Abstract
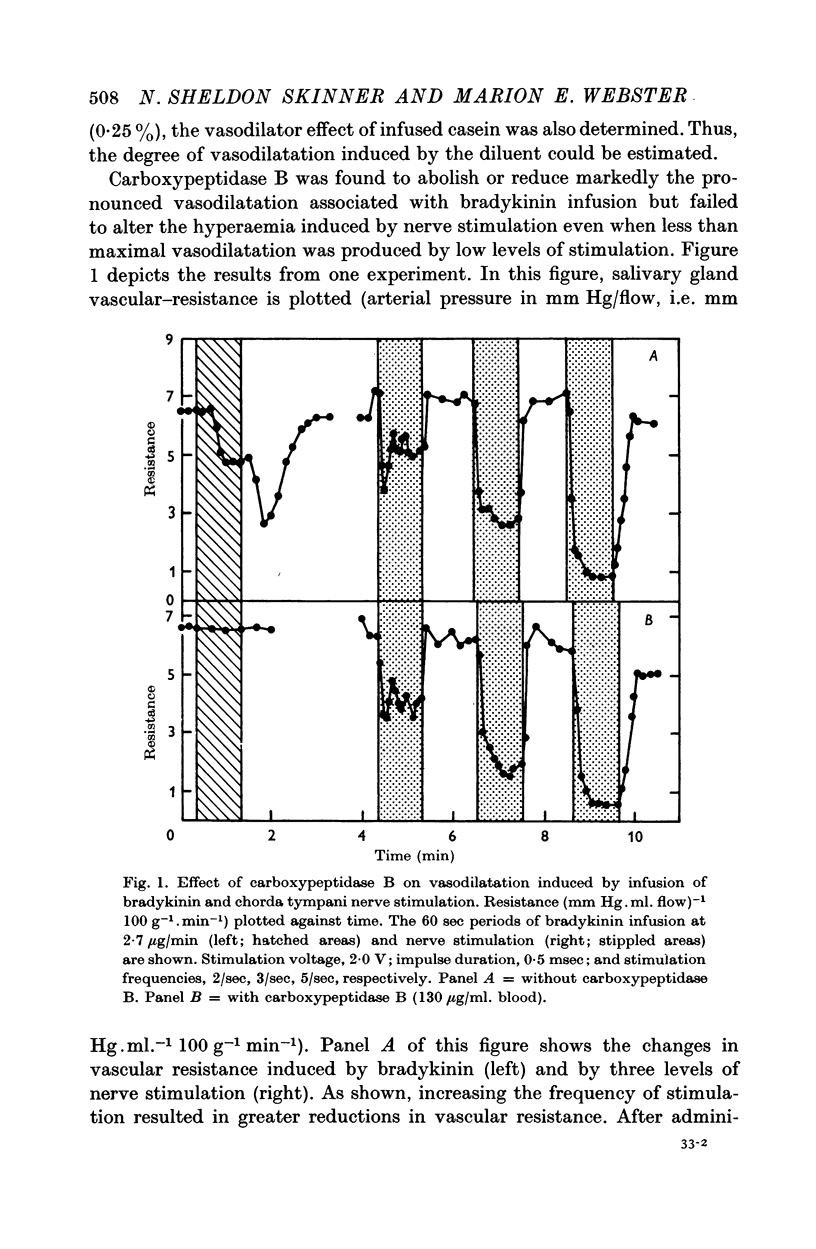
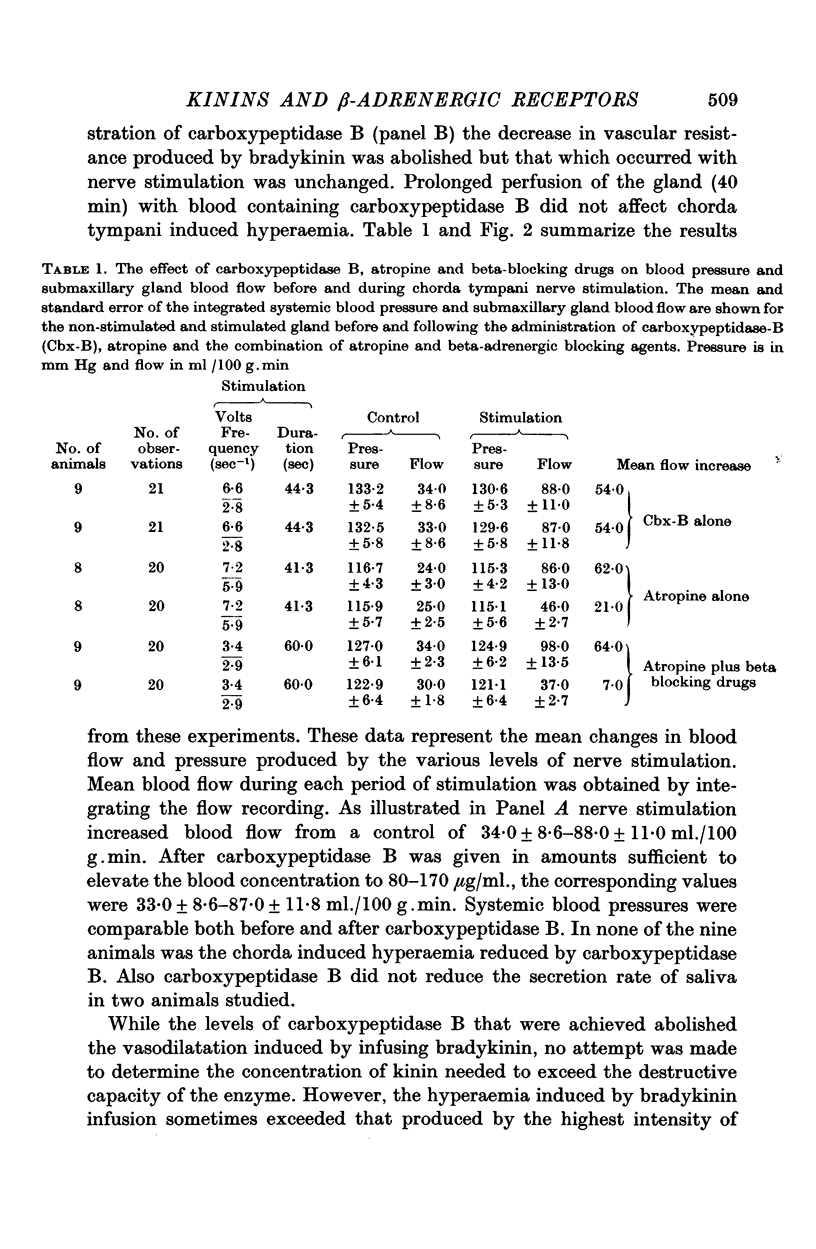
1. The close arterial infusion of bradykinin into the submaxillary gland of the cat produced a pronounced hyperaemia that could be blocked by simultaneous perfusion of the gland with blood containing carboxypeptidase B. Carboxypeptidase B, however, failed to reduce the vasodilatation of chorda tympani nerve stimulation suggesting that the kinins are not involved in the regulation of submaxillary gland blood flow.
