Abstract
1. A study has been made of ATP splitting and ouabain binding to the sodium pump reconstituted from protein and phosphatidylserine.
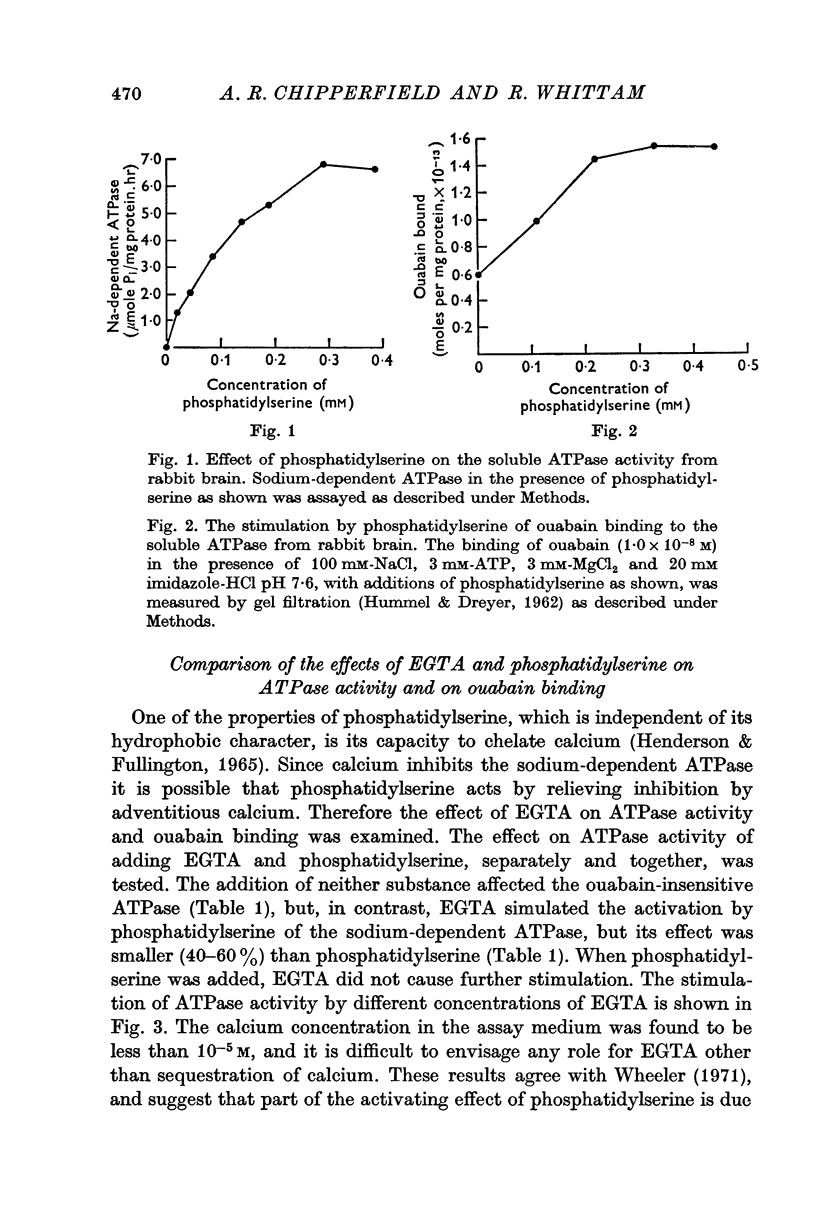
2. Ouabain was bound to protein alone, but when phosphatidylserine was added, binding was increased threefold. The stimulation resembled the course of activation of sodium-dependent ATPase activity.
