Abstract
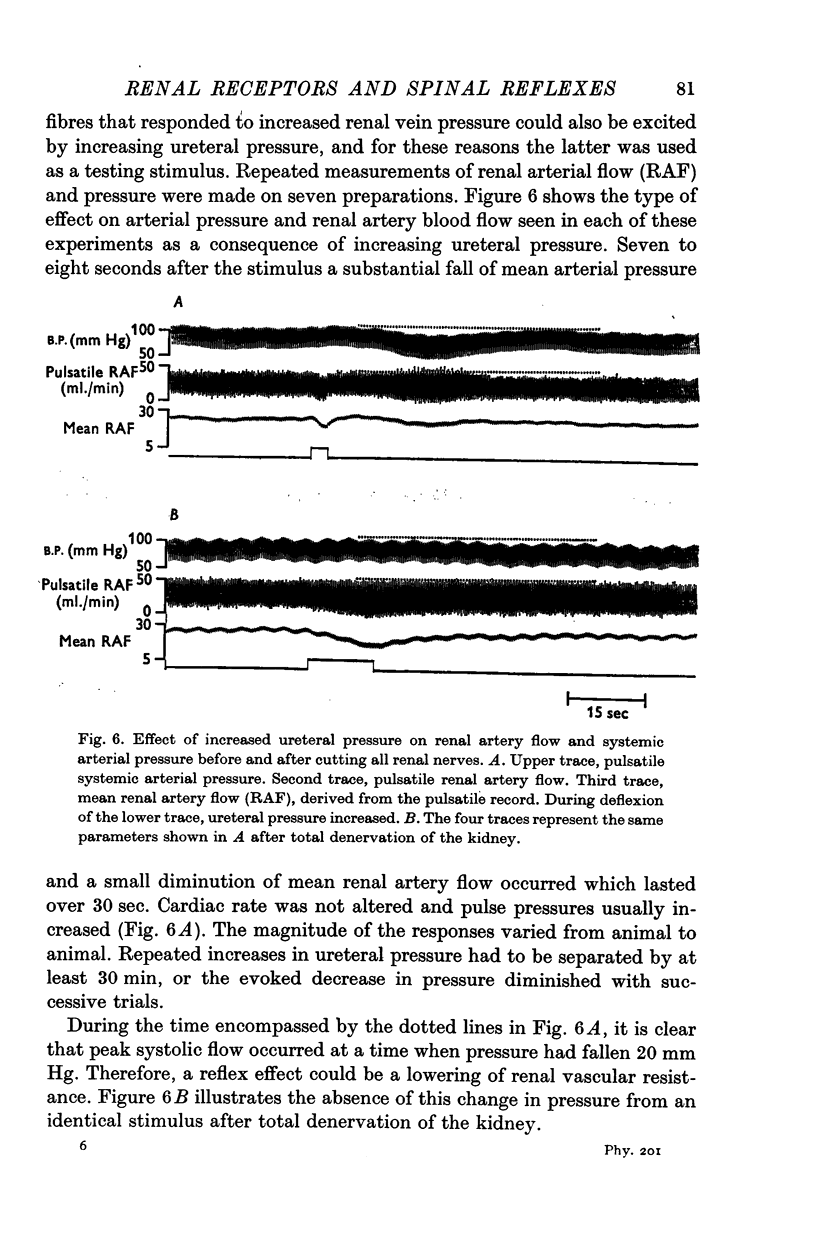
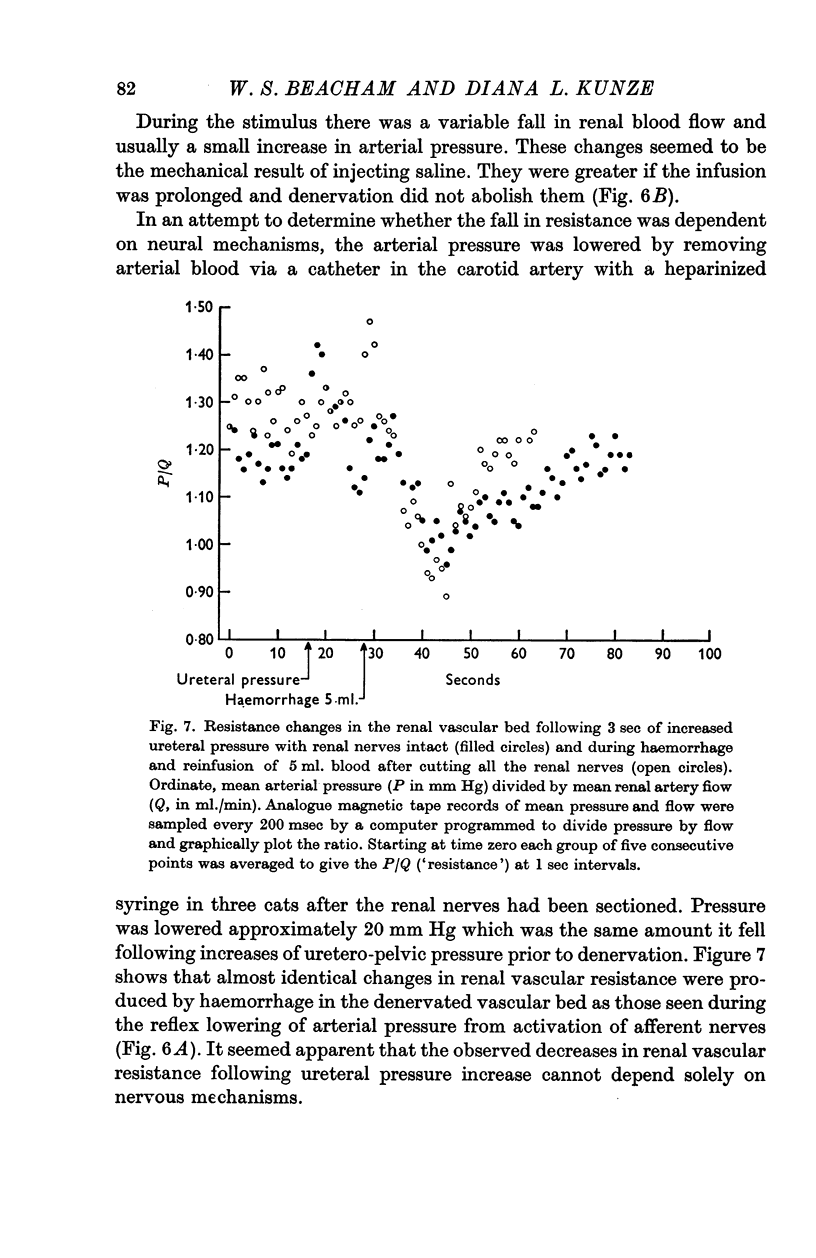
1. Certain afferent fibres in the renal nerves show an increased rate of discharge in response to small increases in renal vein pressure and to substantial increases of ureteral pressure. Such fibres enter the spinal cord largely through the upper lumbar dorsal roots.
2. In spinal cats, stimuli exciting these afferent fibres evoke a reflex discharge in sympathetic nerves to the kidney and a fall in systemic arterial pressure. Change in flow or peripheral resistance, independent of arterial pressure, could not be demonstrated for the renal vascular bed. In spite of a lack of evidence for a renal vasomotor effect, the existence of the reflex fall in arterial pressure following excitation of receptors sensitive to venous pressure strongly implies that there is a form of circulatory regulation at the spinal cord level.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSSON B., KENNEY R. A., NEIL E. The role of the chemoceptors of the carotid and aortic regions in the production of the Mayer waves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1950 Mar 27;20(2-3):203–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1950.tb00699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström A., Crafoord J. Afferent activity recorded in the kidney nerves of rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 May;70(1):10–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCK M. A., WAKIM K. G., MANN F. C. Renal function during stimulation of renal nerves. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):670–677. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RITCHIE J. M. A technique for recording functional activity in specific groups of medullated and non-medullated fibres in whole nerve trunks. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):19–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downman C. B., McSwiney B. A. Reflexes elicited by visceral stimulation in the acute spinal animal. J Physiol. 1946 Jul 15;105(1):80–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRETTI R., CHERNIACK N. S., LONGOBARDO G., LEVINE O. R., MORKIN E., SINGER D. H., FISHMAN A. P. SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY VASOMOTOR WAVES. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jul;209:37–50. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez de Molina A., Perl E. R. Sympathetic activity and the systemic circulation in the spinal cat. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(1):82–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUHZIT C. C., FREYBURGER W. A., MOE G. K. The nature of the reflex vasodilatation induced by epinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Oct;112(2):138–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUYTON A. C., HARRIS J. W. Pressoreceptor-autonomic oscillation; a probable cause of vasomotor waves. Am J Physiol. 1951 Apr 1;165(1):158–166. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.165.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUCK C. R., MOORE A. W., COCHRAN N. H., CANADA A. Alterations in renal hemodynamics and function in separate kidneys during stimulation of renal artery nerves in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1951 Nov;167(2):523–530. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.2.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N. Vaso-motor centres: Part III. Spinal vascular (and other autonomic) reflexes and the effect of strychnine on them. J Physiol. 1924 Oct 9;59(2-3):231–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1924.sp002179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUKHERJEE S. R. Effect of bladder distension on arterial blood pressure and renal circulation in acute spinal cats. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):300–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A., Winter D. L. Baroreceptors in the adrenal gland. Science. 1968 Jan 26;159(3813):434–435. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3813.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINES Iu L. [Electrophysiological characteristics of the afferent connections between the kidneys and the central nervous system]. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im I M Sechenova. 1960 Nov;46:1380–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGAWA K., CARRIER O., GUYTON A. C. Elicitation of theoretically predicated feedback oscillation in arterial pressure. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jul;203:141–146. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDY R. S., SHIPLEY R. E. Comparison of direct with indirect renal blood flow, extraction of inulin and diodrast, before and during acute renal nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1950 Nov;163(2):442–453. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.163.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