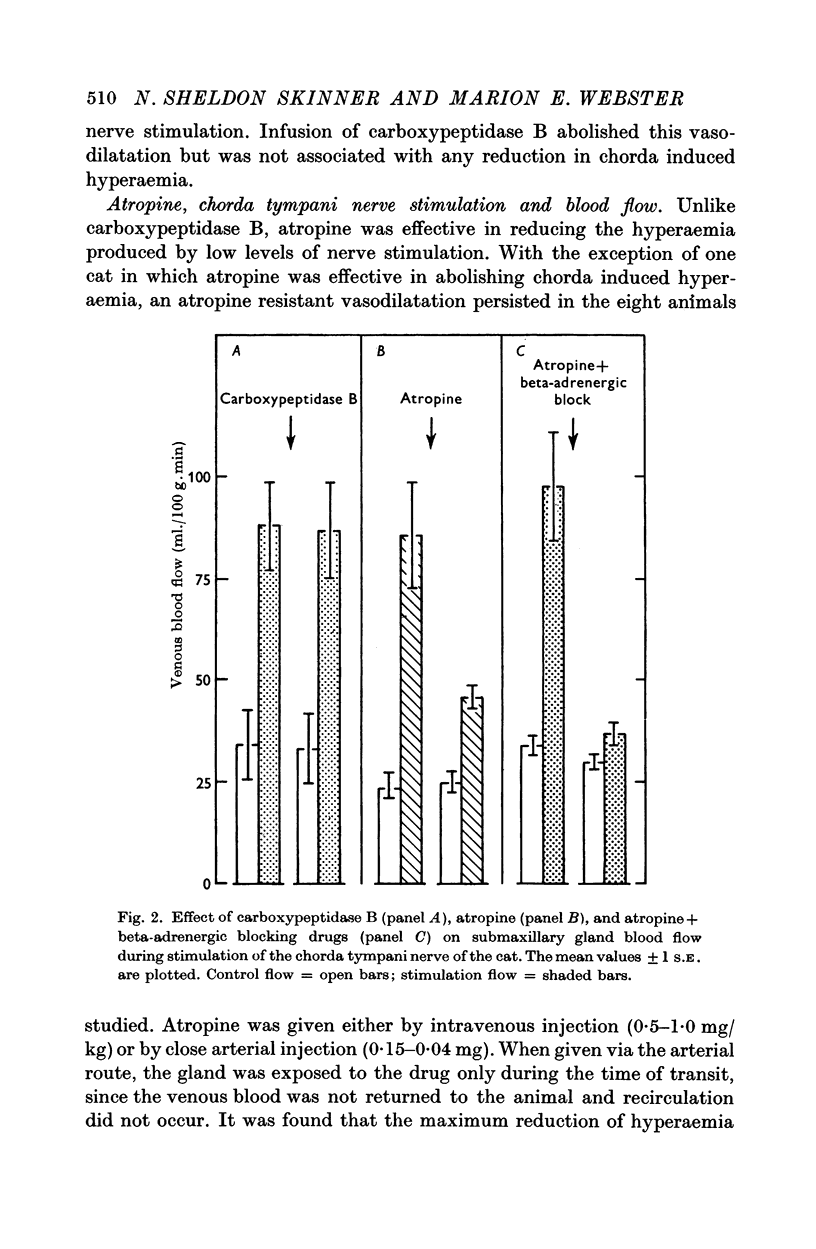
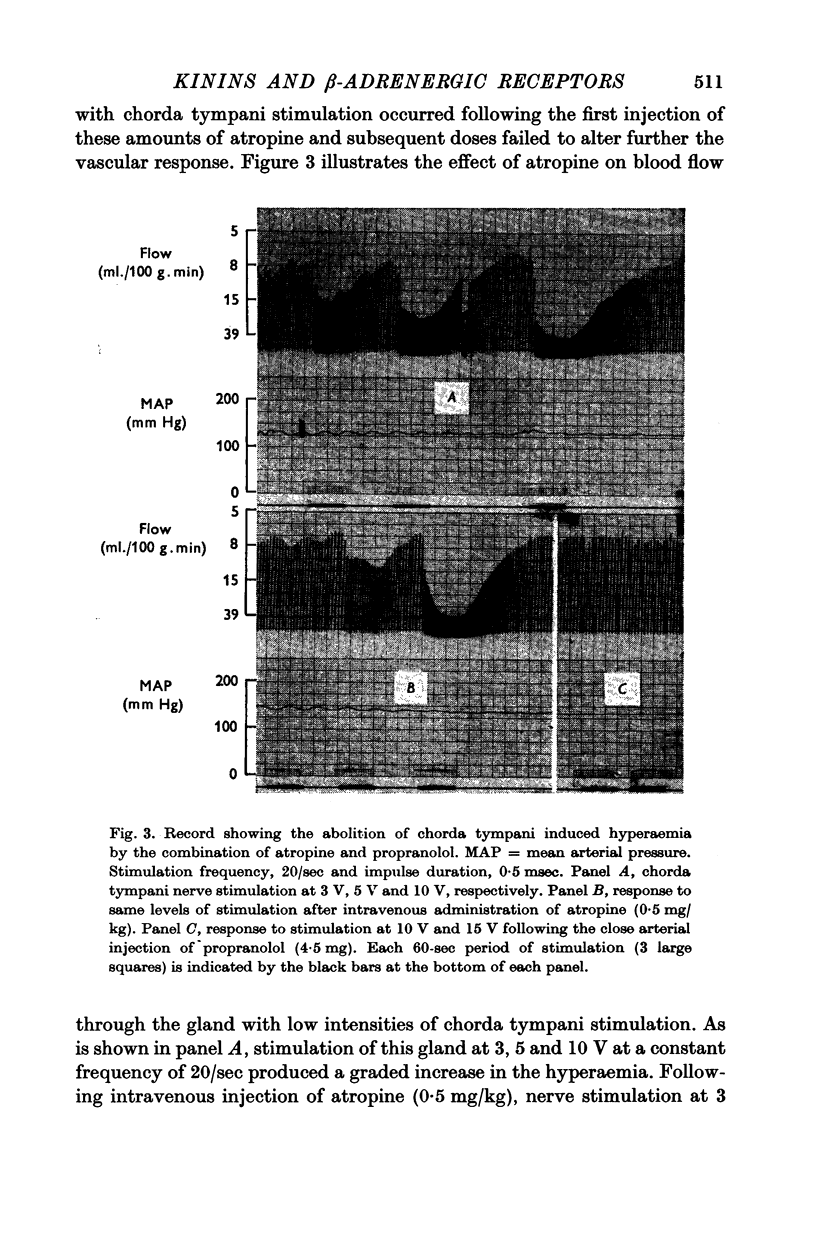
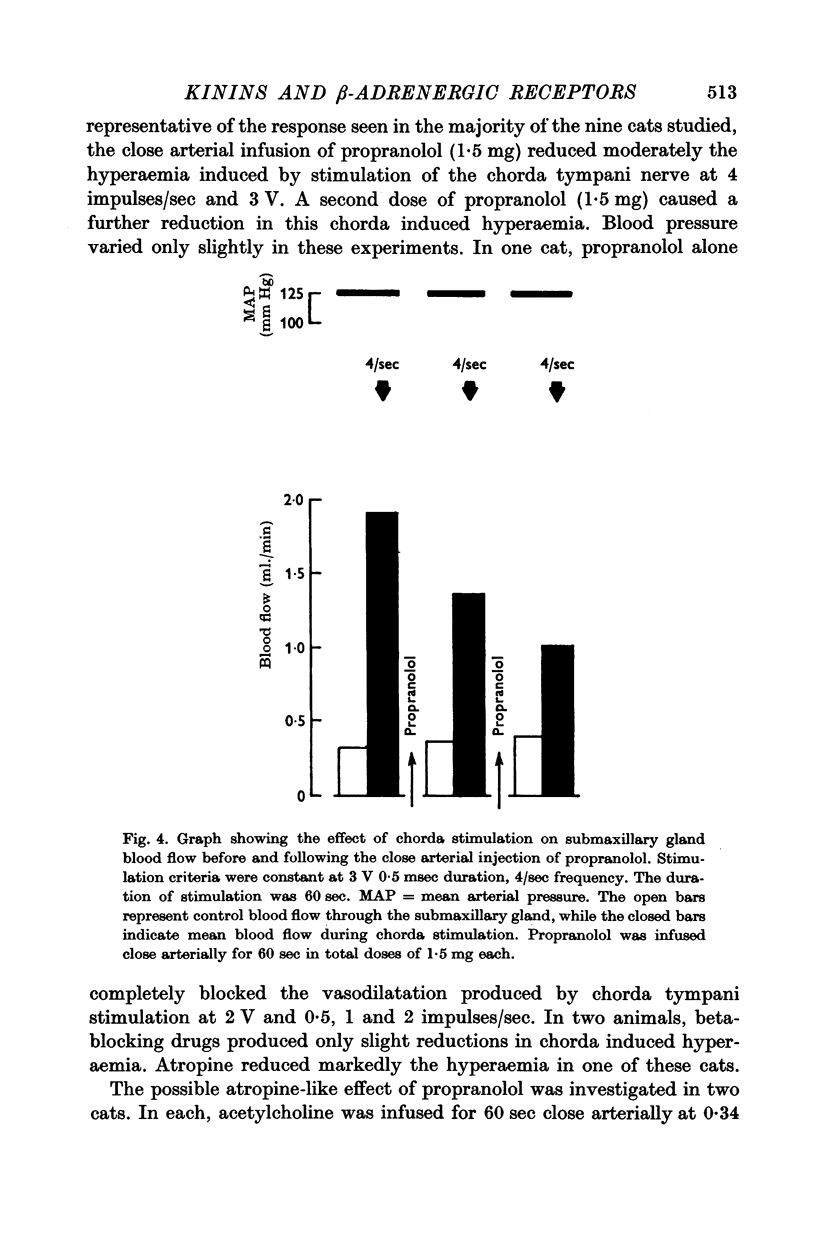
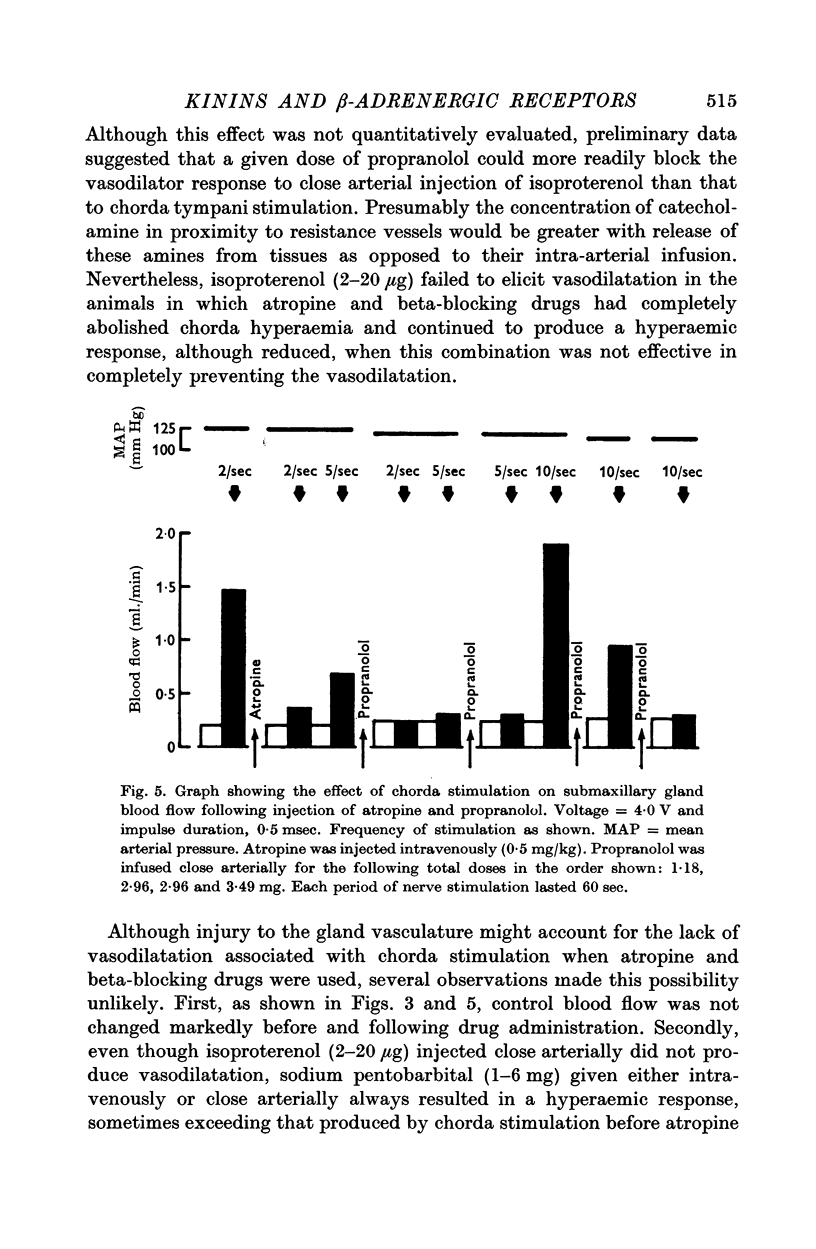
2. Isoproterenol injections produced pronounced salivary gland vasodilatation. Beta-adrenergic blocking drugs reduced or abolished the hyperaemia of isoproterenol and reduced that of chorda tympani nerve stimulation. The combination of beta-blocking drugs and atropine could abolish or reduce further this nerve induced hyperaemia.
3. The above results suggest that stimulation of cholinergic and beta-adrenergic receptors could account for the chorda tympani induced hyperaemia. Conclusive proof of this possibility remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARTURSON G., KJELLMER I. CAPILLARY PERMEABILITY IN SKELETAL MUSCLE DURING REST AND ACTIVITY. