Abstract
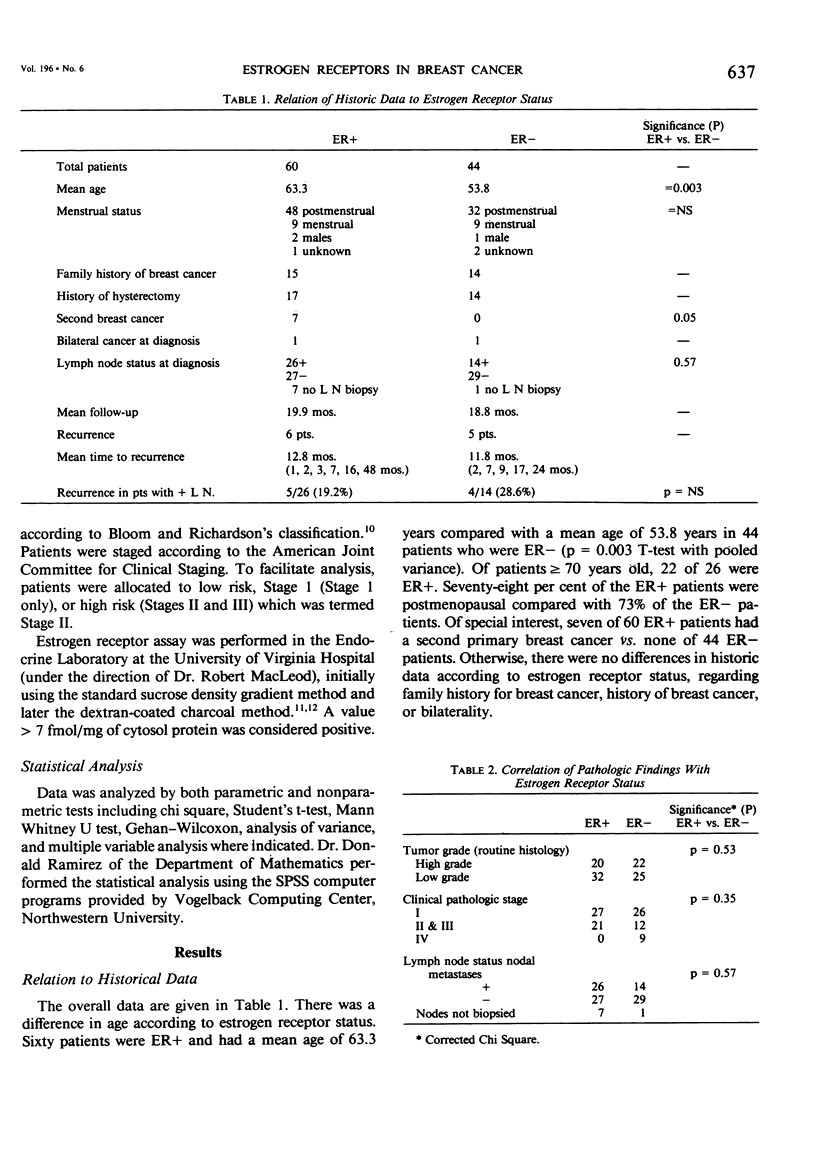
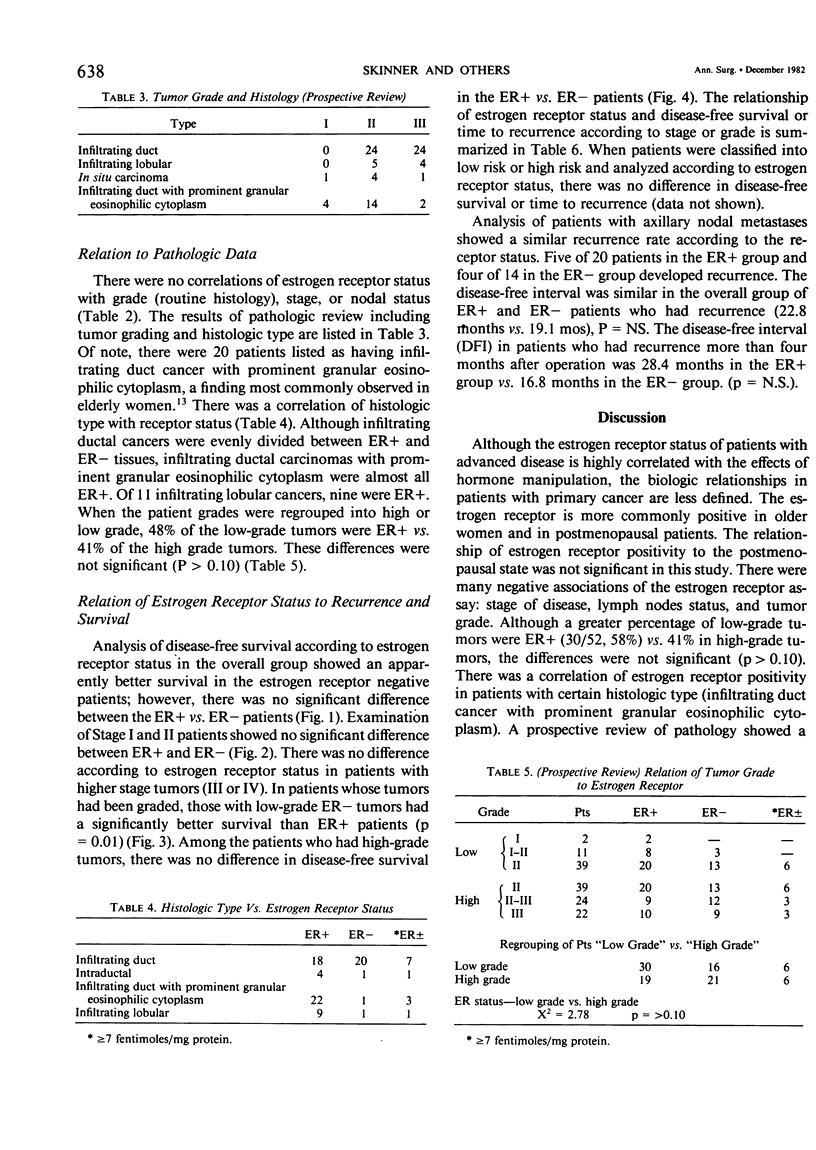
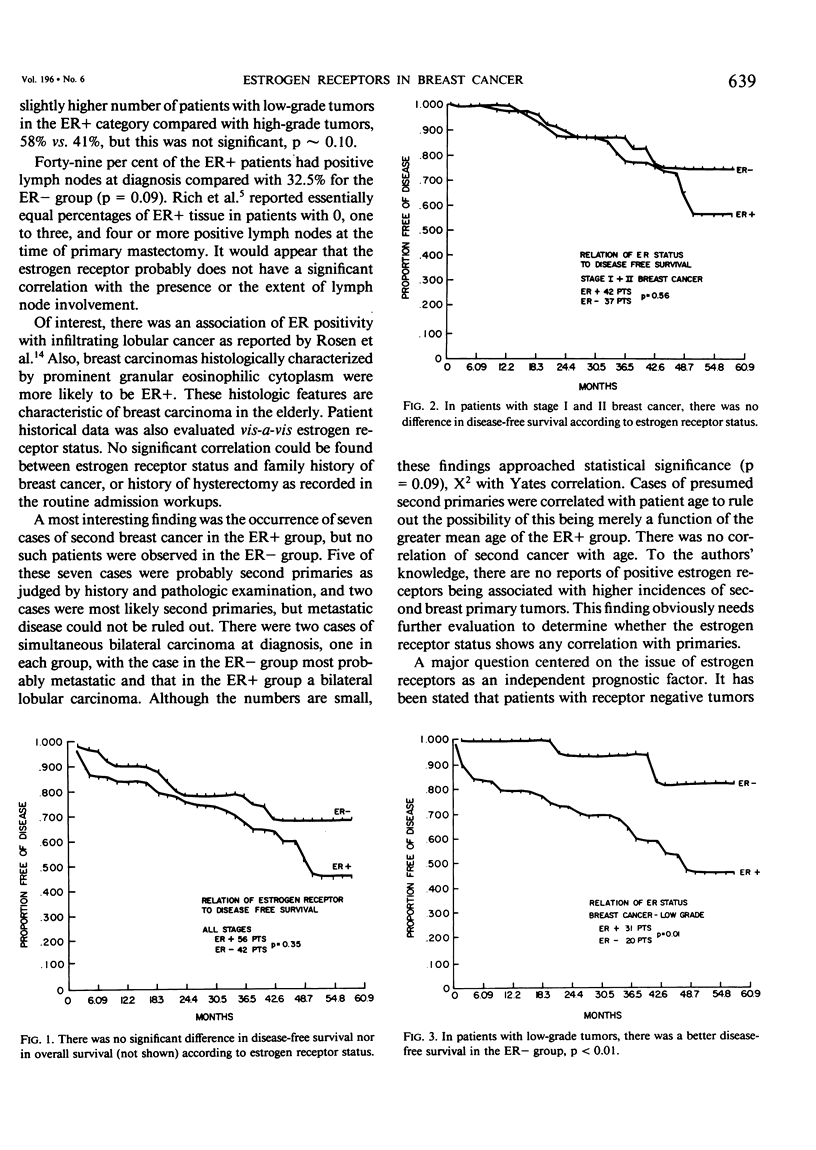
The presence of estrogen receptors in breast cancer tissue has been reported to correlate with improved prognosis in women after mastectomy. The prognostic value (if any) of the presence or absence of estrogen receptors (ER) in malignant breast tissue was evaluated 104 women who were treated for primary breast cancer, whose pathology was re-examined, and whose records were subjected to multifactorial analysis. Sixty patients were ER positive, and 44 were ER negative, and a total of 94 who had curative resections were available for follow-up (mean follow-up time 20 months). The presence of estrogen receptors showed significant positive correlations with age, lobular cancer, and a variant of infiltrating duct cancer that is prevalent in the elderly and characterized by the presence of cells showing granular eosinophilic cytoplasm. Of 26 cases identified as infiltrating duct cancer showing granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, 22 were ER positive, one was ER negative, and three had borderline values. There was no significant difference between the groups with regard to family history of breast cancer or hysterectomy. A striking observation was noted in the ER positive group in which there were seven cases of second primary breast cancers, whereas no such cases occurred in the ER negative patients (p=0.05). There was a higher percentage of nodal metastases in the patients who were ER positive compared with those who were ER negative; 27 of 53 (51%) of the ER positive patients has positive nodes compared with four of 40 (32%) who were ER negative, p = 0.08. There was no significant correlation of disease free survival nor time to recurrence in either the overall group nor according to stage. In patients whose tumors had been reviewed and graded, there was no prognostic relationship of ER status in high grade tumors, but in