Abstract
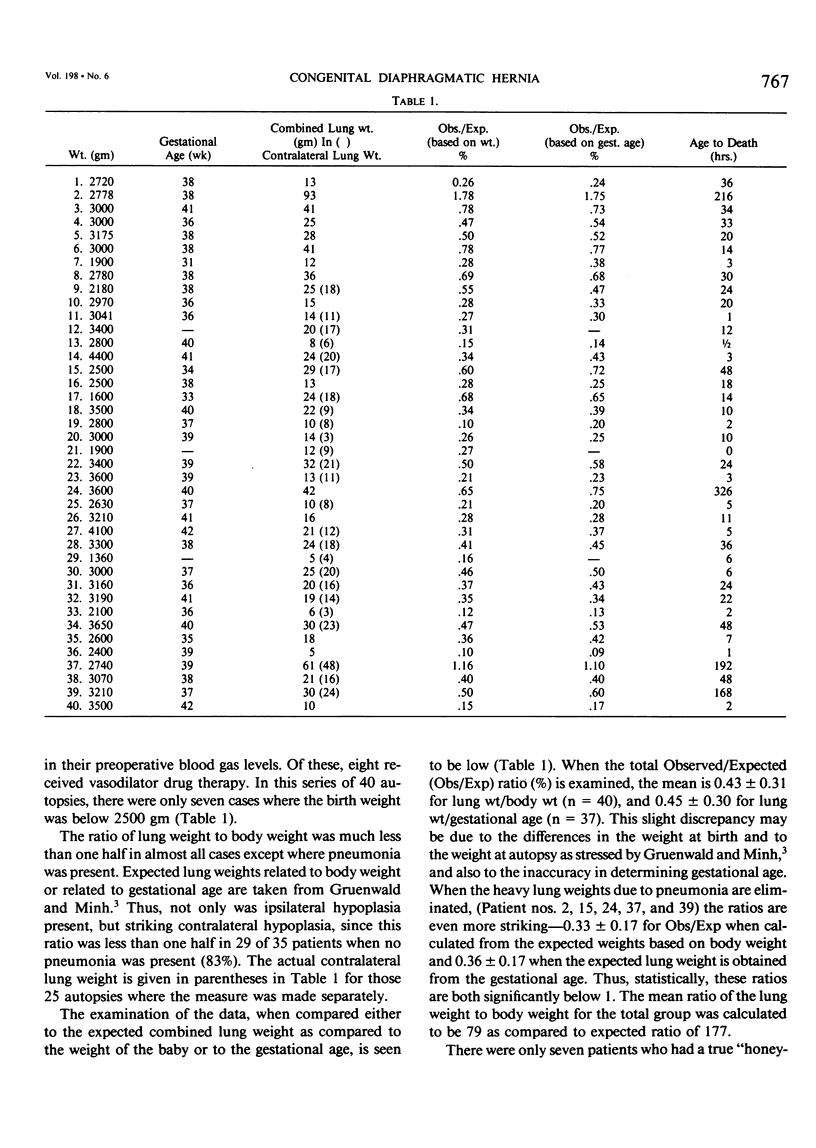
Much progress has been made over the past 20 years in neonatal surgery, but the mortality rate in cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) for babies presenting in the early hours of life has remained high. We have reviewed our experience with special reference to 40 autopsied patients. Hypoplastic lungs were seen in all patients. When the ratio of observed combined lung weight to the expected combined lung weight is calculated, the result is 0.33 +/- 0.17 when the expected lung weights are calculated from the babies' birth weight; and 0.36 +/- 0.17 when the expected lung weights are calculated from the gestational age. In all patients with high ratios, extensive pneumonia was confirmed. Those patients with pneumonia were eliminated from the calculations. We cannot state unequivocably that hypoplasia of both lungs is the cause of death in all patients with CDH. We can affirm that, in our experience, hypoplasia is present and is probably a major factor in the high mortality rate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman S., Benson C. D. Bochdalek hernias in infants: factors determining mortality. J Pediatr Surg. 1976 Aug;11(4):569–573. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(76)80015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER N., CLAIREAUX A. E. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia as a cause of perinatal mortality. Lancet. 1962 Mar 31;1(7231):659–663. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92878-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. H., Andrews A. F., Toomasian J. M., Haiduc N. J., Gazzaniga A. B. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for newborn respiratory failure: forty-five cases. Surgery. 1982 Aug;92(2):425–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloss R. S., Aranda J. V., Beardmore H. E. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: pathophysiology and pharmacologic support. Surgery. 1981 Apr;89(4):518–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boix-Ochoa J., Peguero G., Seijo G., Natal A., Canals J. Acid-base balance and blood gases in prognosis and therapy of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 1974 Feb;9(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(74)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPANALE R. P., ROWLAND R. H. Hypoplasia of the lung associated with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Ann Surg. 1955 Aug;142(2):176–189. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195508000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatrath R. R., el-Shafie M., Jones R. S. Fate of hypoplastic lungs after repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Oct;46(249):633–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.249.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUENWALD P., HOANG NGOC MINH Evaluation of body and organ weights in perinatal pathology. I. Normal standards derived from autopsies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Sep;34:247–253. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosfeld J. L., O'Neill J. A., Jr, Boles E. T., Jr, Clatworthy H. W., Jr Monitoring venous pH and gas tensions during operations on infants and children. Arch Surg. 1970 May;100(5):584–588. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340230050011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman F. M., Racette P., Abi-Haïdar A., Collin P. P. Hernies diaphragmatiques en pédatrie. Union Med Can. 1971 Jul;100(7):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. R., Bressack M. A., Churg A. M., de Lorimier A. A. Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero. II. Simulated correction permits fetal lung growth with survival at birth. Surgery. 1980 Aug;88(2):260–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. Persistent hypoplasia of the lung after repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Thorax. 1976 Aug;31(4):450–455. doi: 10.1136/thx.31.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Deaner R. M., Koop C. E. Diaphragmatic hernia in infancy: factors affecting the mortality rate. Surgery. 1967 Dec;62(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel T. M., Greenfield L. J., Kirkpatrick B. V., Mueller D. G., Ormazabal M., Salzberg A. M. Clinical use of an extracorporeal membrane oxygenator in neonatal pulmonary failure. J Pediatr Surg. 1982 Oct;17(5):525–531. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(82)80102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishalany H. G., Nakada K., Woolley M. M. Congenital diaphragmatic hernias: eleven years' experience. Arch Surg. 1979 Oct;114(10):1118–1123. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370340024003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdock A. I., Burrington J. B., Swyer P. R. Alveolar to arterial oxygen tension difference and venous admixture in newly born infants with congenital diaphragmatic herniation through the foramen of Bochdalek. Biol Neonate. 1971;17(3):161–172. doi: 10.1159/000240311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raphaely R. C., Downes J. J., Jr Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: prediction of survival. J Pediatr Surg. 1973 Oct;8(5):815–823. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(73)90426-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale F. R., Esterly J. R. Pulmonary hypoplasia: a morphometric study of the lungs of infants with diaphragmatic hernia, anencephaly, and renal malformations. Pediatrics. 1973 Jan;51(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M. I., Uribe F. L. Diaphragmatic hernia in the newborn infant: blood gas and pH considerations. Surgery. 1971 Nov;70(5):758–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]