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Sep-Oct;62:41–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb03949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Morley J., Schachter M., Smaje L. H. Vasodilatation in the submaxillary gland of the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(1):172–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVY M. J., DAVIES R. F., REINERT H., SCHOLFIELD P. C. EFFECTS OF ADRENERGIC NEURONE-BLOCKING AGENTS ON THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND OF THE CAT. Nature. 1965 Feb 13;205:673–675. doi: 10.1038/205673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOES E. G., WOHLER J. R., LEVINE M. I. BLOCKING OF THE IN VIVO EFFECTS OF BRADYKININ AND KALLIDIN WITH CARBOXYPEPTIDASE B. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Dec;142:327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G. Hypotensive peptides: bradykinin, kallidin, and eledoisin. Adv Pharmacol. 1966;4:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLK J. E., PIEZ K. A., CARROLL W. R., GLADNER J. A. Carboxy-peptidase B. 4. Purification and characterization of the porcine enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2272–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSCHMIDT H., LINDGREN P. An electronic interval recorder for measuring peripheral blood flow and heart rate. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Jan;17:169–171. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M. A discussion of the evidence for kinins as the agents of vasodilator reactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 4;104:275–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. The cause of the vasodilatation accompanying activity in the submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. The mechanism of the functional hyperaemia in the submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol. 1955 Aug 29;129(2):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M., LEWIS G. P. The relationship between glandular activity, bradykinin formation and functional vasodilatation in the submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):471–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J., Schachter M., Smaje L. H. Vasodilatation in the submaxillary gland of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1966 Dec;187(3):595–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M., Beilenson S. Kallikrein and vasodilation in the submaxillary gland. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERROUX K. G., SEKELJ P., BURGEN A. S. Oxygen consumption and blood flow in the submaxillary gland of the dog. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Jan;37(1):5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster M. E., Skinner N. S., Jr, Powell W. J., Jr Role of the kinins in vasodilatation of skeletal muscle of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1967 Mar;212(3):553–558. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.3.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]