Abstract
This report describes an experience with operative restoration of hepatopedal portal blood flow in five patients intolerant of total splanchnic shunting. Portal flow was reestablished by takedown of the total shunt and construction of a selective, distal splenorenal shunt, or by isolation and arterialization of the hepatic limb of the shunted portal vein. In two patients, shunt revision was undertaken electively for chronic encephalopathy, which had been unresponsive to low-protein diet, intestinal antibiosis and oral lactulose. Eighteen and 48 months after operation, both patients have had no encephalopathy on an unrestricted protein intake, and work actively as homemakers. Needle liver biopsies showed enhanced mitotic activity in the early postoperative period, suggesting hepatocyte regeneration. In three patients, shunt conversion or arterialization was undertaken in desperate circumstances, characterized by liver failure (bilirubin greater than 10 mg/dl, albumin less than 2.5 g/dl, prothrombin time greater than 16 sec), coma, and respirator dependency. Although the patients showed immediate, marked improvement in mentation, all three died of intraabdominal hemorrhage in the first few postoperative days, in spite of maximum blood product support. Two conclusions can be drawn from this limited experience: (1) at a time of election, restoration of hepatopedal portal flow can be accomplished with considerable benefit in patients with side-to-side portacaval or hemodynamically equivalent shunts, and (2) similar procedures in patients with fulminant liver failure are unlikely to succeed.
Full text
PDF
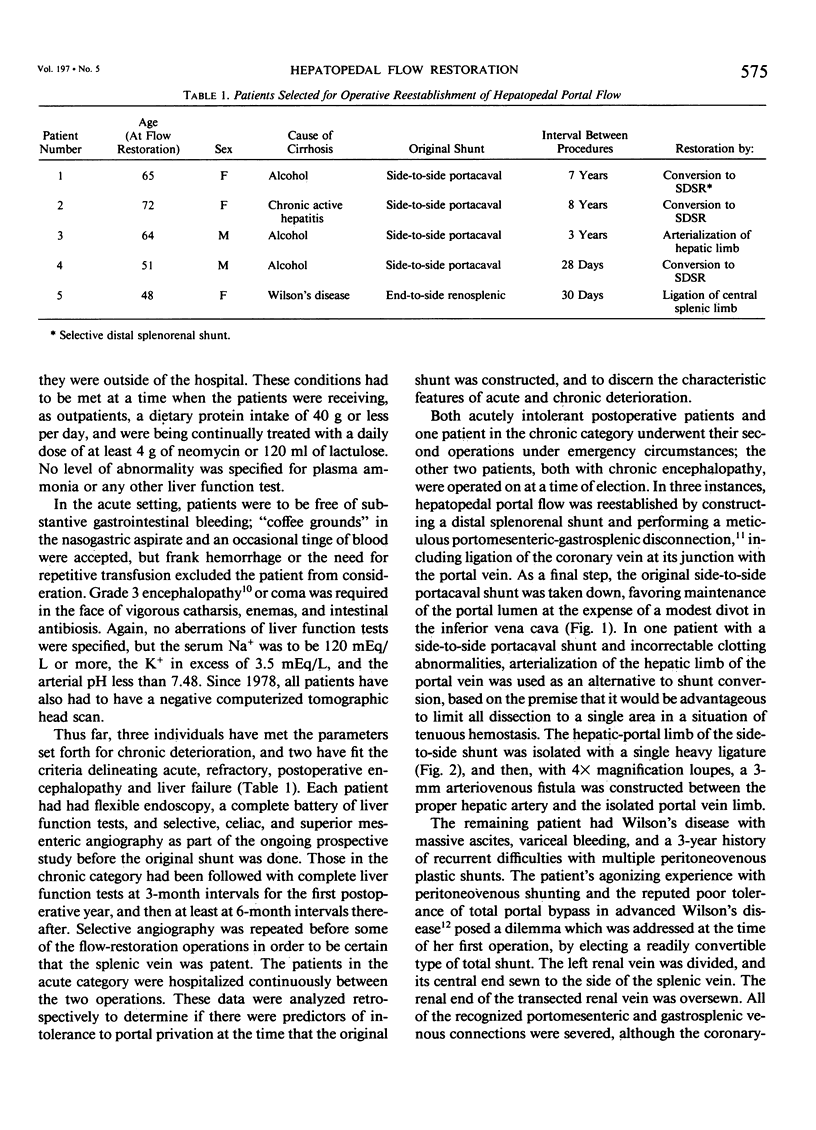

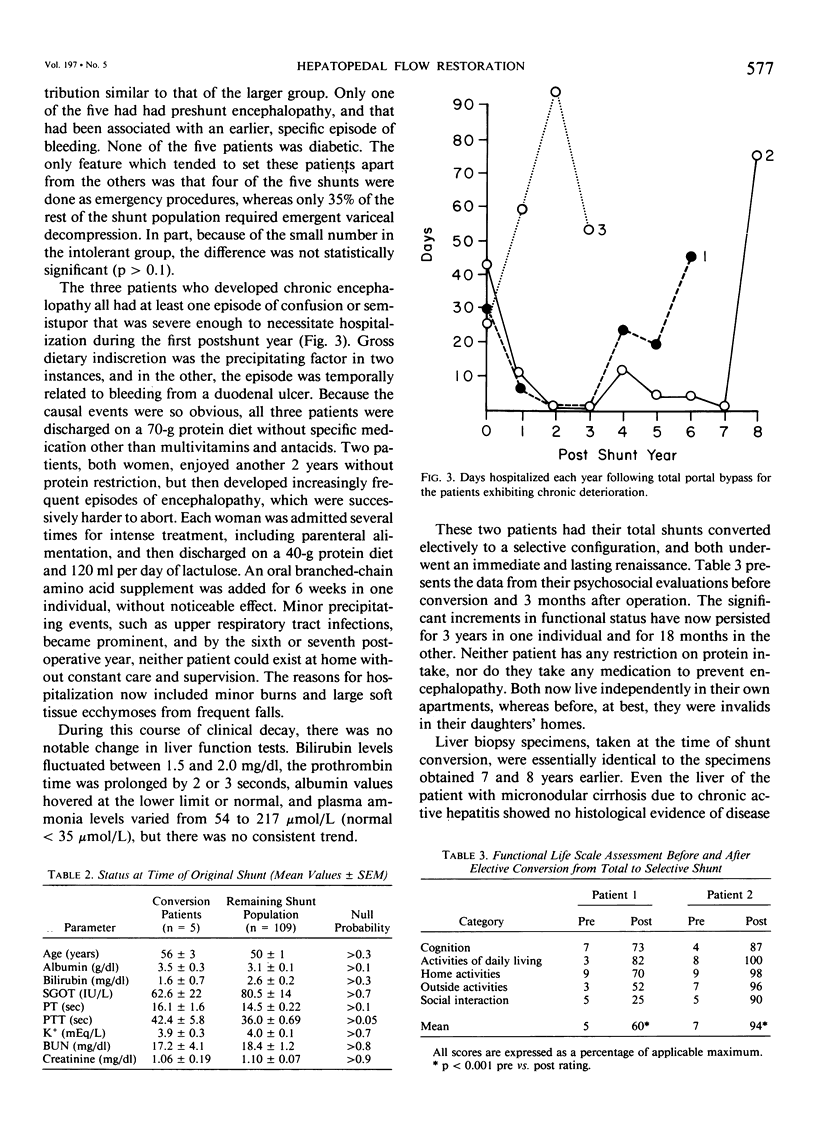
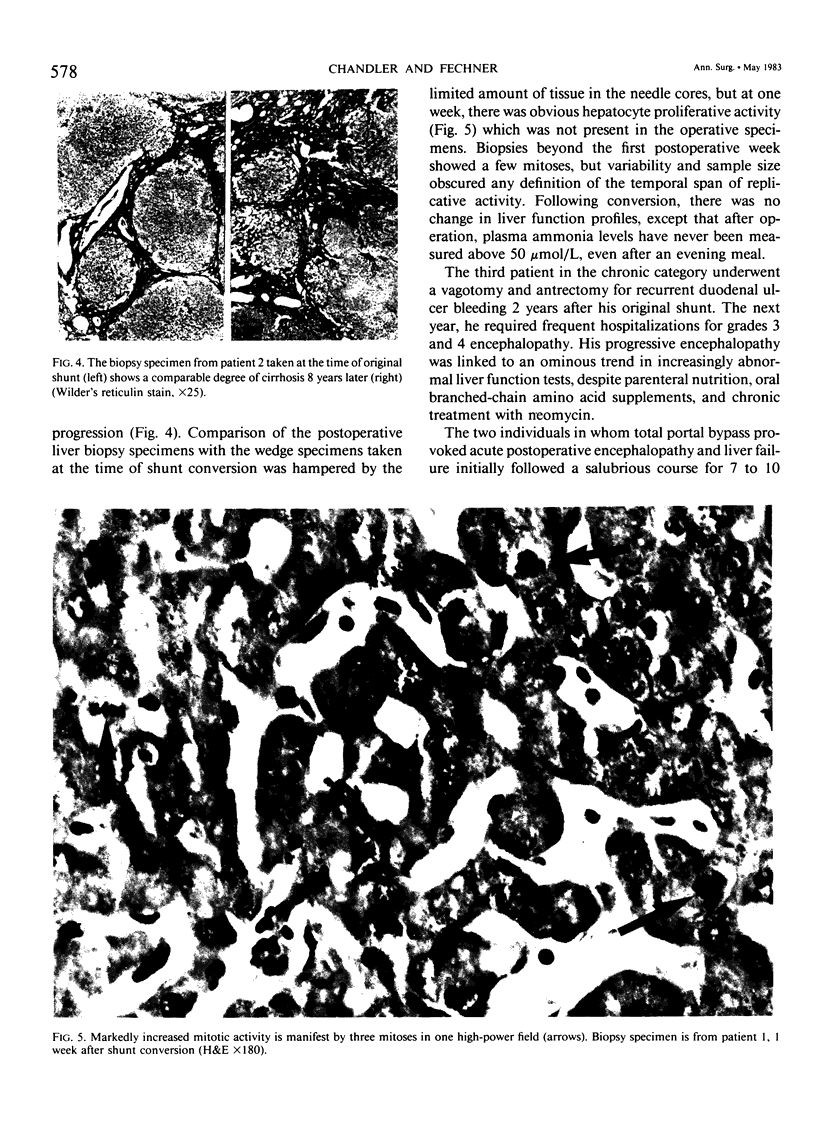




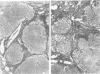