patients with low-grade tumors, improved disease-free survival was demonstrated in patients who were ER negative. Although the estrogen receptor assay is a highly useful tumor marker and guide for therapy of advanced breast cancer, its relationship to the prognostic variables of primary breast cancer is complex and controversial and merits continued study.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM H. J., RICHARDSON W. W. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957 Sep;11(3):359–377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T., George D., Shields R., Maynard P., Griffiths K. Oestrogen receptors and prognosis in early breast cancer. Lancet. 1979 May 12;1(8124):995–997. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92752-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Roberts M. M., Forrest A. P. Oestrogen receptors and breast cancer: current status. Br J Surg. 1980 Mar;67(3):153–169. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800670302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiang D. T., Frenning D. H., Goldman A. I., Ascensao V. F., Kennedy B. J. Estrogen receptors and responses to chemotherapy and hormonal therapy in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 14;299(24):1330–1334. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812142992403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne D. W., Ashikari R., Butler A., Menendez-Botet C., Rosen P. P., Schwartz M. Estrogen receptor protein in breast cancer as a predictor of recurrence. Cancer. 1981 May 15;47(10):2364–2367. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810515)47:10<2364::aid-cncr2820471007>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight W. A., Livingston R. B., Gregory E. J., McGuire W. L. Estrogen receptor as an independent prognostic factor for early recurrence in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1977 Dec;37(12):4669–4671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman S. G., Dukes B. A. Specific estrogen binding by the cytoplasm fof human breast carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 May;30(5):639–645. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-5-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard P. V., Blamey R. W., Elston C. W., Haybittle J. L., Griffiths K. Estrogen receptor assay in primary breast cancer and early recurrence of the disease. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4292–4295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., DeLaGarza M. Improved sensitivity in the measurement of estrogen receptor in human breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Dec;37(6):986–989. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-6-986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., Zava D. T., Horwitz K. B., Chamness G. C. Steroid receptors in breast tumors--current status. Curr Top Exp Endocrinol. 1978;3:93–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich M. A., Furmanski P., Brooks S. C. Prognostic value of estrogen receptor determinations in patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4296–4298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P. P., Menendez-Botet C. J., Nisselbaum J. S., Urban J. A., Miké V., Fracchia A., Schwartz M. K. Pathological review of breast lesions analyzed for estrogen receptor protein. Cancer Res. 1975 Nov;35(11 Pt 1):3187–3194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhakowinta A., Potter H. G., Buroker T. R., Samal B., Brooks S. C., Vaitkevicius V. K. Estrogen receptor and natural course of breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1976 Jan;183(1):84–88. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197601000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walt A. J., Singhakowinta A., Brooks S. C., Cortez A. The surgical implications of estrophile protein estimations in carcinoma of the breast. Surgery. 1976 Oct;80(4):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


