Abstract
1. The effect of age and androgen level on enzyme activity and cellular structure has been determined in the mouse submaxillary gland.
2. A new protease which resembles chymotrypsin in its substrate specificity has been characterized in the gland.
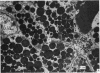
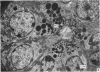
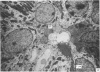
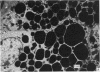
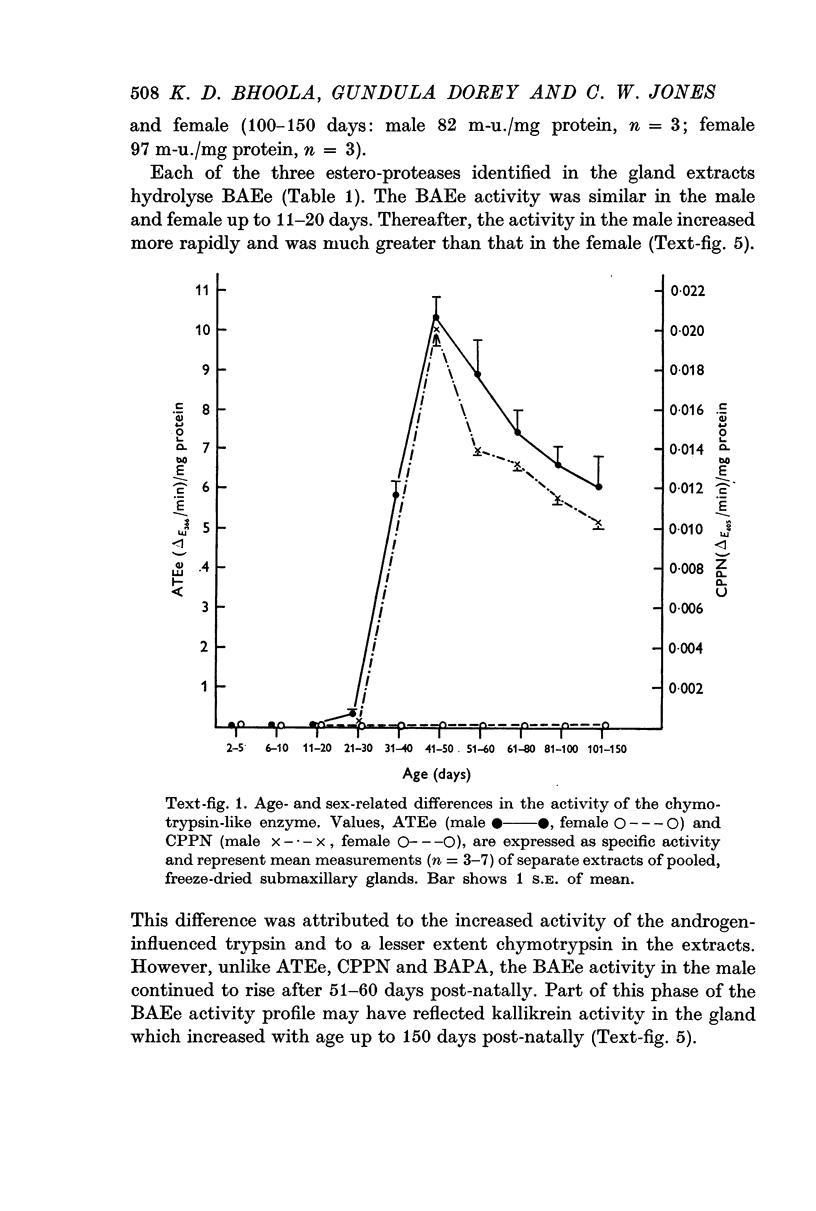
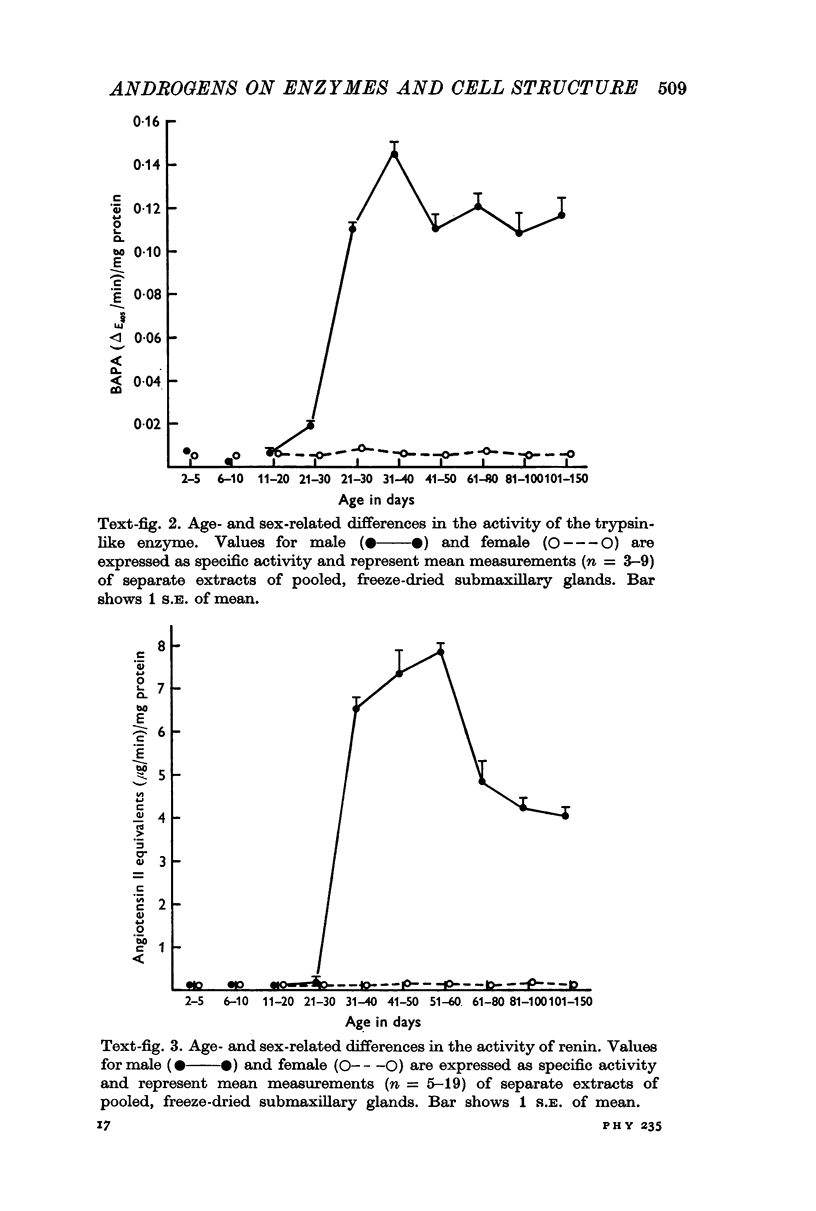
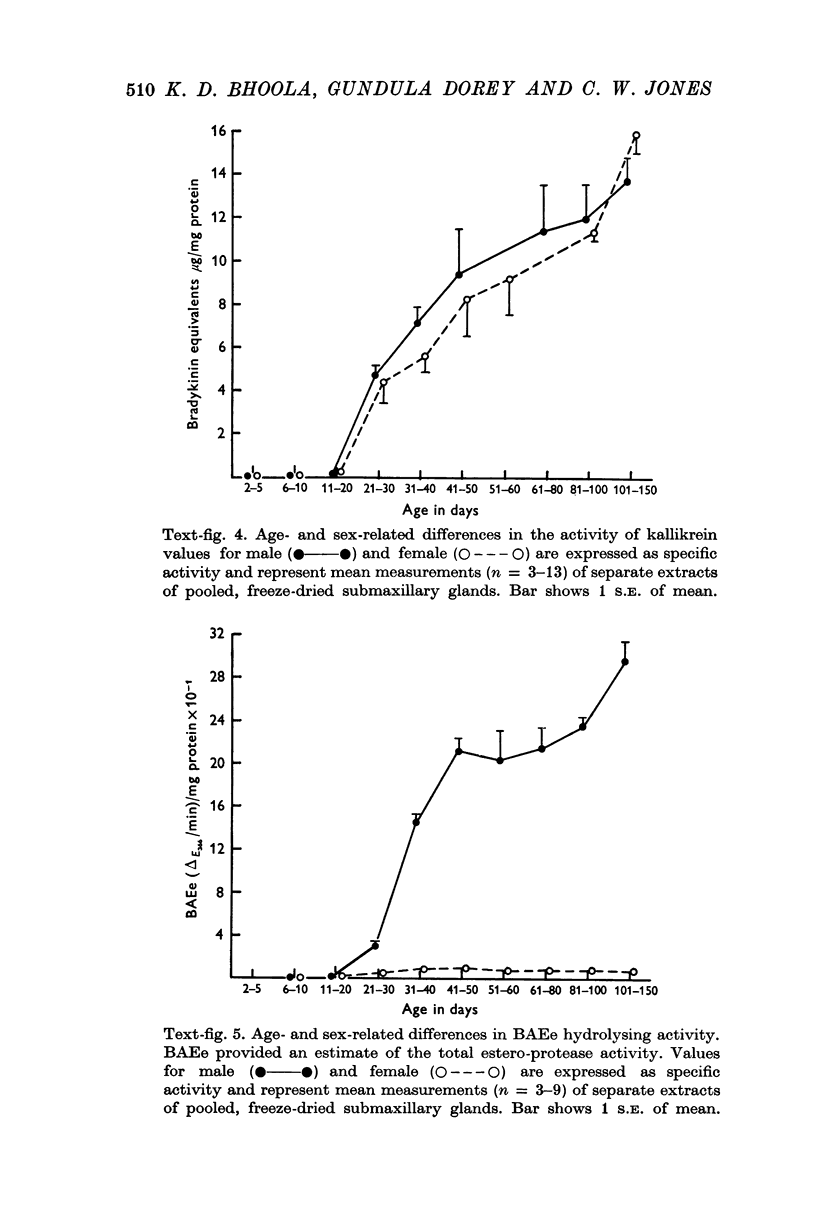
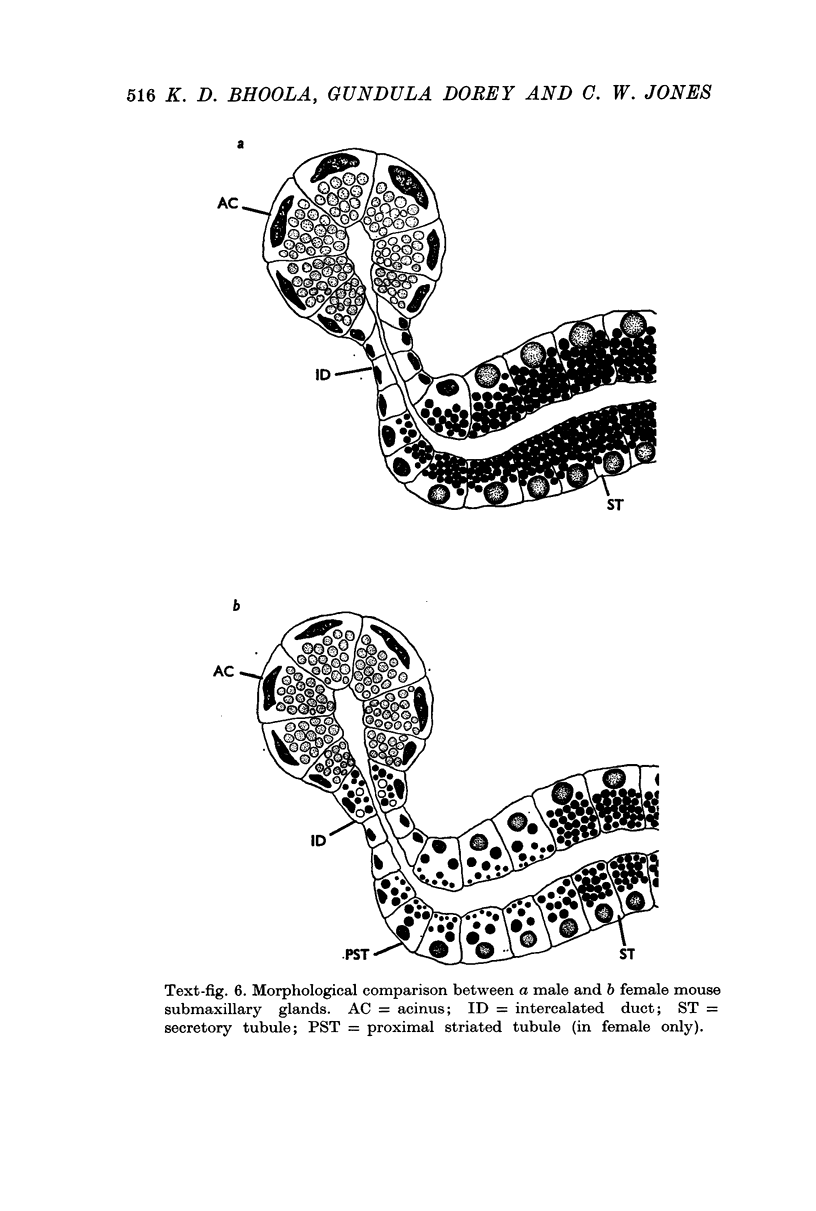
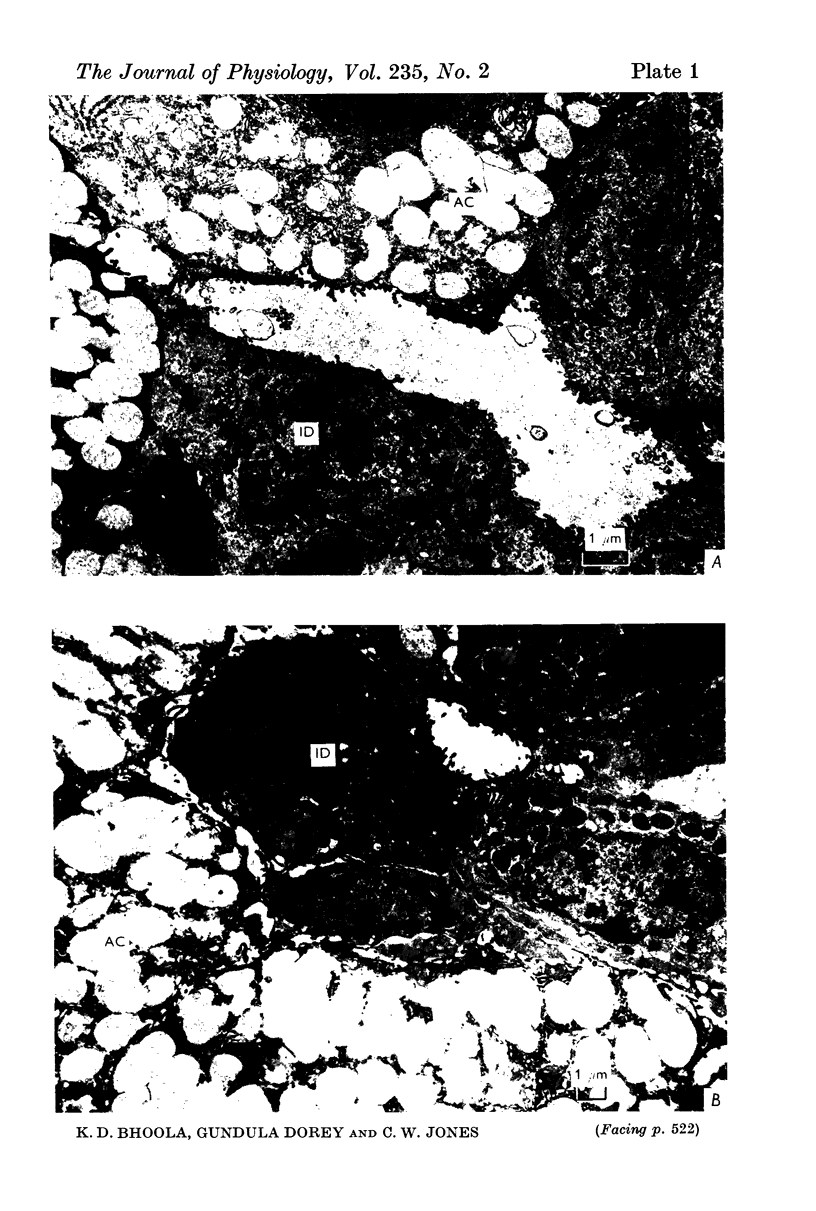
