Abstract
1. The effects of Mn on the electrical and mechanical properties of frog muscle fibres have been studied.
2. In normal saline 10 or 20 mM-Mn hyperpolarized the fibres and had no effect on the membrane resistance. In isotonic K2SO4 saline, Mn increased the membrane resistance indicating that this agent reduced the conductance to K.
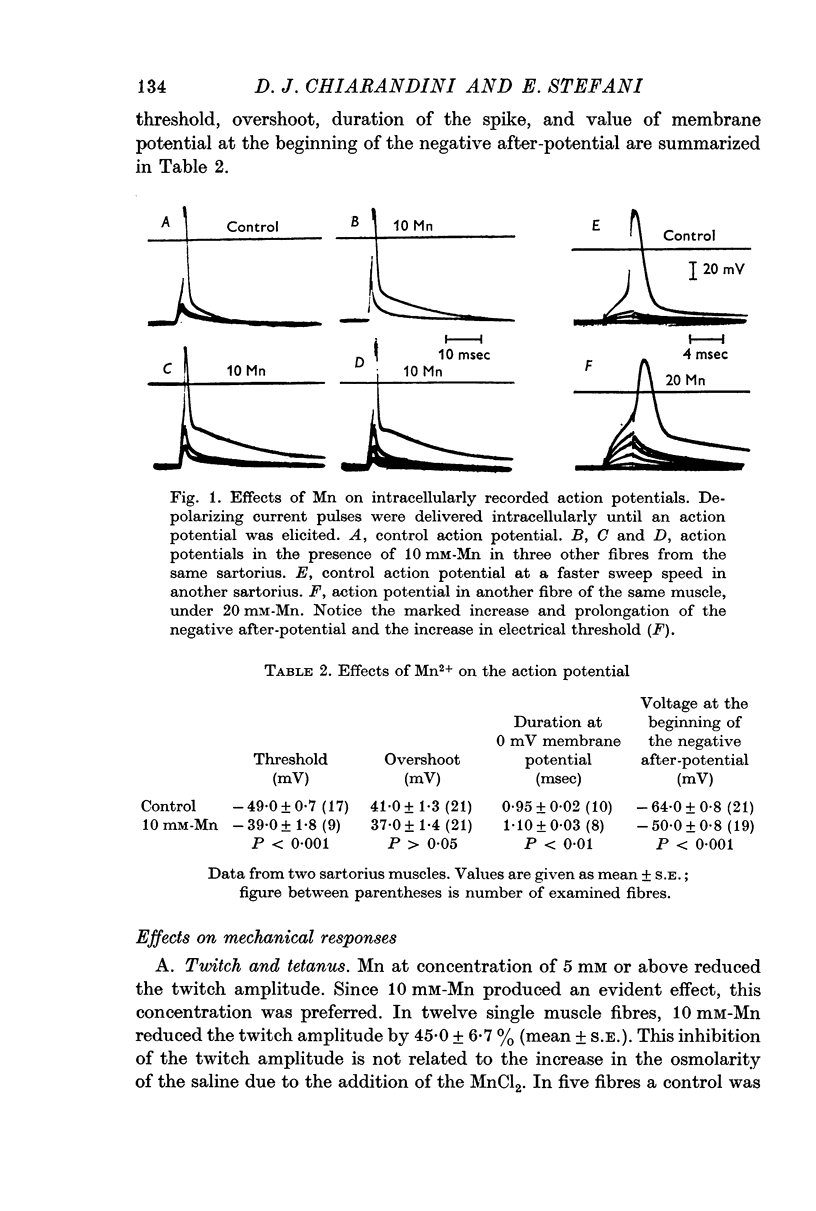
3. The action potential is prolonged by Mn while the overshoot amplitude is unaffected. The threshold of the action potential is shifted to more positive values of membrane potential.
