Abstract
1. Isometric responses of rat inferior rectus muscle to indirect and direct stimulation were compared, and conditions were found for selective direct stimulation of twitch fibres in vitro.
2. Most of the twitch fibres were qualitatively `fast'.
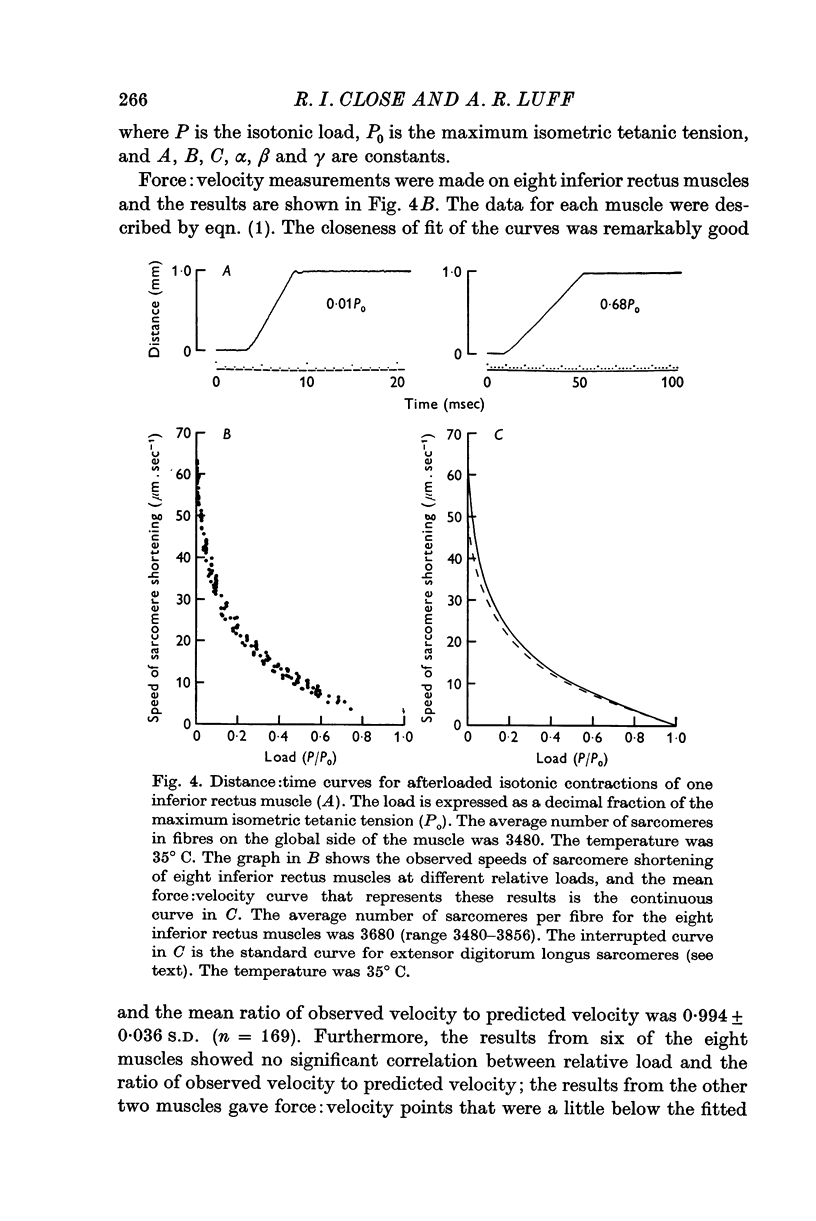
3. The influence of length on isometric contractions and the relation between relative load and speed of sarcomere shortening of fast-twitch fibres were determined.
