Abstract
1. The ouabain-sensitive component of Na efflux and K influx amount to 58 and 72% respectively. Taking into account also (a) the diffusional passive fluxes of Na (5%) and K (13%), as estimated by Ussing's equation and (b) the ouabain-insensitive Na-Na exchange (28%), 85% (K) and 90% (Na) of the measured total fluxes can be accounted for.
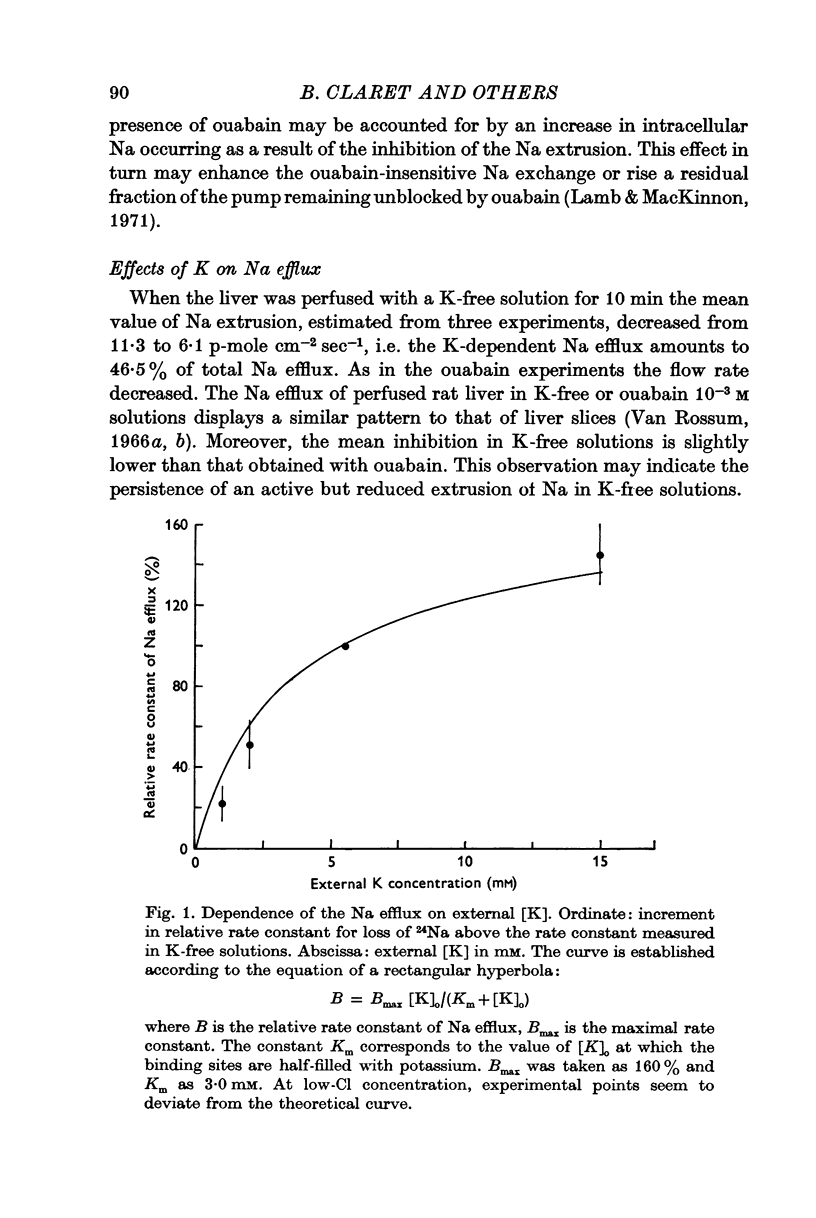
2. Na efflux is diminished when K is partially or totally removed from the medium. This effect is reversible, indicating probably activation of the Na pump by external K.
3. The coupling ratio of Na and K ouabain-sensitive fluxes is equal to 1·58, suggesting that three Na ions are removed from and two K ions are carried into the cell in one cycle of the pump. Hence, in liver cell membranes, the Na pump must be electrogenic.
