Abstract
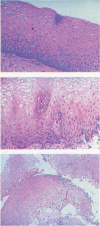
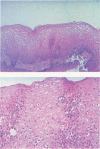
Little is known about the fate of histologic changes of esophagitis following an antireflux procedure. In a widely quoted paper (Gastroenterology 1979; 76:1393), initial healing of esophagitis was reported, but it was noted that normal biopsies reversed to abnormal in a small number of patients who were followed for up to 69 months. The authors studied esophageal histology in 21 patients undergoing a Nissen fundoplication by a standardized technique. All patients underwent biopsy after operation from 5 to 96 months (mean, 39 months). Nineteen of 21 patients had esophagitis typified by leukocytic infiltration shown on preoperative biopsy. Only two patients had these changes after operation, and one subsequently returned to normal. No patient had evidence of worsening of his esophageal mucosa over time, but several persisted with epithelial changes that included basal cell hyperplasia and papillary elevation. The authors conclude that the Nissen fundoplication, when performed by a standardized technique, leads to reversal of histologic evidence of esophagitis, even for follow-up periods of 96 months, and that the symptomatic status of a patient correlates well with the histologic level of esophagitis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behar J., Sheahan D. G., Biancani P., Spiro H. M., Storer E. H. Medical and surgical management of reflux esophagitis. A 38-month report of a prospective clinical trial. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 7;293(6):263–268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508072930602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Sheahan D. Histologic abnormalities in reflux esophagitis. Arch Pathol. 1975 Jul;99(7):387–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J. Surgical treatment of reflux esophagitis: how does it work? Gastroenterology. 1979 Jul;77(1):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand D. L., Eastwood I. R., Martin D., Carter W. B., Pope C. E., 2nd Esophageal symptoms, manometry, and histology before and after antireflux surgery: a long-term follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1393–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushkin F. L., Neustein C. L., Parker T. H., Woodward E. R. Nissen fundoplication for reflux peptic esophagitis. Ann Surg. 1977 Jun;185(6):672–677. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197706000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Johnson L. F. Evaluation of the Nissen antireflux procedure by esophageal manometry and twenty-four hour pH monitoring. Am J Surg. 1975 Jan;129(1):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Kent A. H. Evaluation of current operations for the prevention of gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):511–525. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarino A. J., Rosato E., Rosato F., Cohen S. Improvement in lower esophageal sphincter pressure following surgery for complicated gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1975 Feb;181(2):239–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Helm J. F., Dent J. Pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1981 Aug;81(2):376–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. H., Jr, El-Kard M. F., Gibb S. P. The effect of fundoplication on the lower esophageal sphincter. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Jul;143(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill L. D. An effective operation for hiatal hernia: an eight year appraisal. Ann Surg. 1967 Oct;166(4):681–692. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196710000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Horton P. F., Pope C. E., 2nd Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Pope C. E., 2nd Distribution of the histological changes of gastroesophageal reflux in the distal esophagus of man. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jun;66(6):1109–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., DeMeester T. R., Haggitt R. C. Endoscopic signs for gastroesophageal reflux objectively evaluated. Gastrointest Endosc. 1976 Feb;22(3):151–155. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(76)73731-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R., Haggitt R. C. Esophageal epithelial response to gastroesophageal reflux. A quantitative study. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Jun;23(6):498–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01072693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kasugai T. Endoscopic and biopsy criteria for the diagnosis of esophagitis with a fiberoptic esophagoscope. Am J Dig Dis. 1974 Apr;19(4):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01072525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISSEN R. Gastropexy and "fundoplication" in surgical treatment of hiatal hernia. Am J Dig Dis. 1961 Oct;6:954–961. doi: 10.1007/BF02231426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER E. D. Subacute erosive (peptic) esophagitis; histopathologic study. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Jan;59(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS P. M. The pathology of severe digestion oesophagitis. Thorax. 1955 Dec;10(4):270–286. doi: 10.1136/thx.10.4.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr, Zeppa R. Hiatal hernia and esophagitis: a survey of indications for operation and technic and results of fundoplication. Ann Surg. 1971 May;173(5):775–781. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197105000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seefeld U., Krejs G. J., Siebenmann R. E., Blum A. L. Esophageal histology in gastroesophageal reflux. Morphometric findings in suction biopsies. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Nov;22(11):956–964. doi: 10.1007/BF01076193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Belsey R. H. Surgical management of esophageal reflux and hiatus hernia. Long-term results with 1,030 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1967 Jan;53(1):33–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Riddell R. H., Willoughby J. M. Oesophagoscopy, biopsy, and acid perfusion test in diagnosis of "reflux oesophagitis". Br Med J. 1975 Jan 11;1(5949):71–76. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5949.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Lepsien G., Müller-Lissner S. A., Koelz H. R., Siewert J. R., Blum A. L. When is esophagitis healed? esophageal endoscopy, histology and function before and after cimetidine treatment. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Apr;27(4):297–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01296747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Bogoch E. R., Bowes K. L. The normal human esophageal mucosa: a histological reappraisal. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):40–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward E. R., Thomas H. F., McAlhany J. C. Comparison of crural repair and Nissen fundoplication in the treatment of esophageal hiatus hernia with peptic esophagitis. Ann Surg. 1971 May;173(5):782–792. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197105000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]