Abstract
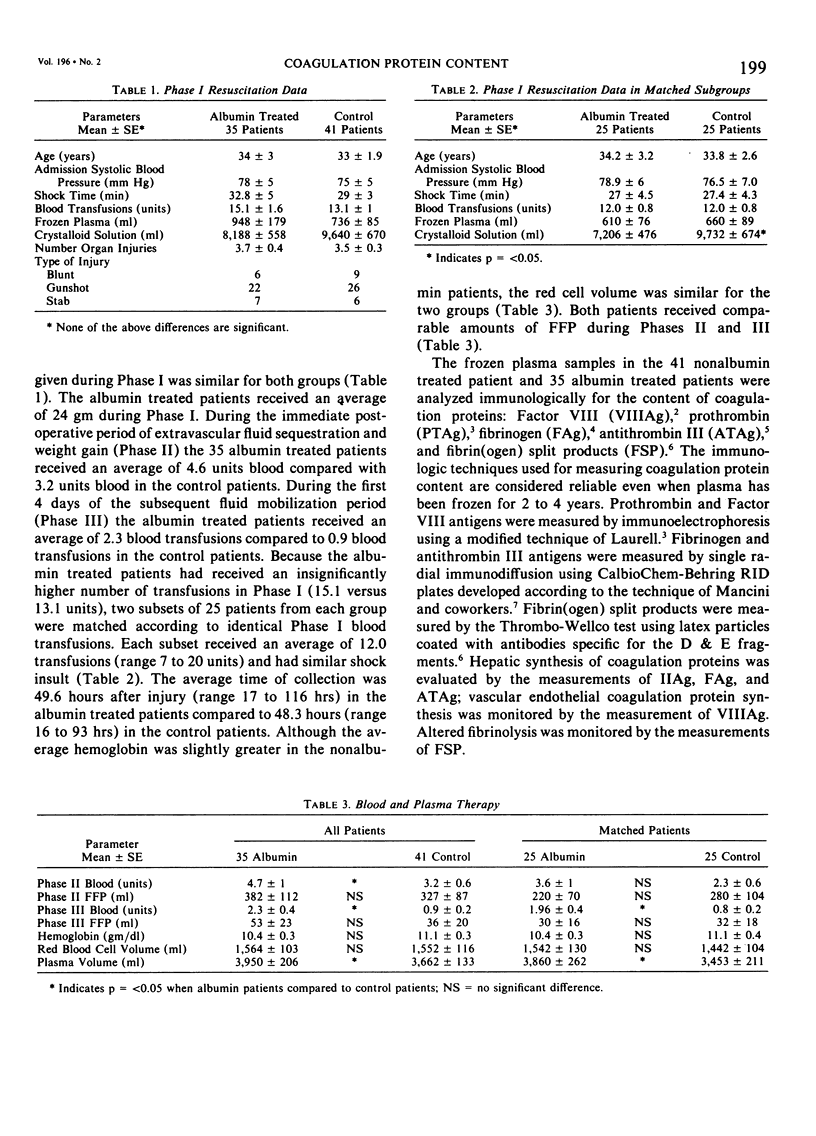
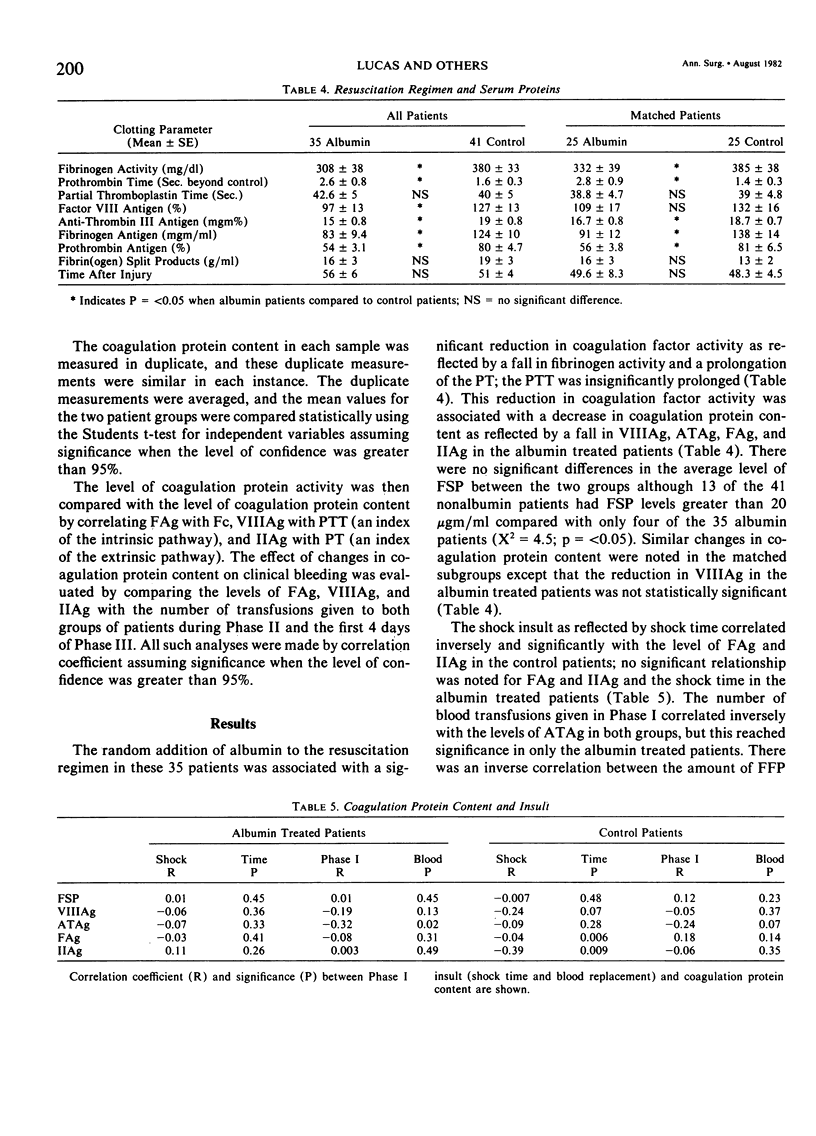
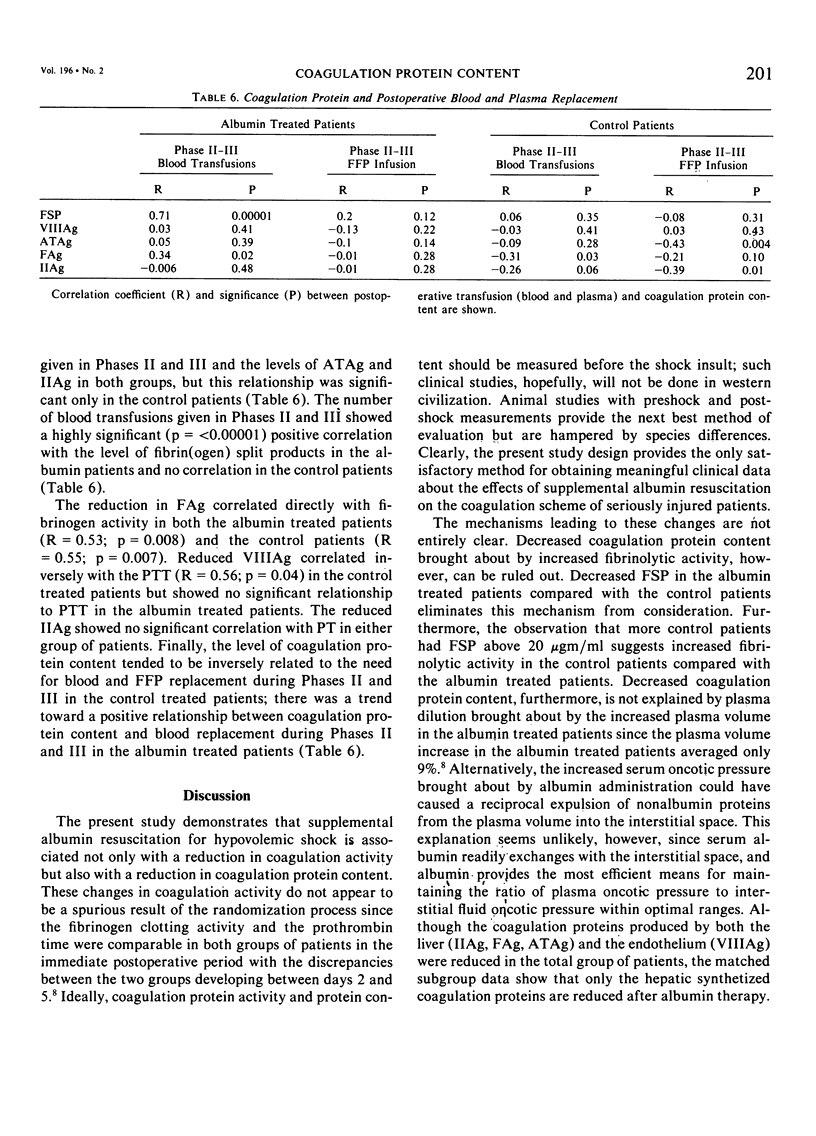
Previous studies showed that the random addition of supplemental albumin to a resuscitation regimen of blood, salt, and frozen plasma caused a significant (p = less than 0.05) fall in fibrinogen clotting activity (FC) and a rise in prothrombin times (PT) in seriously injured patients; the partial thromboplastin times (PTT) were insignificantly prolonged. Based upon these findings, frozen plasma samples, prospectively collected in 41 non-albumin patients and 35 albumin patients, were analyzed immunologically, in duplicate, for protein content of coagulation factor VIII (VIIIAg), prothrombin (IIAg), fibrinogen (FAg), antithrombin III (ATAg), and fibrin(ogen) split products (FSP). Supplemental albumin resuscitation was associated with a significant fall in FAg (83 +/- 9 versus 124 +/- 10 SE mg/dl), VIIIAg (97 +/- 13 versus 127 +/- 135 SE %), IIAg (54 +/- 3 versus 80 +/- 4 SE %), and ATAg (14 +/- 0.8 +/- 19 +/- 0.8 SE mg%) with no significant changes in FSP. FSP, however, were more than 20 micrograms/ml in 13 of 41 nonalbumin patients versus four of 35 albumin patients (X2 = 4.5, p less than 0.05). Reduced coagulation activity following albumin supplementation seems partly caused by a decrease of coagulation protein content; increased fibrinolysis in the albumin patients is not the cause. Decreased coagulation protein content parallels the fall in coagulation activity and the need for postresuscitation blood transfusions. The role of reduced coagulation synthesis in these changes needs further study.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garvey M. B., Black J. M. The detection of fibrinogen-fibrin degradation products by means of a new antibody-coated latex particle. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;25(8):680–682. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.8.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. D., Lucas C. E., Gerrick S. J., Ledgerwood A. M., Higgins R. F. Altered coagulation after albumin supplements for treatment of oligemic shock. Arch Surg. 1979 Apr;114(4):379–383. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370280033005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledgerwood A. M., Lucas C. E. Proceedings: Postresuscitation hypertension. Etiology, morbidity, and treatment. Arch Surg. 1974 Apr;108(4):531–538. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350280133022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. E., Ledgerwood A. M. Clinical significance of altered coagulation tests after massive transfusion for trauma. Am Surg. 1981 Mar;47(3):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