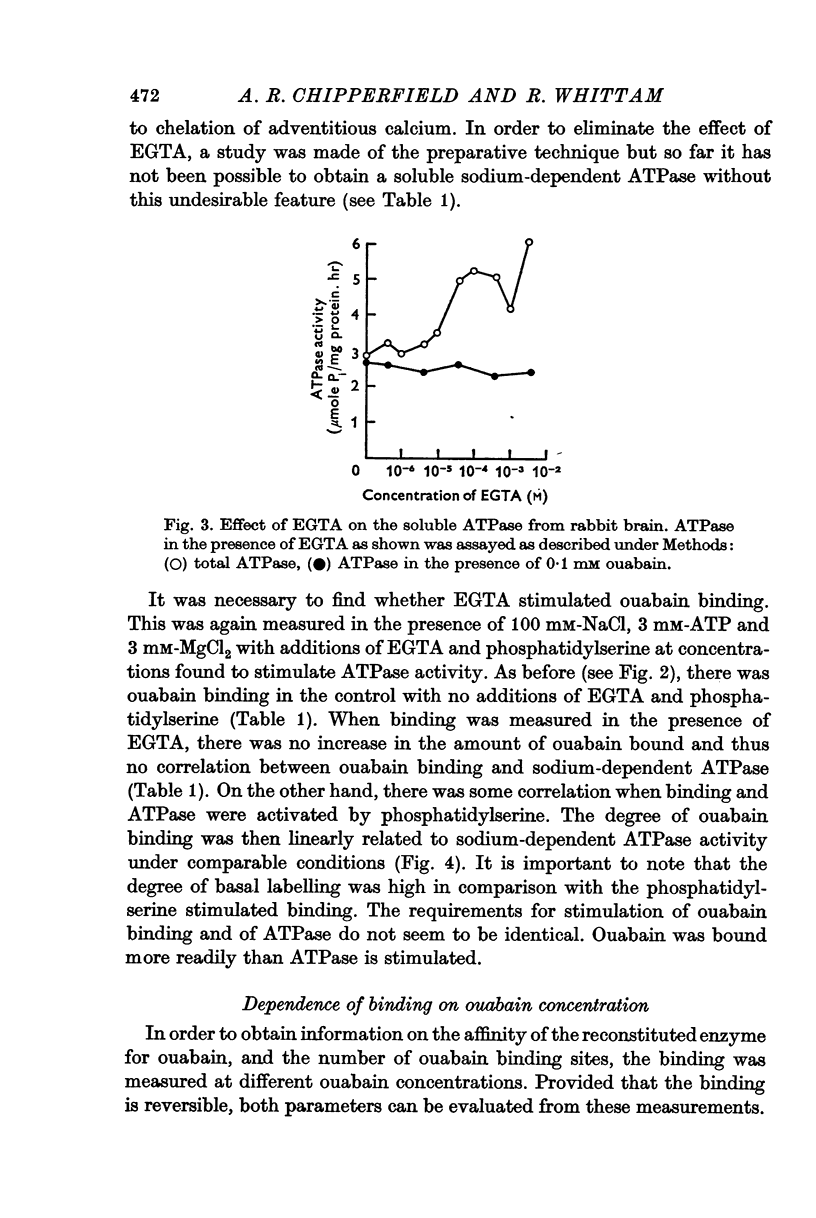
3. EGTA partly simulated the activation of ATPase by phosphatidylserine but did not enhance binding.
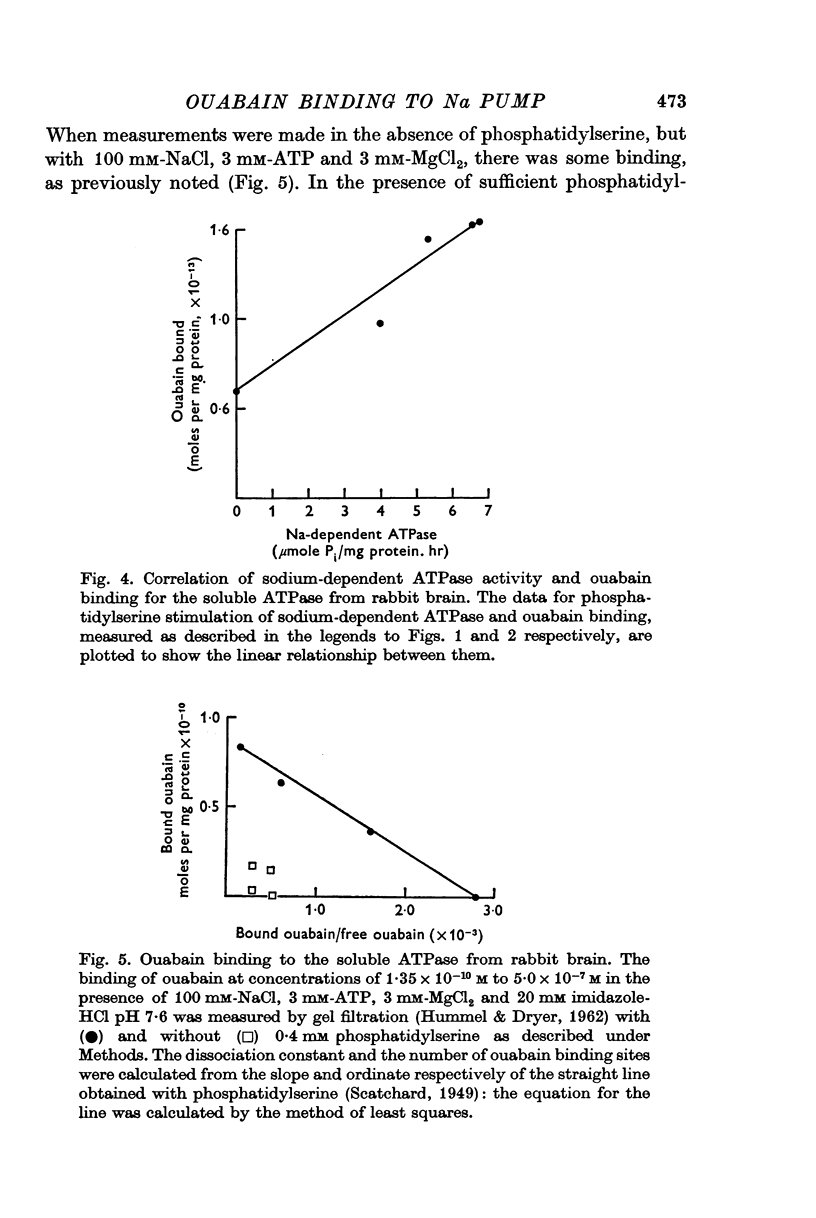
4. The dissociation constant for the enzyme-ouabain complex was 3·5 × 10-8 M. The turnover number (2,000 molecules of ATP per minute) and the number of receptor sites (3·8 × 1013 per mg protein) were calculated.
5. The results provide further evidence of the involvement of phosphatidylserine in the action of the sodium pump.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Willis J. S. Binding of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to intact cells. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenster L. J., Copenhaver J. H., Jr Phosphatidyl serine requirement of (Na+-K+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from rat kidney and brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):406–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. The relationship between G-strophanthin-binding capacity and ATPase activity in plasma-membrane fragments from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):122–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. S., Fullington J. G. Stabilities of metal complexes of phospholipids: Ca(II), Mg(II), and Ni(II) complexes of phosphatidylserine and triphosphoinositide. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1599–1605. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestland R. N., Whittam R. The temperature dependence of activation by phosphatidylserine of the sodium pump adenosine triphosphatase. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(2):353–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R., Strickland K. P. Role of phospholipid in the activation of Na+, Ka+-activated adenosine triphosphatase of beef brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Sep;111(3):583–592. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Iida S. The binding of ouabain to Na + -K + -dependent ATPase treated with phospholipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):831–833. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler K. P., Whittam R. The involvement of phosphatidylserine in adenosine triphosphatase activity of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):303–328. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R., Wheeler K. P. Transport across cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:21–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