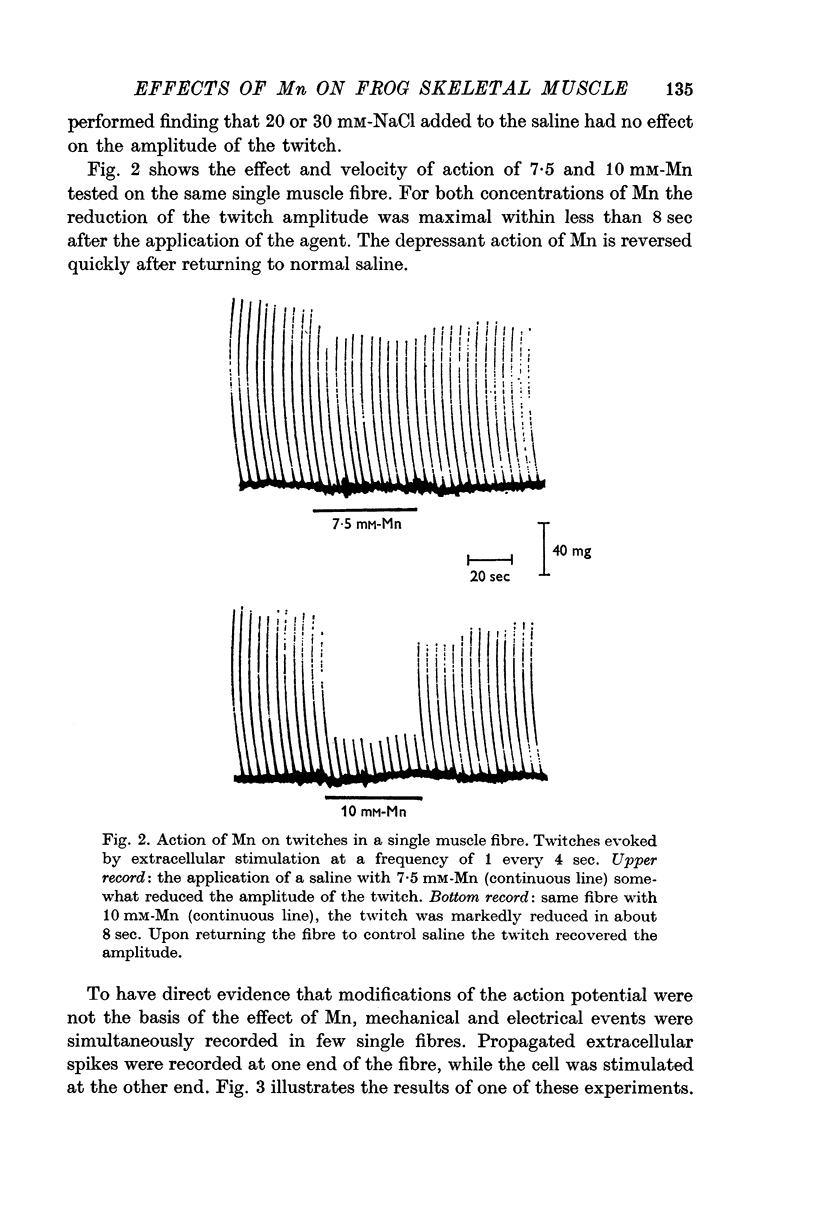
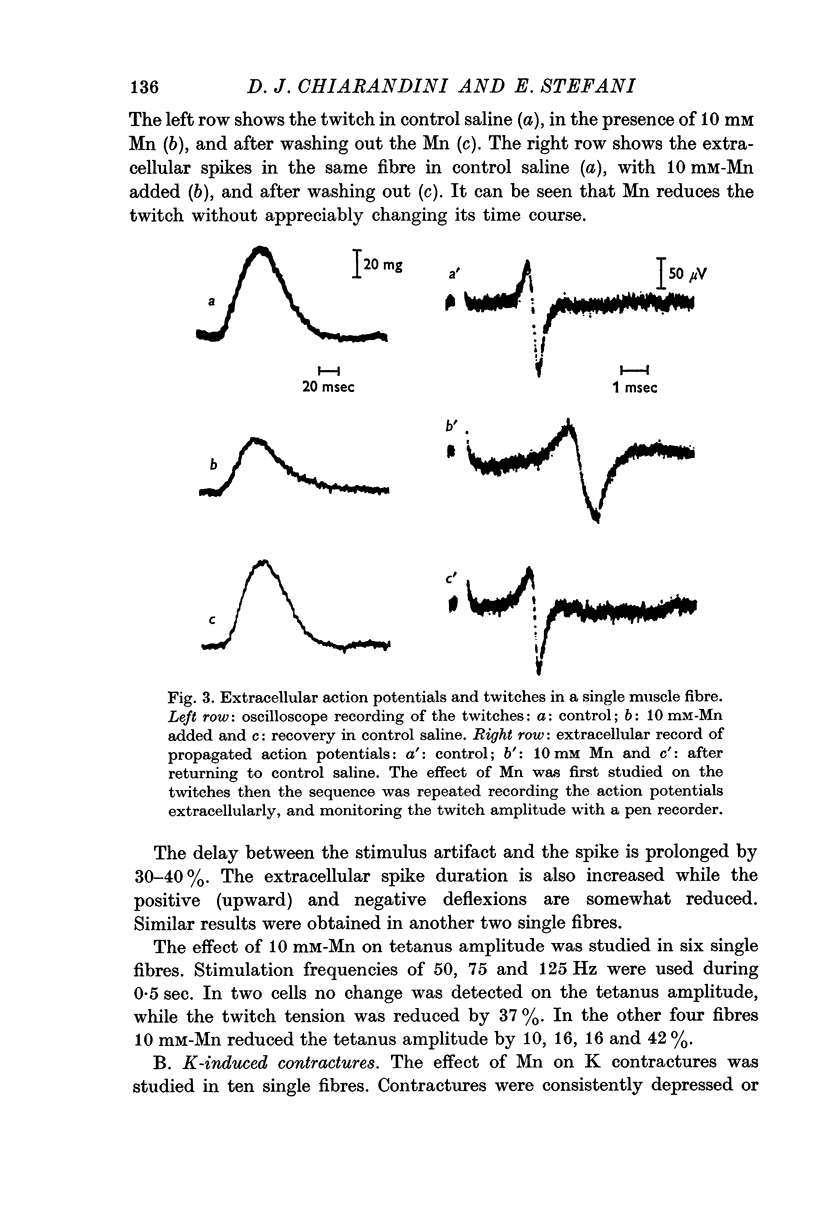
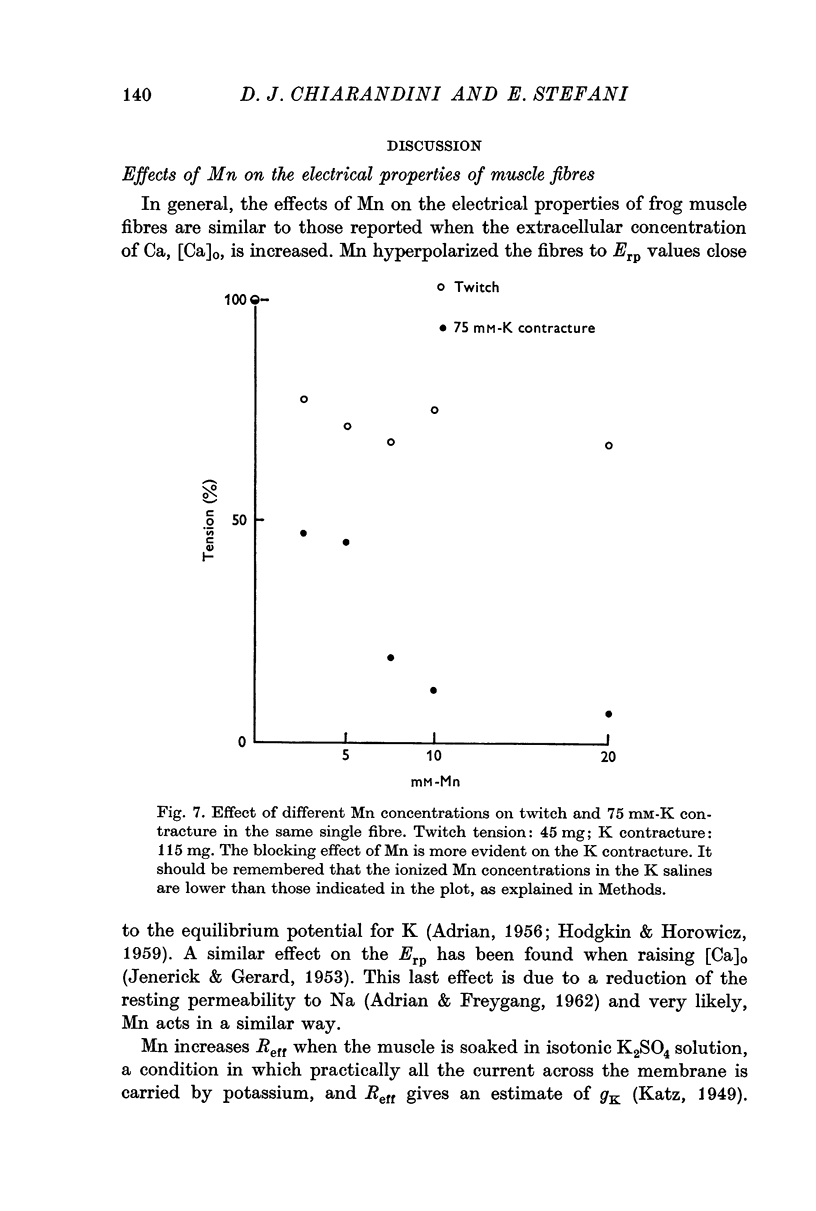