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamons R. J., Butt K., Iyer S., DeRose J., Dennis C. R., Kinkhabwala M., Gordon D., Martin E. Portacaval shunt with arterialization of the portal vein by means of a low flow arteriovenous fistula. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978 Jun;146(6):869–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamsons R. J., Arif S., Babich A., Butt K., Lam A., Minkowitz S. Arterialization of the liver in combination with a portacaval shunt in the dog. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Apr;140(4):594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. H., Jr, Hyde P. V., Skivolocki W. P., Brimm J. E., Orloff M. J. Prospective study of portasystemic encephalopathy after emergency portacaval shunt for bleeding varices. Am J Surg. 1981 Jul;142(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(81)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler J. G. Hepatotrophic activity in nonpancreatic, nonduodenal portal blood. Surg Forum. 1976;27(62):360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H., Dienstag J., Lehrich J., Yoshimura N., Bradford R. R., Rosen H., Atamian S., Slemmer E., Holroyde J., Fischer J. E. Infusion of branched-chain enriched amino acid solution in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Surg. 1982 Aug;196(2):209–220. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198208000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna S. S., Smith R. S., 3rd, Henderson J. M., Millikan W. J., Jr, Warren W. D. Reversal of hepatic encephalopathy after occlusion of total portasystemic shunts. Am J Surg. 1981 Aug;142(2):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison I. D., Smith A. H., Shields R. Ammonia absorption from the canine colon after portacaval shunt. Br J Surg. 1977 Dec;64(12):851–856. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800641205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. C., Perrin E. B., Felix W. R., Smith A. G. A clinical investigation of the portacaval shunt. V. Survival analysis of the therapeutic operation. Ann Surg. 1971 Oct;174(4):672–701. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197110000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakos G. S., Evans W. E., Czuba M., Spiegel J., Greenberger N. J. Subtotal portacaval shunt obliteration for chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Surg. 1973 Mar;177(3):276–279. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197303000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Broelsch C. E., Flamant Y. M., Chandler J. G., Charters A. C., 3rd, Orloff M. J. Liver regeneration after portacaval transportation in rats. Surgery. 1975 Jan;77(1):144–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maillard J. N., Flamant Y. M., Hay J. M., Chandler J. G. Selectivity of the distal splenorenal shunt. Surgery. 1979 Nov;86(5):663–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maillard J. N., Rueff B., Prandi D., Sicot C. Hepatic arterialization and portacaval shunt in hepatic cirrhosis. An assessment. Arch Surg. 1974 Mar;108(3):315–320. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350270049009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzander U. 13. Spätergebnisse nach veno-venösem Shunt mit gleichzeitiger Arterialisation. Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1976 Nov 15;342:145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF01267361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutchnick M. G., Lerner E., Conn H. O. Portal-systemic encephalopathy and portacaval anastomosis: a prospective, controlled investigation. Gastroenterology. 1974 May;66(5):1005–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff M. J., Bell R. H., Jr, Hyde P. V., Skivolocki W. P. Long-term results of emergency portacaval shunt for bleeding esophageal varices in unselected patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 1980 Sep;192(3):325–340. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198009000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte J. B., Reynaert M., De Hemptinne B., Geubel A., Carlier M., Jamart J., Lambotte L., Kestens P. J. Arterialization of the portal vein in conjunction with a therapeutic portacaval shunt. Hemodynamic investigations and results in 75 patients. Ann Surg. 1982 Dec;196(6):656–663. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198212001-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichle F. A., Rao N. S., Reichle R. M., Chang K. H. The mechanism of postshunt liver failure. Surgery. 1977 Nov;82(5):738–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R. H., Ishihara A., Chalmers T. C., Schimmel E. M. A controlled trial of colon bypass in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology. 1968 Jun;54(6):1057–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarno J. E., Sarno M. T., Levita E. The functional life scale. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1973 May;54(5):214–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H., Walshe J. M. Bleeding oesophageal varices in patients with Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1970 Mar 28;1(7648):638–641. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale G., Jennett B. Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1976;34(1-4):45–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01405862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Millikan W. J., Jr, Henderson J. M., Wright L., Kutner M., Smith R. B., 3rd, Fulenwider J. T., Salam A. A., Galambos J. T. Ten years portal hypertensive surgery at Emory. Results and new perspectives. Ann Surg. 1982 May;195(5):530–542. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198205000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Millikan W. J., Jr, Smith R. B., 3rd, Rypins E. B., Henderson J. M., Salam A. A., Hersh T., Galambos J. T., Faraj B. A. Noncirrhotic portal vein thrombosis. Physiology before and after shunts. Ann Surg. 1980 Sep;192(3):341–349. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198009000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Zeppa R., Fomon J. J. Selective trans-splenic decompression of gastroesophageal varices by distal splenorenal shunt. Ann Surg. 1967 Sep;166(3):437–455. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196709000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]