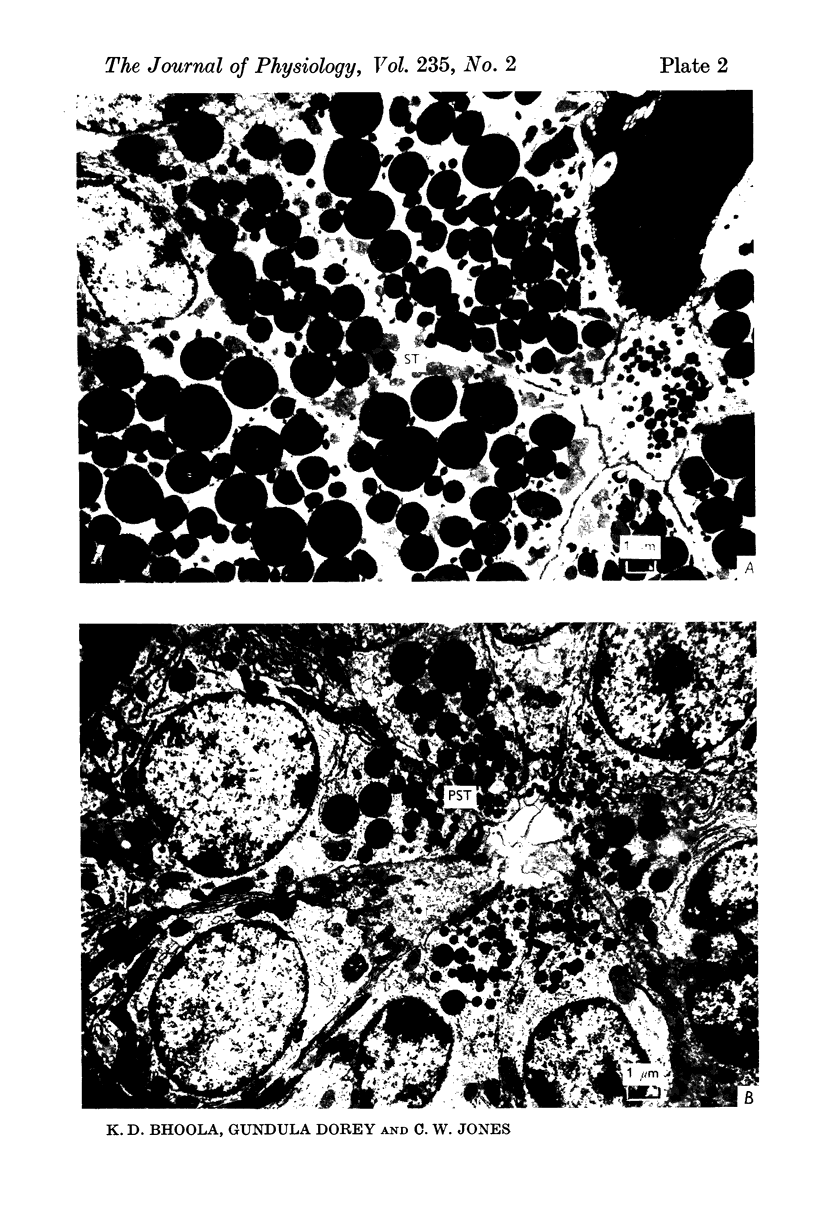
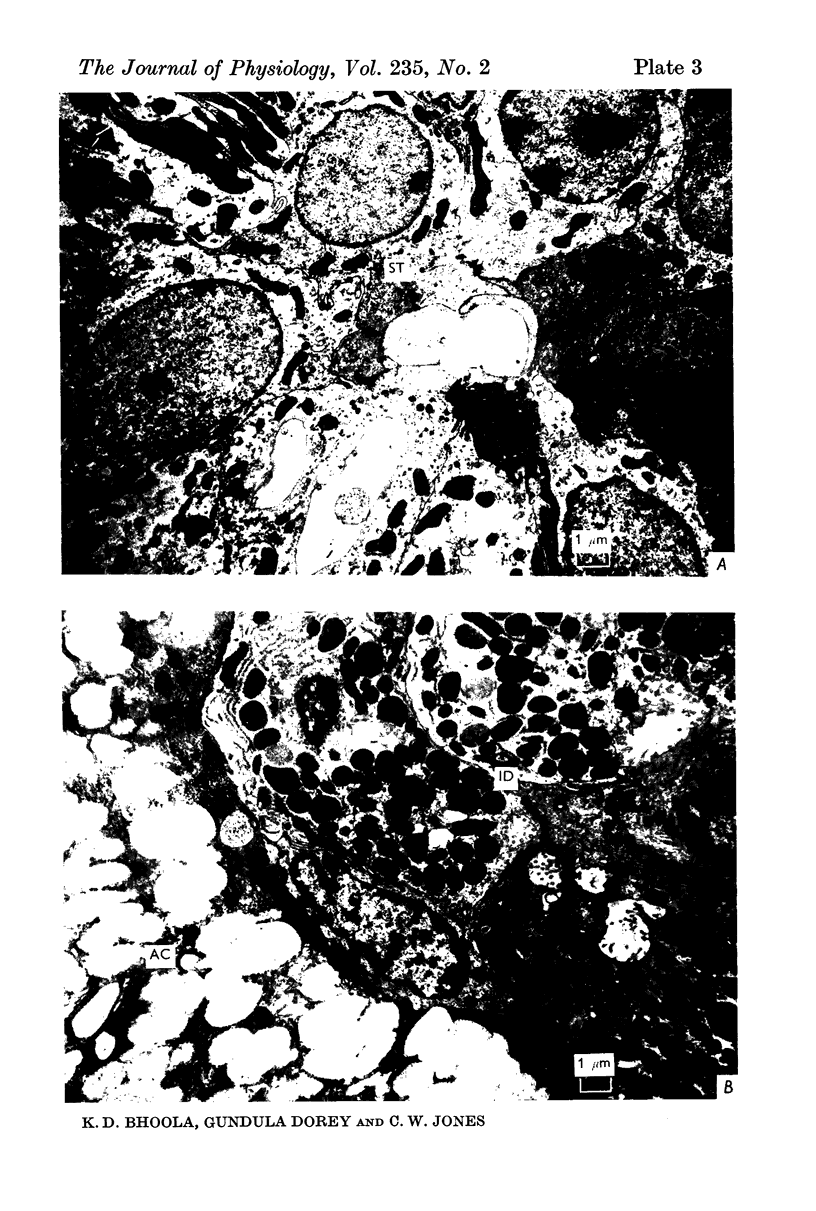
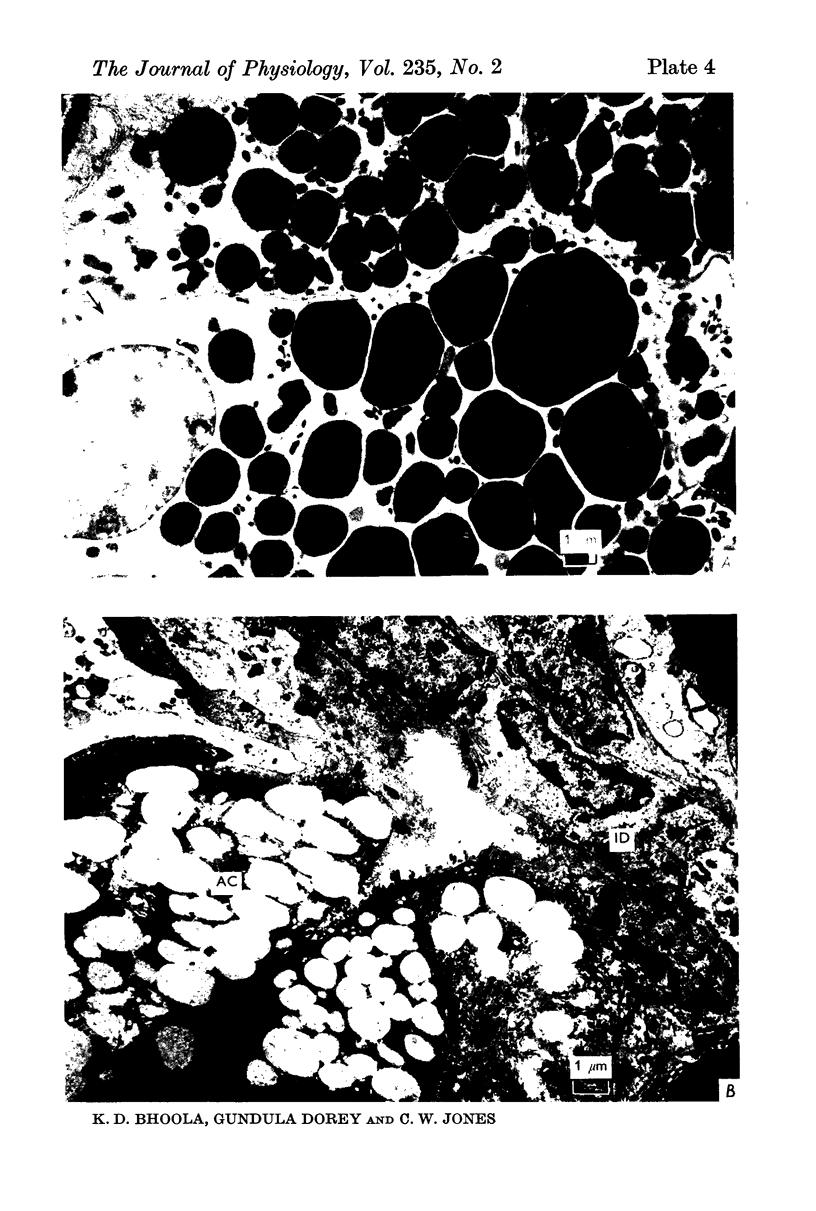
3. Activity of the chymotrypsin- and trypsin-like proteases