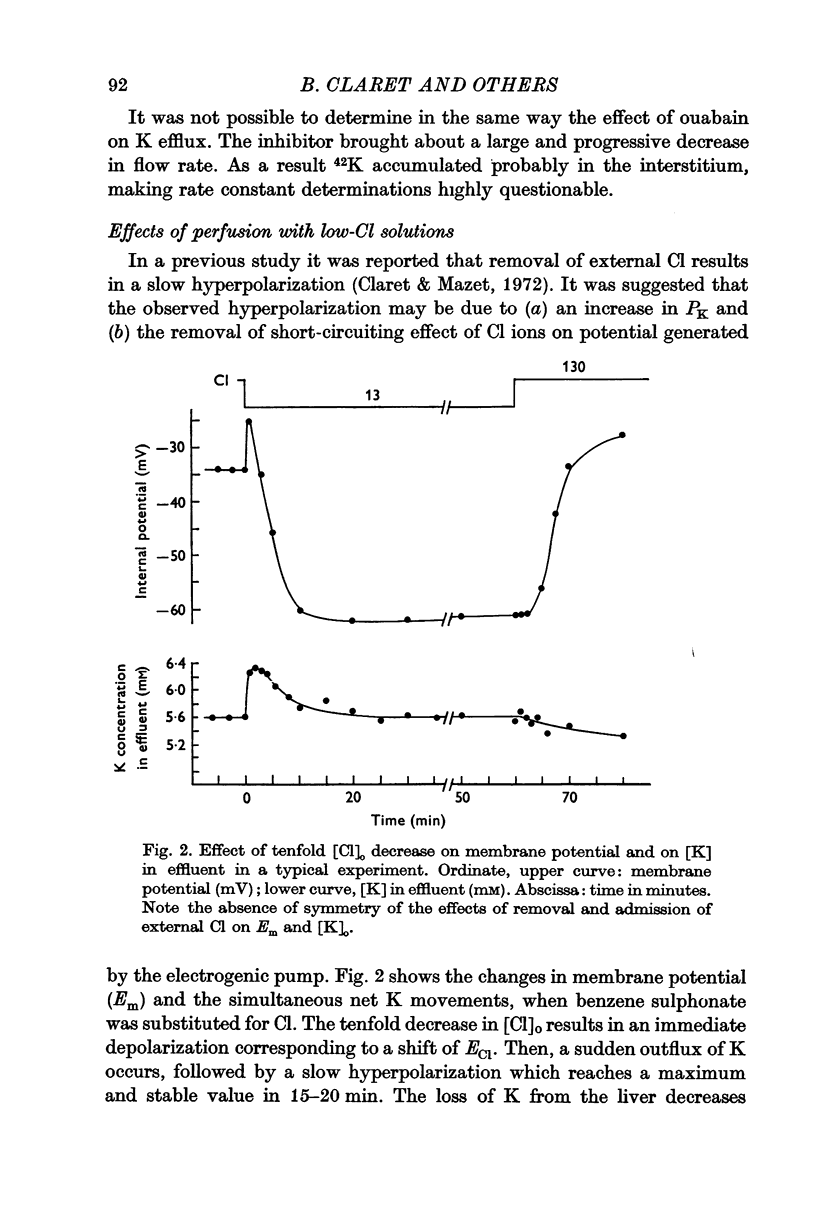
4. A tenfold decrease in [Cl]o by substitution with an impermeant anion results in a membrane hyperpolarization and a decrease in [Cl]i. Cl loss from the liver is compensated by an equivalent loss of intracellular K to preserve electroneutrality.
5. The measurement of passive fluxes indicates that Cl removal from the perfusing solutions increases PK but does not alter PNa.
6. Addition of ouabain brings about a depolarization which is three times greater in low-Cl solutions (21·9 mV) than in normal-Cl solutions (6·8 mV).
7. It is concluded that hyperpolarization which develops when Cl ions are removed can be accounted for entirely by (a) the increase in PK, (b) the increase of the contribution of the electrogenic pump to membrane potential.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Slayman C. L. Membrane potential and conductance during transport of sodium, potassium and rubidium in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):970–1014. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Keynes R. D., Manil J., Shaw T. I., Steinhardt R. A. The ouabain-sensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):459–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Levitan H. Salicylate: effect on membrane permeability of molluscan neurons. Science. 1971 Jun 18;172(3989):1245–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beigelman P. M., Thomas L. J., Jr Liver cell potentials: in vitro effects of metabolic inhibitors, cardiac glycosides, and hormones. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(2):181–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01868101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L. Canalicular bile formation in the isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1156–1163. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. The distribution of chloride ions in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):225–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Coraboeuf E. Membrane potential of perfused and isolated rat liver. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):137P–138P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Mazet J. L. Ionic fluxes and permeabilities of cell membranes in rat liver. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):279–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claret M., Mazet J. L. Perméabilités au potassium, au sodium et chlore des membranes de cellules hépatiques. J Physiol (Paris) 1971;63(6):190A–190A. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELOT P., BOS C. J., BENEDETTI E. L., RUEMKE P. STUDIES ON PLASMA MEMBRANES. I. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND ENZYME CONTENT OF PLASMA MEMBRANES ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:126–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECKMANN K. D., PARSONS D. S. Changes in the water and electrolyte content of rat-liver slices in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Nov;36:203–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Active transport of cations in giant axons from Sepia and Loligo. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):28–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Steinhardt R. A. The components of the sodium efflux in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Oct;198(3):581–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. On the mechanism of fluid exchange of tissues in vitro. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj0620241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. F., MacKinnon M. G. Effect of ouabain and metabolic inhibitors on the Na and K movements and nucleotide contents of L cells. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):665–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambotte L. Hepatic cell membrane potential a new assay for preserved organs viability. Eur Surg Res. 1970;2(4):241–250. doi: 10.1159/000127520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., NODA K. THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM-FREE SOLUTIONS ON THE MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF FROG MUSCLE FIBERS. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:117–132. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J., Jr Potassium fluxes in dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jun;53(6):704–740. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.6.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieth J. O. Effect of some monovalent anions on chloride and sulphate permeability of human red cells. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):581–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Withrow C. D., Woodbury D. M. Effects of nephrectomy and KC1 on transmembrane potentials, intracellular electrolytes, and cell pH of rat muscle and liver in vivo. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):117–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Withrow C. D., Woodbury D. M. Effects of ouabain and diphenylhydantoin on transmembrane potentials, intracellular electrolytes, and cell pH of rat muscle and liver in vivo. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):101–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