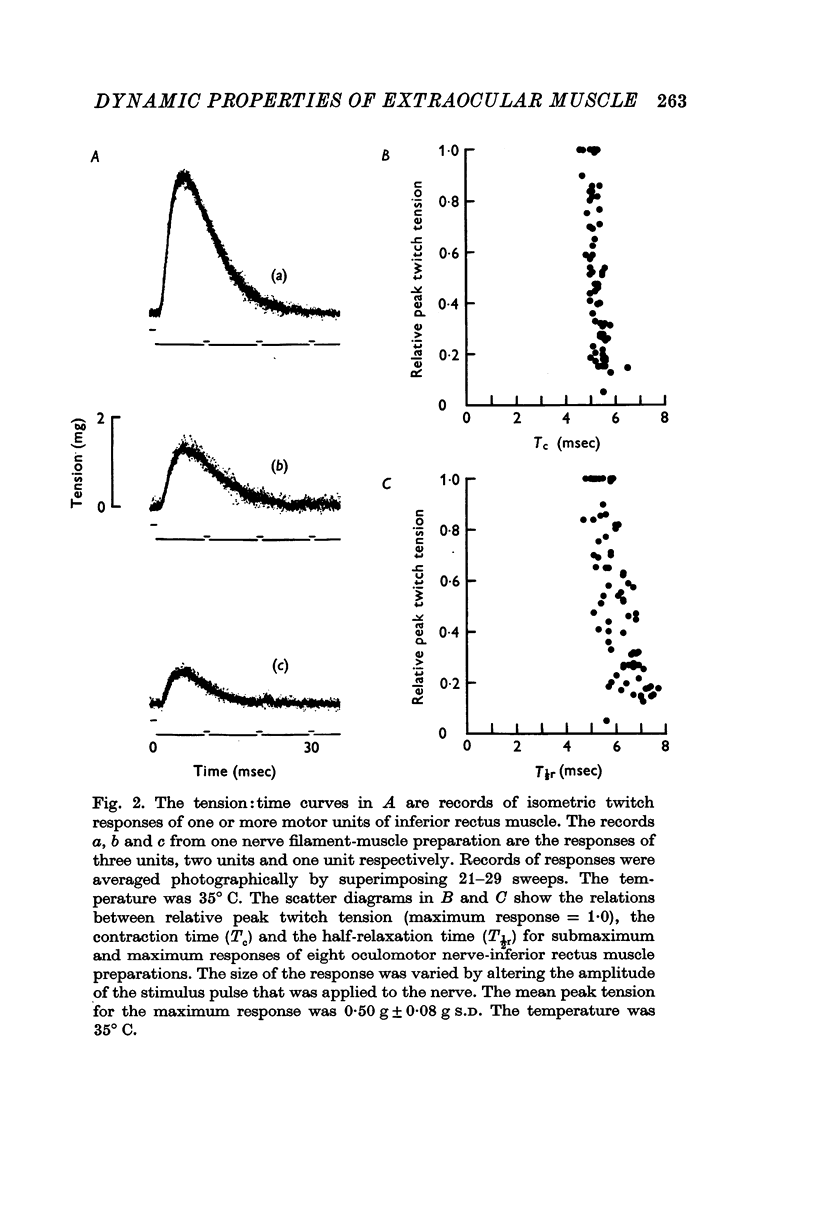
4. The isometric twitch contraction and half-relaxation times of fast-twitch inferior rectus fibres were only about one half of those of rat extensor digitorum longus fibres in the same conditions, whereas the force: velocity properties of these two fibre groups were virtually the same. These results show that the relation between intrinsic speed of shortening and duration of the active state of the contractile material is not the same for rat extraocular and hind-limb muscles.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach-y-Rita P., Ito F. In vivo studies on fast and slow muscle fibers in cat extraocular muscles. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):1177–1198. doi: 10.1085/jgp.0491177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barmack N. H., Bell C. C., Rence B. G. Tension and rate of tension development during isometric responses of extraocular muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Nov;34(6):1072–1079. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.6.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Harvey A. M. Neuro-muscular transmission in the extrinsic muscles of the eye. J Physiol. 1941 Mar 25;99(3):379–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M., Close R. I. The transformation of myosin in cross-innervated rat muscles. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(2):455–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat after nerve cross-union. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):331–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R., Hoh J. F. Influence of temperature on isometric contractions of rat skeletal muscles. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1179–1180. doi: 10.1038/2171179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R., Hoh J. F. The after-effects of repetitive stimulation on the isometric twitch contraction of rat fast skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):461–477. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. The relation between intrinsic speed of shortening and duration of the active state of muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):542–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. The isometric responses of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1930 Jun 27;69(4):377–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A. F., Luschei E. S. Development of isometric tension in simian extraocular muscle. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):155–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A., PILAR G. SLOW FIBRES IN THE EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:780–798. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinacker A., Bach-y-Rita P. A mechanical study of the cat retractor bulbi muscle. Experientia. 1968 Nov 15;24(11):1138–1139. doi: 10.1007/BF02147810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teräväinen H. Electron microscopic and histochemical observations on different types of nerve endings in the extraocular muscles of the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;90(3):372–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00341993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teräväinen H., Huikuri K. Effect of oculomotor and trigeminal nerve section on the ultrastructure of different myoneural junctions in the rat extraocular muscles. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;102(4):466–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00335489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin H. Unique intrafusal and extraocular muscle fibers exhibiting dual actomyosin ATPase activity. Exp Neurol. 1969 Sep;25(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