and renin increased considerably in male mice concomitantly with proliferation of granules in the secretory tubules of the gland.
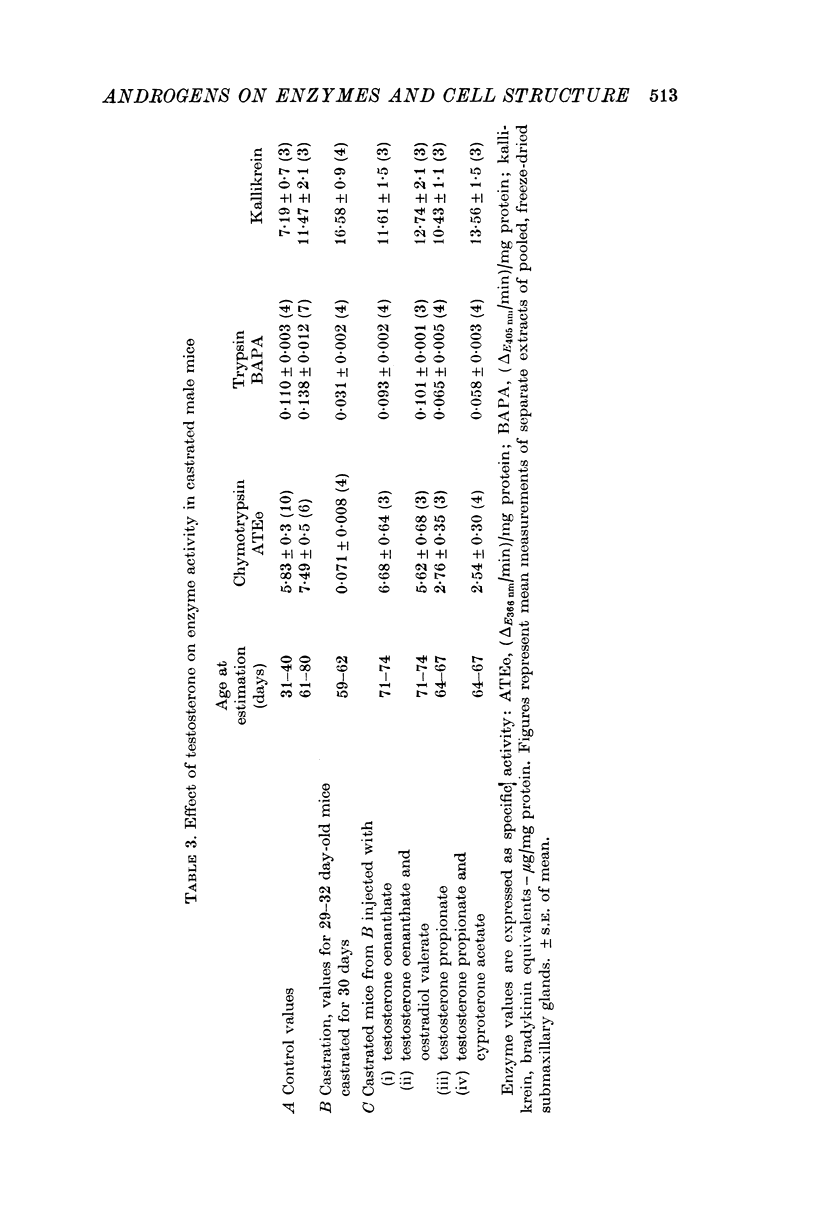
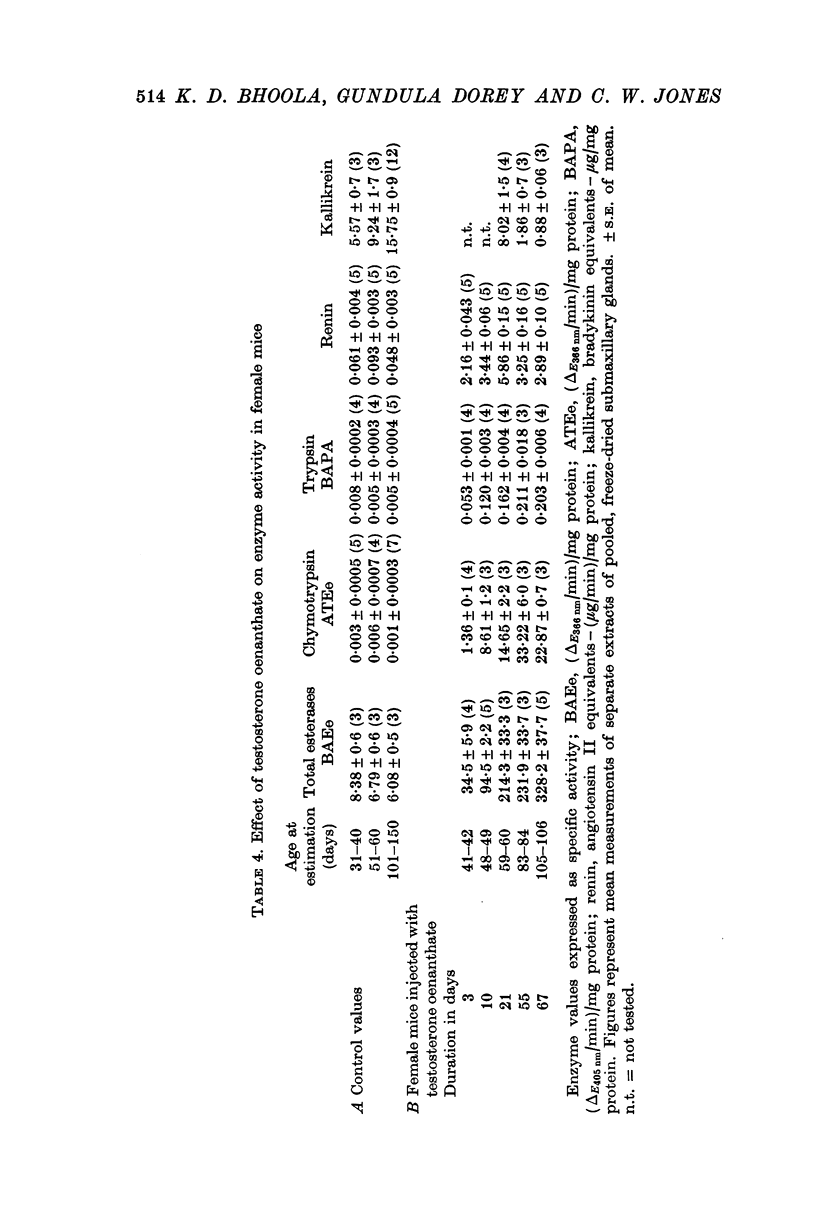
4. The androgen dependence of the chymotrypsin- and trypsin-like enzymes, renin and the organelles within the secretory tubules was confirmed in castrated male mice. The activity of these enzymes increased and correlated with the appearance of intracellular granules in the secretory tubules when the castrated male mice and in addition female mice were treated with testosterone preparations.