4. The isometric twitch is reduced by 45% in 10 mM-Mn; this effect is observed within 8 sec of the application.
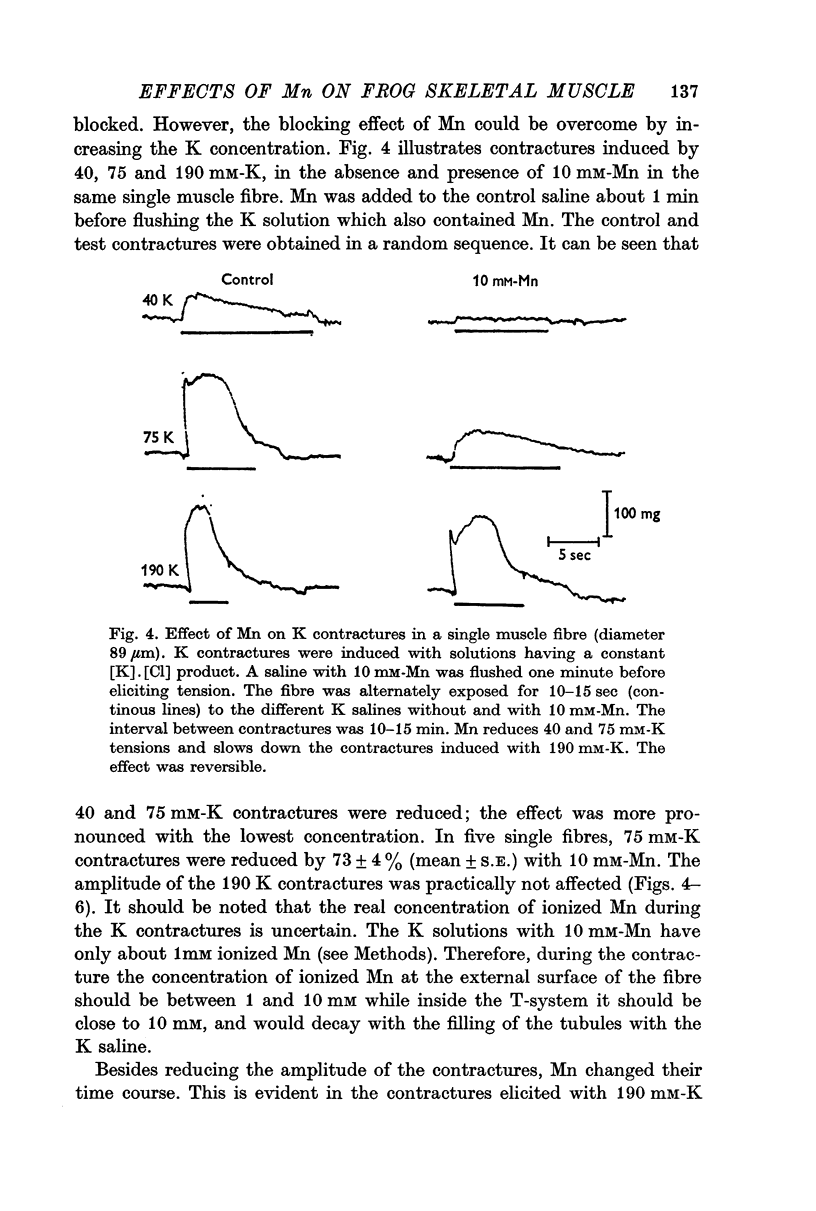
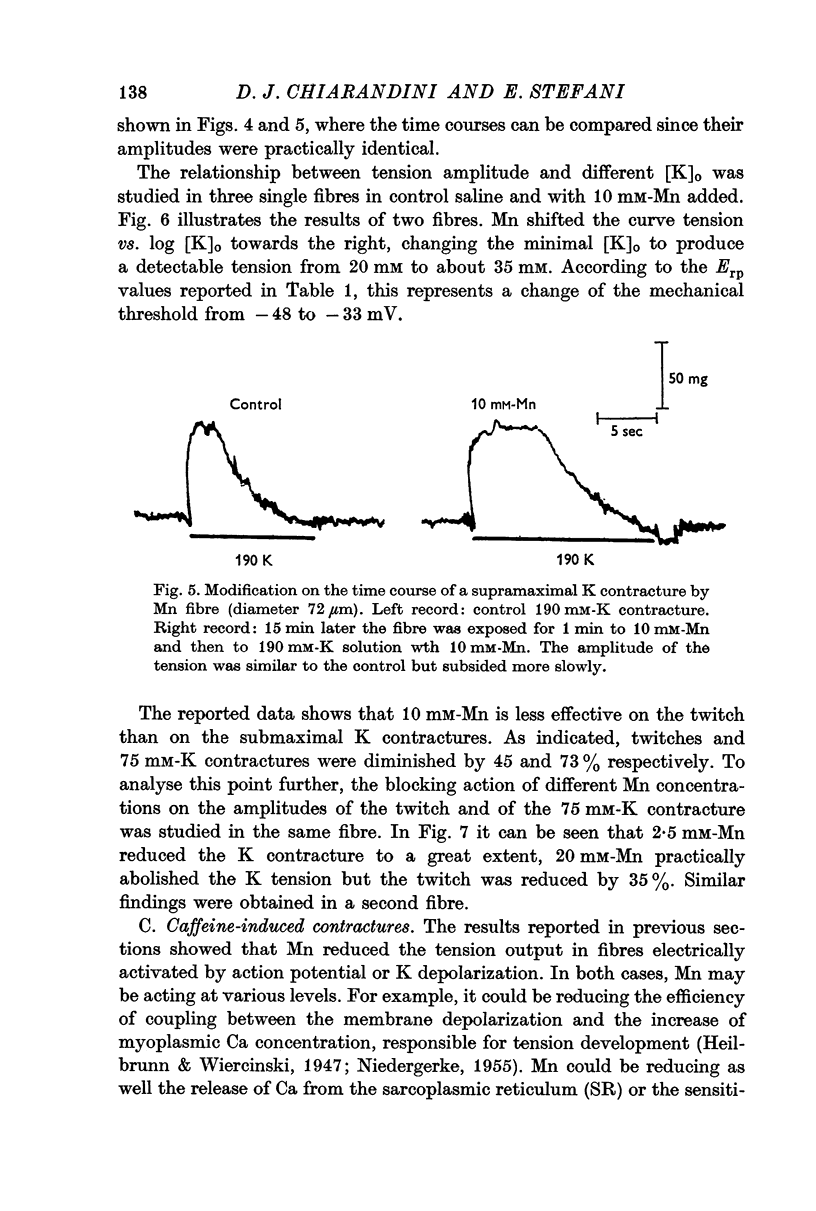
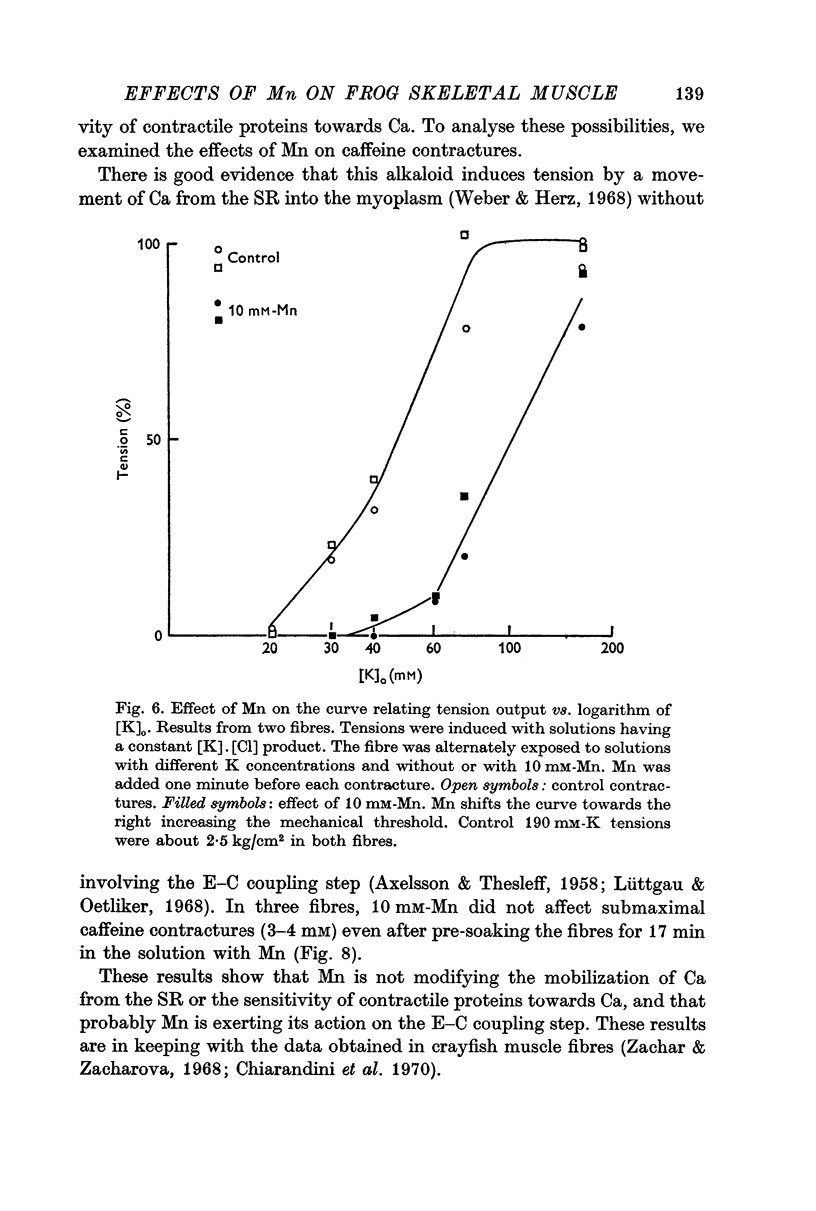
5. Mn (10 mM) reduced K contractures induced by 40 or 75 mM-K (constant [K].[Cl] product) and shifted to the right in a parallel manner the curve tension vs. log K concentration. The calculated mechanical threshold for K contractures was shifted from -48 to -33 mV.
