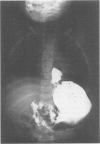
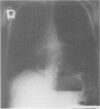
Abstract
Successful surgical correction of gastroesophageal reflux has prompted frequent and early referral of children for antireflux surgery. This report describes the results and defines the complications in a series of children treated surgically for gastroesophageal reflux. Methods are suggested to reduce the occurrence of these postoperative complications. In five years (1977-1981), 117 children, 3 weeks to 16 years old, were operated on for gastroesophageal reflux at The Oklahoma Childrens Memorial Hospital. Nissen fundoplication was performed on 111 of them. Patients have been followed for 3 months to five years. At most recent examination, clinical success (remission of symptoms) has been accomplished in 81 of 92 patients (90%). In 86 patients evaluated radiographically, gastroesophageal reflux was absent in 83 and persistent in 3. There were no operative deaths. Twenty-three major complications occurred in 21 patients, 13 of whom required reoperation. These major complications were paraesophageal hiatal hernia (ten patients), small bowel obstruction (eight patients), and wrap malalignment (5 patients). Observations of and reoperation on these children suggests the following necessary steps for avoidance of complications in children: (1) Nissen fundoplication in childhood should be accompanied by an accurate multi-suture crural repair and by suture fixation of the fundal wrap to the crura and to the abdominal surface of the diaphragm; (2) appropriate alignment of the fundal wrap and of the crural repair is best accomplished with a large indwelling esophageal bougie of sufficient size to efface and blanche the esophageal musculature; and (3) appropriate care in avoiding small bowel obstruction mandates meticulous avoidance of trauma to the liver capsule and small bowel serosa.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcraft K. W., Holder T. M., Amoury R. A. Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children by Thal fundoplication. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1981 Nov;82(5):706–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettex M., Kuffer F. Long-term results of fundoplication in hiatus hernia and cardio-esophageal chalasia in infants and children. Report of 112 consecutive cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1969 Oct;4(5):526–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(69)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARRE I. J. The natural history of the partial thoracic stomach (hiatus hernia) in children. Arch Dis Child. 1959 Aug;34:344–353. doi: 10.1136/adc.34.176.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Kent A. H. Evaluation of current operations for the prevention of gastroesophageal reflux. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):511–525. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festen C. Paraesophageal hernia: a major complication of Nissen's fundoplication. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Aug;16(4):496–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(81)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festen C. Postoperative small bowel obstruction in infants and children. Ann Surg. 1982 Nov;196(5):580–583. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198211000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonkalsrud E. W., Ament M. E., Byrne W. J., Rachelefsky G. S. Gastroesophageal fundoplication for the management of reflux in infants and children. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978 Nov;76(5):655–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann T. H., McDaniel A., Polk H. C., Jr Slipped Nissen's fundoplication: a stitch in time. Arch Surg. 1981 Sep;116(9):1239–1239. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380210101024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Jolley S. G. Gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children. Recognition and treatment. Surg Clin North Am. 1981 Oct;61(5):1101–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leape L. L., Holder T. M., Franklin J. D., Amoury R. A., Ashcraft K. W. Respiratory arrest in infants secondary to gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatrics. 1977 Dec;60(6):924–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leape L. L., Ramenofsky M. L. Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children. Results of Nissen's fundoplication in 100 children. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Oct;134(10):935–938. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130220013004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi H. K., Crozier R. E., Ellis F. H., Jr Reoperation for complications of the Nissen fundoplication. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1981 Jan;81(1):50–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly J. R., Randolph J. G. Hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1968 Jan;55(1):42–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers W. F., Herbst J. J. Effectiveness of positioning therapy for gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatrics. 1982 Jun;69(6):768–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISSEN R. Gastropexy and "fundoplication" in surgical treatment of hiatal hernia. Am J Dig Dis. 1961 Oct;6:954–961. doi: 10.1007/BF02231426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr Fundoplication for reflux esophagitis: misadventures with the operation of choice. Ann Surg. 1976 Jun;183(6):645–652. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197606000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzlein M. H., Ballantine T. V., Thirunavukkarasu S., Fitzgerald J. F., Grosfeld J. L. Gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children. Diagnosis and management. Arch Surg. 1979 Apr;114(4):505–510. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370280159026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunell W. P., Smith E. I. Suture alignment for cuff creation in Nissen fundoplication. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Mar;152(3):347–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. D., Dudgeon D. L., Sondheimer J. M. A comparison of medical and surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in severely retarded children. J Pediatr. 1981 Aug;99(2):202–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80450-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]