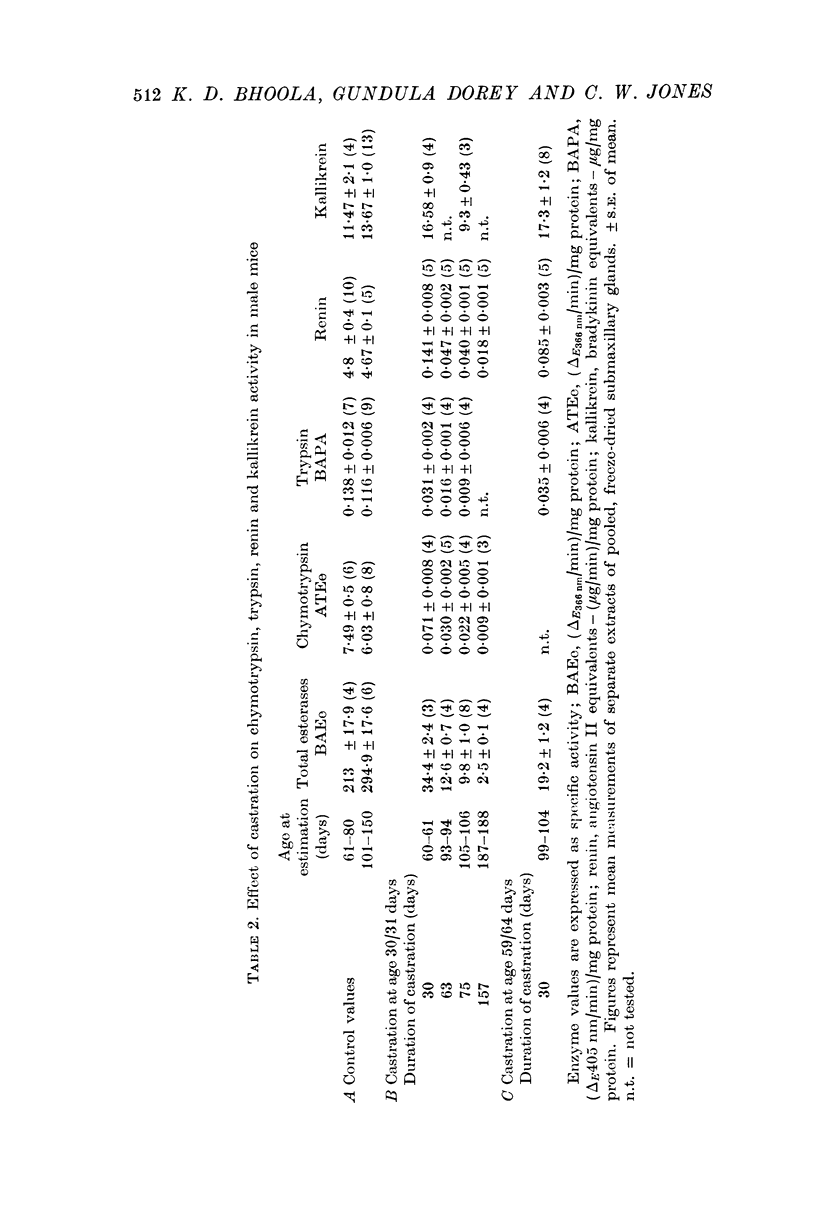
5. Kallikrein, a closely related protease, and amylase increased in activity with age but showed no sex-linked differences.
6. The results suggest that kallikrein is sequestered in acinar cells whereas the androgen-dependent enzymes (chymotrypsin, trypsin and renin) are located in the secretory tubules.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhoola K. D., Dorey G. Kallikrein, trypsin-like proteases and amylase in mammalian submaxillary glands. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;43(4):784–793. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Heap P. F. Properties of kallikrein-containing granules isolated from the submaxillary gland of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):421–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Ogle C. W. The subcellular localization of kallikrein, amylase and acetylcholine in the submaxillary gland of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(3):663–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caramia F. Ultrastructure of mouse submaxillary gland. I. Sexual differences. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Dec;16(5):505–523. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caramia F. Ultrastructure of mouse submaxillary gland. II. Effect of castration in the male. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Dec;16(5):524–536. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T. S., Erdös E. G., Miwa I., Tague L. L., Coalson J. J. Isolation from a salivary gland of granules containing renin and kallikrein. Circ Res. 1968 Oct;23(4):507–517. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekfors T. O., Riekkinen P. J., Malmiharju T., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Four isozymic forms of a peptidase resembling kallikrein purified from the rat submandibular gland. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jan;348(1):111–118. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1967.348.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang S., Anderson K. M., Liao S. Receptor proteins for androgens. On the role of specific proteins in selective retention of 17-beta-hydroxy-5-alpha-androstan-3-one by rat ventral prostate in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 25;244(24):6584–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNQUEIRA L. C., FAJER A. Biochemical and histochemical observations on the sexual dimorphism of mice submaxillary glands. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Aug;34(1):129-58, incl 6 pl. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver W. J., Gross F. Effect of testosterone and duct ligation on submaxillary renin-like principle. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):341–346. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Ekfors T. O., Hollmén T., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Purification and physical characteristics of a trypsin-like protease from the rat submandibular gland. Enzymologia. 1967 Feb 28;32(2):97–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Ekfors T. O., Hopsu V. K. Purification and characteristics of an alkaline protease from rat-submandibular gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 15;118(3):604–620. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Niemi M. Androgen-dependent salivary gland protease in the rat. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1224–1231. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., TAKENAKA Y. A spectrophotometric determination of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Apr;16(4):570–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SREEBNY L. M. Studies of salivary gland proteases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Mar 29;85:182–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb49956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTSCHOLD I., WERLE E. [Spectrophotometric determination of kallikrein and its inactivators]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1961 Jun 30;325:48–59. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1961.325.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]