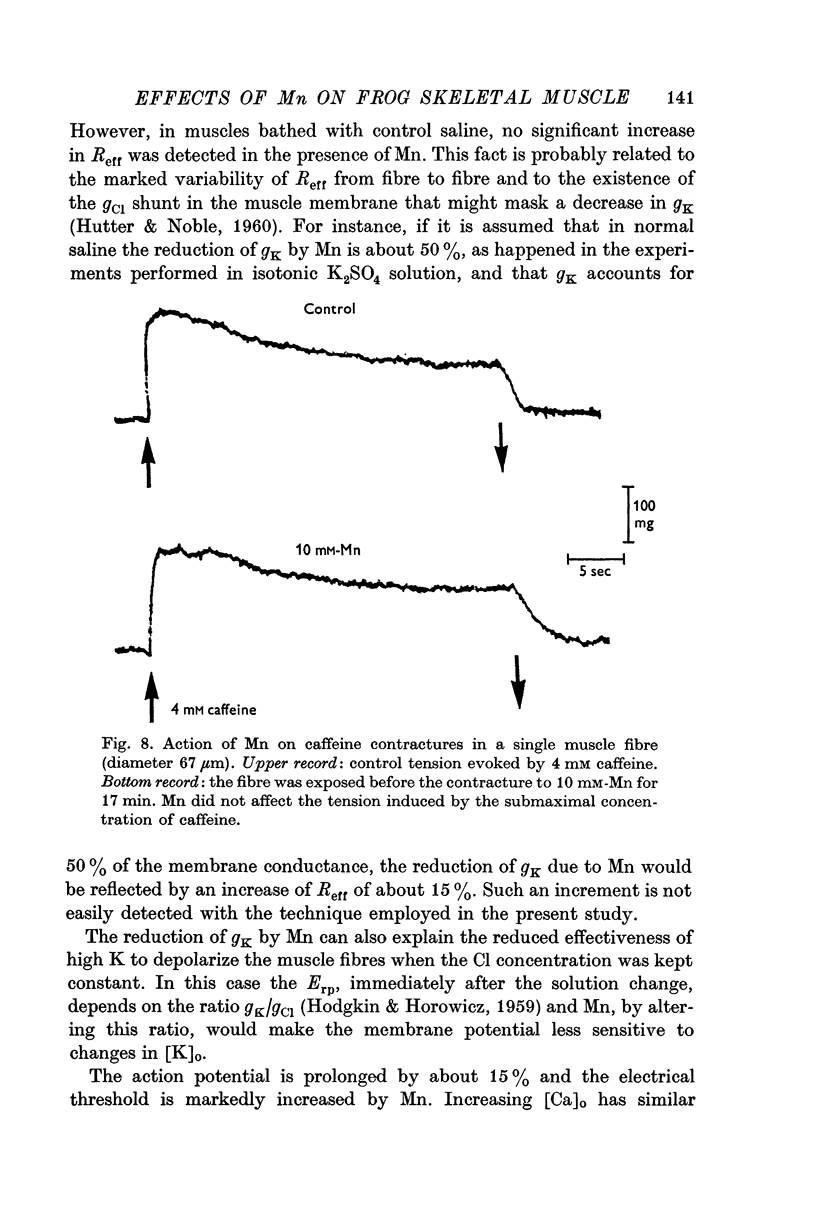
6. Caffeine contractures (3-4 mM) and supramaximal K contractures (190 mM-K) were unaffected by 10 mM indicating that contractile proteins and the ability of the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release Ca are not impaired.
