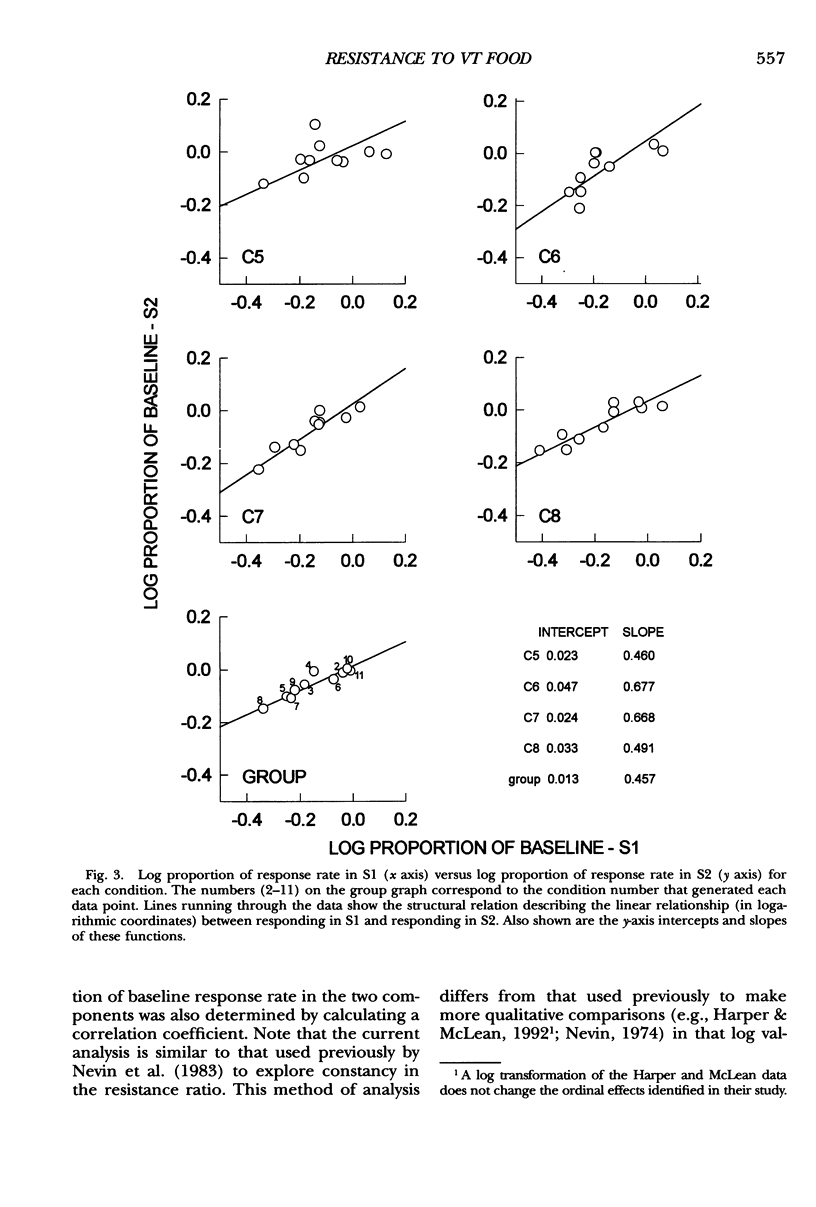
Response-independent food was delivered during a dark-key phase between two multiple-schedule components to explore its disruptive effects on responding. Responding in components was maintained by separate variable-interval 120-s schedules, with a 2-s reinforcer in Component 1 and a 6-s reinforcer in Component 2. Across conditions the rate and duration of response-independent food presentations were manipulated. The results showed that response rates in both components decreased as a function of the duration and the rate of response-independent food presentations; moreover, the decrease in response rate relative to the baseline level was larger in Component 1 than in Component 2. These findings were consistent with expectations from behavioral momentum theory, which predicts that if equal disruption (response-independent food in this case) is applied to responding in two components, then the ratio of response-rate change in Component 1 versus Component 2 should remain constant, irrespective of the magnitude of that disruption.
Keywords: behavioral momentum, resistance to change, multiple schedules, pigeons
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouzas A. The relative law of effect: effects of shock intensity on response strength in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Nov;30(3):307–314. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath S. J., Fields L., Malott M. K., Grossett D. Response rate, latency, and resistance to change. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Mar;39(2):267–274. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. N., McLean A. P. Resistance to change and the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1992 May;57(3):317–337. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1992.57-317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. An integrative model for the study of behavioral momentum. J Exp Anal Behav. 1992 May;57(3):301–316. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1992.57-301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Mandell C., Atak J. R. The analysis of behavioral momentum. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jan;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. On the form of the relation between response rates in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):237–248. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Tota M. E., Torquato R. D., Shull R. L. Alternative reinforcement increases resistance to change: Pavlovian or operant contingencies? J Exp Anal Behav. 1990 May;53(3):359–379. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1990.53-359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliskoff S. S., Shull R. L., Gollub L. R. The relation between response rates and reinforcement rates in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3):271–284. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