7. It is concluded that Mn is mainly affecting the excitation-contraction coupling by altering the mechanical threshold. Since Mn reduces the permeability to Ca in several excitable membranes, it is suggested that the mechanical threshold depends on the entry of Ca to the muscle.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. Activation of the contractile mechanism in striated muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 28;44(1):55–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCHI C. P., SHANES A. M. Calcium influx in skeletal muscle at rest, during activity, and during potassium contracture. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):803–815. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Two phases of calcium entry during the action potential in giant axons of Loligo. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):80P–82P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C. P., Bolton T. C. Action of local anesthetics on coupling systems in muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Aug;157(2):388–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C. P. The Effect of Caffeine on Radiocalcium Movement in Frog Sartorius. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May 1;44(5):845–858. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Reuben J. P., Girardier L., Katz G. M., Grundfest H. Effects of caffeine on crayfish muscle fibers. II. Refractoriness and factors influencing recovery (repriming) of contractile responses. J Gen Physiol. 1970 May;55(5):665–687. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The effect o f calcium on contraction and conductance thresholds in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):119–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Lorkovic H. The roles of calcium in excitation-contraction coupling in various muscles of the frog, mouse, and barnacle. Am Zool. 1967 Aug;7(3):615–622. doi: 10.1093/icb/7.3.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINSTEIN M. B. INHIBITION OF CAFFEINE RIGOR AND RADIOCALCIUM MOVEMENTS BY LOCAL ANESTHETICS IN FROG SARTORIUS MUSCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:151–172. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Intracellular calcium movements in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):21–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser B., Lännergren J. The effect of calcium on the mechanical response of single twitch muscle fibres of Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Mar;69(3):242–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The effect of nitrate and other anions on the mechanical response of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:404–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. The chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Membrane properties of the barnacle muscle fiber. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):1015–1024. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistracher P., Hunt C. C. The relation of membrane changes ot contraction in twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):589–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIKO N., SATO M. The effect of calcium ions on electrical properties of striated muscle fibres. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Mar 15;7(1):51–63. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENERICK H. P., GERARD R. W. Membrane potential and threshold of single muscle fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1953 Aug;42(1):79–102. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030420106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Livengood D. R., Werman R. Correlation of transmitter release with membrane properties of the presynaptic fiber of the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2579–2601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETTGAU H. C. THE ACTION OF CALCIUM IONS ON POTASSIUM CONTRACTURES OF SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:679–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in helix pomatia neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1968;304(3):215–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00592126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORKAND R. K. Chemical inhibition of contraction in directly stimulated crayfish muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1962 Oct;164:103–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Garnier D., Gargouil Y. M., Coraboeuf E. Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):91–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00587018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOW A., TAYLOR S. R., ISAASON A., SEGUIN J. J. ELECTROCHEMICAL COUPLING IN POTENTIATION OF MUSCULAR CONTRACTION. Science. 1964 Feb 7;143(3606):577–579. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3606.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini-Smith S., Holland W. C. Influence of manganese and ouabain on the rate of action of calcium on atrial contractions. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):244–248. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Sep;17(3):265–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:87–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A., Taylor S. R., Preiser H. Role of the action potential in excitation-contraction coupling. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1116–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K. Permeability changes associated with the action potential in procaine-treated crayfish abdominal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Mar;50(4):1049–1074. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. R., Preiser H., Sandow A. Mechanical threshold as a factor in excitation-contraction coupling. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Sep;54(3):352–368. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.3.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G. B., Bianchi C. P. The effect of potassium concentration on Ca45 uptake in frog sartorius muscle. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Jun;65(3):385–392. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030650312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad S. The intracellular site of calcium activaton of contraction in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):77–88. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


